Abstract
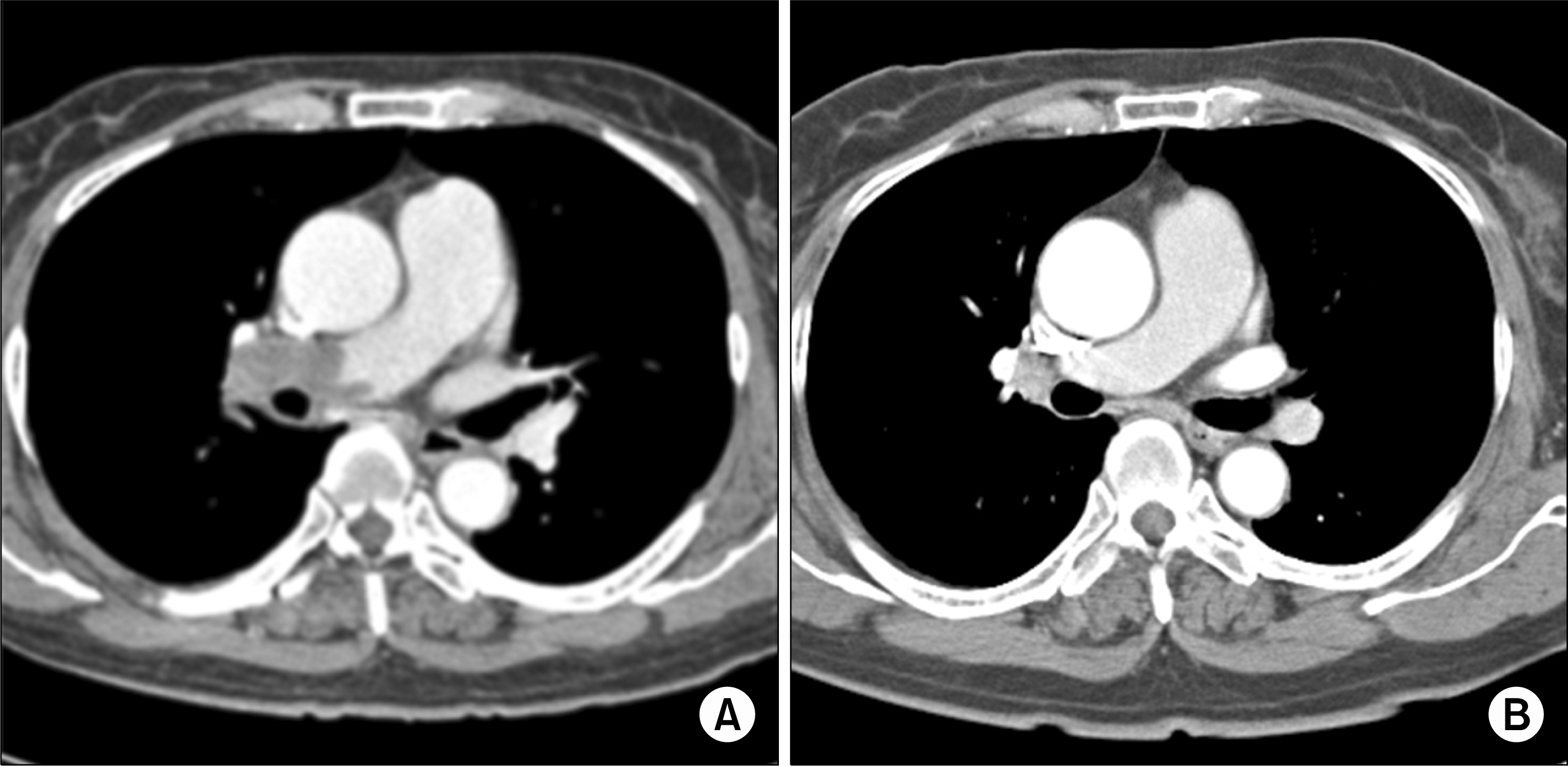
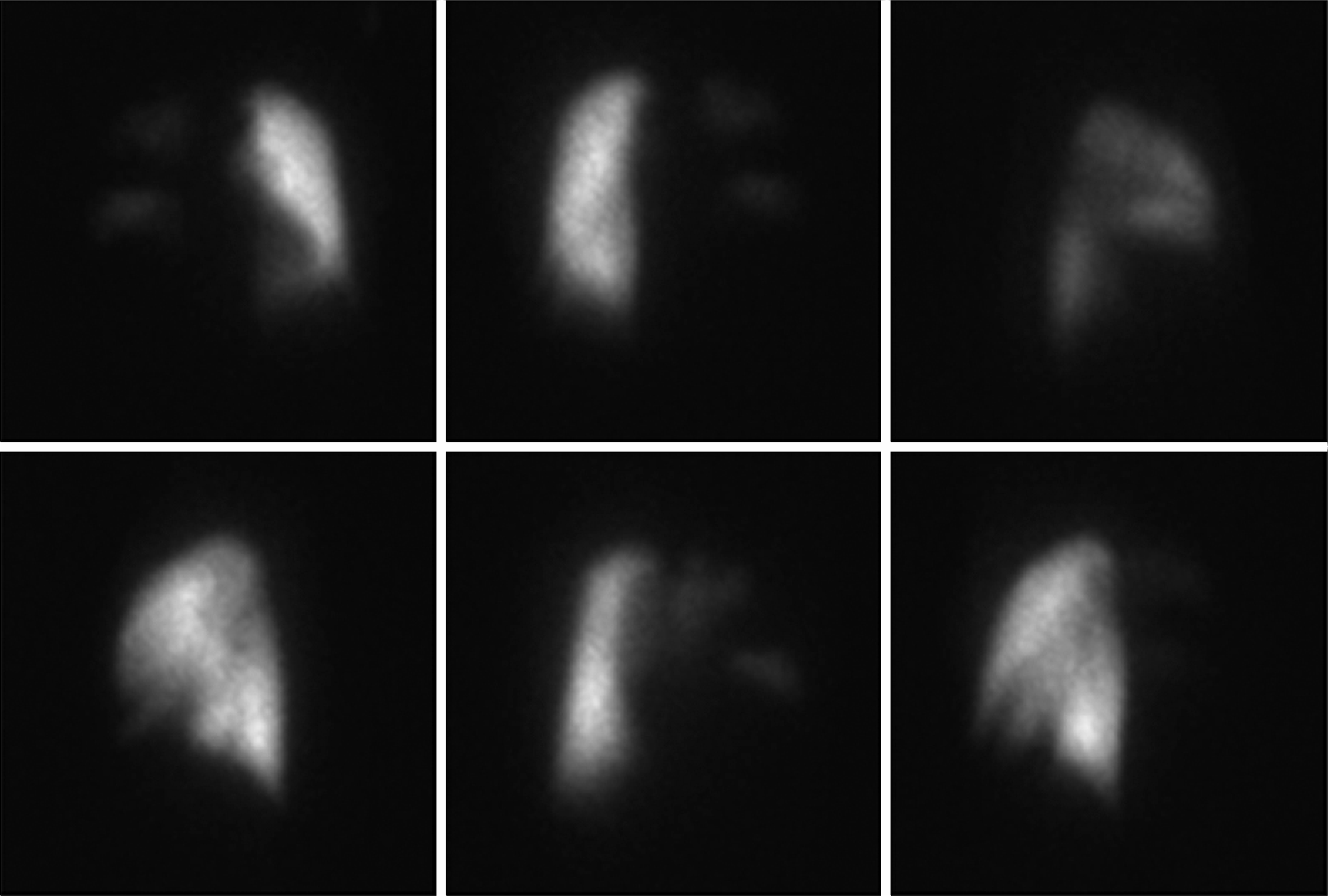
Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) are at an increased risk of developing thromboses with antiphospholipid anti-bodies (aPL). The presence of aPL is related to an increased risk of thrombotic events. However, thromboembolic events can occur in SLE patients without aPL, and pulmonary emboli are rarely reported manifestations of SLE without aPL. Here, we report on a case of massive pulmonary embolism in a 58-year-old woman with aPL-negative SLE. She presented with chest pain and dyspnea, and chest computed tomography (CT) and lung perfusion ventilation scans showed pulmonary thromboembolism. She was administered thrombolytic agents, heparin, and warfarin. Two months later, no remarkable residual thromboembolism was observed on chest CT.
REFERENCES
1. Rezaei N, Yeganeh MZ, Ahmadi F. Antiphospholipid anti-body syndrome presenting with pulmonary embolism. Tanaffos. 2008; 7:71–4.
3. Matta BN, Uthman I, Taher AT, Khamashta MA. The current standing of diagnosis of antiphospholipid syndrome associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2013; 9:659–68.

4. Gari AG, Telmesani A, Alwithenani R. Pulmonary manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Almoallim H, editor. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Rijeka, Croatia: InTech;2012. p. 313–36.

5. Gladman DD, Urowitz MB. Venous syndromes and pulmonary embolism in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 1980; 39:340–3.

6. Love PE, Santoro SA. Antiphospholipid antibodies: anti-cardiolipin and the lupus anticoagulant in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and in non-SLE disorders. Prevalence and clinical significance. Ann Intern Med. 1990; 112:682–98.
7. Ruiz-Irastorza G, Egurbide MV, Ugalde J, Aguirre C. High impact of antiphospholipid syndrome on irreversible organ damage and survival of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arch Intern Med. 2004; 164:77–82.

8. Hughes GR, Khamashta MA. Seronegative antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003; 62:1127.
9. Mahler M, Norman GL, Meroni PL, Khamashta M. Autoantibodies to domain 1 of beta 2 glycoprotein 1: a promising candidate biomarker for risk management in antiphospholipid syndrome. Autoimmun Rev. 2012; 12:313–7.

10. Rodriguez-Garcia JL, Bertolaccini ML, Cuadrado MJ, Sanna G, Ateka-Barrutia O, Khamashta MA. Clinical manifestations of antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) with and without antiphospholipid antibodies (the so-called ‘seronegative APS’). Ann Rheum Dis. 2012; 71:242–4.

11. Cipil H, Kargili A, Senaran H, Uz E, Kasapoglu B, Alici Ö, et al. Thrombosis and thrombocytosis in a thousand rheumatologic cases. New J Med. 2011; 28:38–42.
12. Romero-Díaz J, García-Sosa I, Sánchez-Guerrero J. Thrombosis in systemic lupus erythematosus and other autoimmune diseases of recent onset. J Rheumatol. 2009; 36:68–75.

13. Çobanoğlu U. Risk factor for pulmonary embolism. Çobanoğlu U, editor. Pulmonary embolism. Rijeka, Croatia: InTech;2012. p. 1–18.

14. Espinosa G, Cervera R, Font J, Asherson RA. The lung in the antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002; 61:195–8.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download