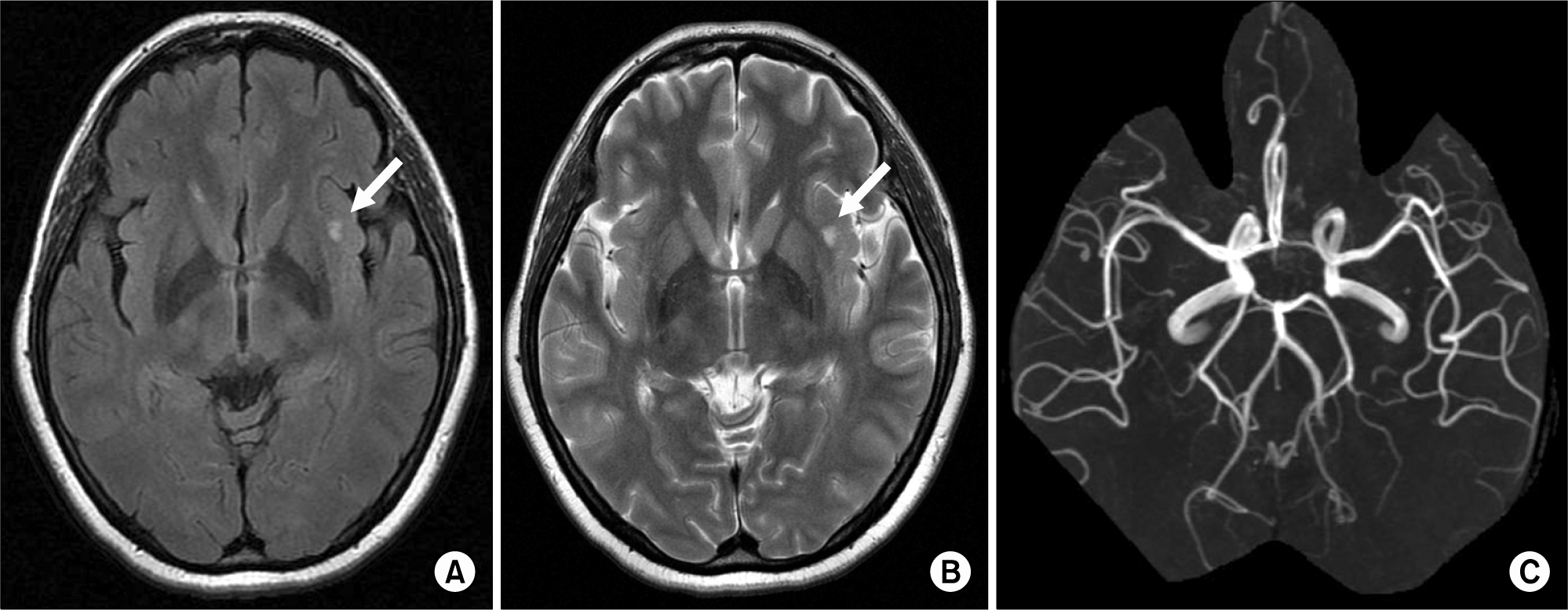
Abstract
Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS) is a coagulation disorder associated with antiphospholipid antibodies. Headache is common in APS patients and often un-responsive to analgesics. We report a case of refractory headache in a patient with APS, who was improved by high-intensity warfarin treatment. The mechanisms of the headache in patients with APS were presumed to be hyper-coagulability of microcirculation and thrombotic occlusion of the capillaries, which were associated with antiphospholipid antibodies. Therefore, high-intensity warfarin could be considered as one of the treatments for refractory headache in patients with APS.
REFERENCES
1. Sanna G, Bertolaccini ML, Cuadrado MJ, Khamashta MA, Hughes GR. Central nervous system involvement in the antiphospholipid (Hughes) syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2003; 42:200–13.

4. Cuadrado MJ, Khamashta MA, D'Cruz D, Hughes GR. Migraine in Hughes syndrome–heparin as a therapeutic trial? QJM. 2001; 94:114–5.

5. BH H. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Longo DL FA, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Jameson JL, Loscalzo J, editors. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine. 18th ed.New York: McGraw-Hill;2012.
6. Sanna G, D'Cruz D, Cuadrado MJ. Cerebral manifestations in the antiphospholipid (Hughes) syndrome. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2006; 32:465–90.

7. Hughes GR, Cuadrado MJ, Khamashta MA, Sanna G. Headache and memory loss: rapid response to heparin in the antiphospholipid syndrome. Lupus. 2001; 10:778.
8. Moutsopoulos HM VP. Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome. Longo DL FA, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Jameson JL, Loscalzo J, editors. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine. 18th ed.New York: McGraw-Hill;2012.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download