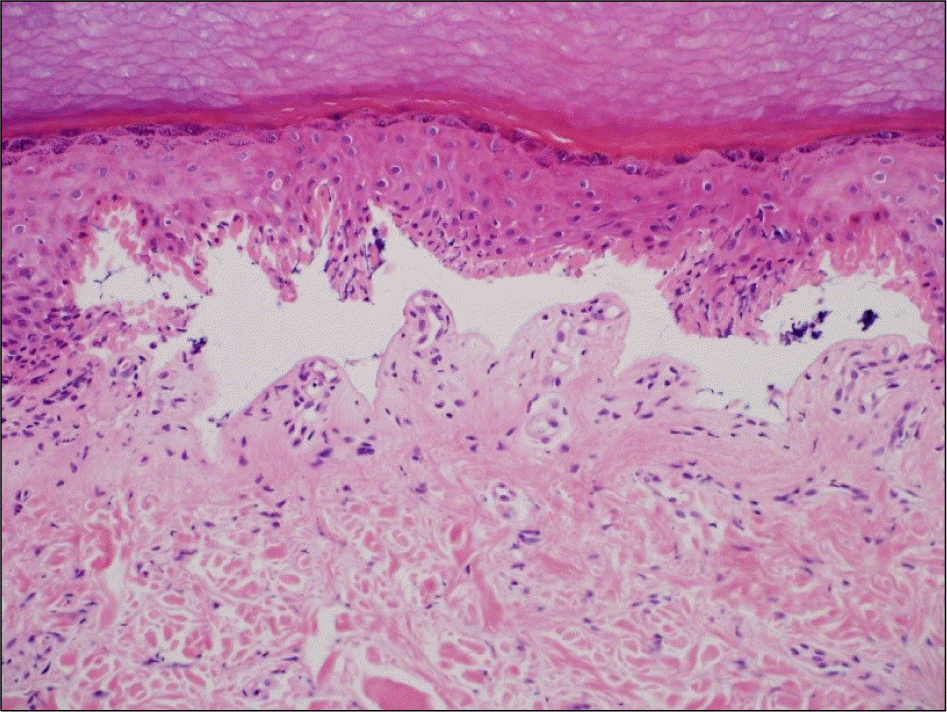
Abstract
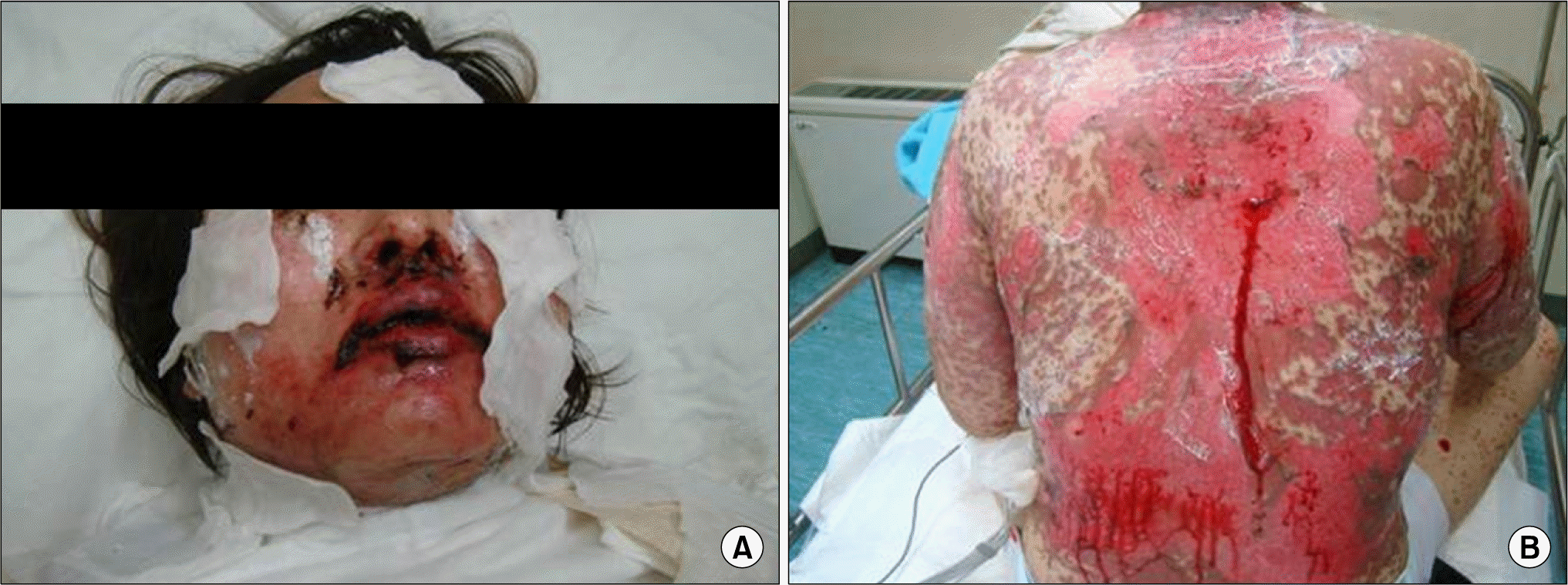
Leflunomide was licensed for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in 1998 and has been available in Korea since 2003. Allergic cutaneous reactions (rash, purpura) are common (<10%) side effects of leflunomide, but severe cases such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) or toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) are rarely reported. There has not been a report of SJS or TEN induced by leflunomide in Korea. Here we report a case of leflunomide-induced TEN in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Leflunomide was discontinued, and the TEN was treated with methylprednisolone, cholestyramine and immunoglobulin. The skin lesion eventually resolved over four weeks with residual post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
REFERENCES
1. van Riel PL, Smolen JS, Emery P, Kalden JR, Dougados M, Strand CV, et al. Leflunomide: a manageable safety profile. J Rheumatol Suppl. 2004; 71:21–4.
2. Osiri M, Shea B, Robinson V, Suarez-Almazor M, Strand V, Tugwell P, et al. Leflunomide for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and metaanalysis. J Rheumatol. 2003; 30:1182–90.
3. Smolen JS, Emery P. Efficacy and safety of leflunomide in active rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2000; 39(Suppl 1):48–56.

4. Schmutz JL, Barbaud A, Tréchot P. Leflunomide and Lyell syndrome. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2009; 136:395.
5. Hassikou H, El Haouri M, Tabache F, Baaj M, Safi S, Hadri L. Leflunomide-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2008; 75:597–9.

6. El Aïdli S, Salouage I, Kastalli S, Srairi S, Daghfous R, Loueslati MH, et al. Leflunomide-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis. Therapie. 2008; 63:157–8.
7. Teraki Y, Hitomi K, Sato Y, Hamamatsu Y, Izaki S. Leflunomide-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis. Int J Dermatol. 2006; 45:1370–1.

8. Bolognia J, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV. Dermatology. 3rd ed.p. 325. Salt Lake City: Elsevier;2012.
9. Kim HW, Park HC, Kim JE, Ko JY, Ro YS. Drug hypersensitivity syndrome induced by leflunomide. Korean J Dermatol. 2013; 51:226–7.
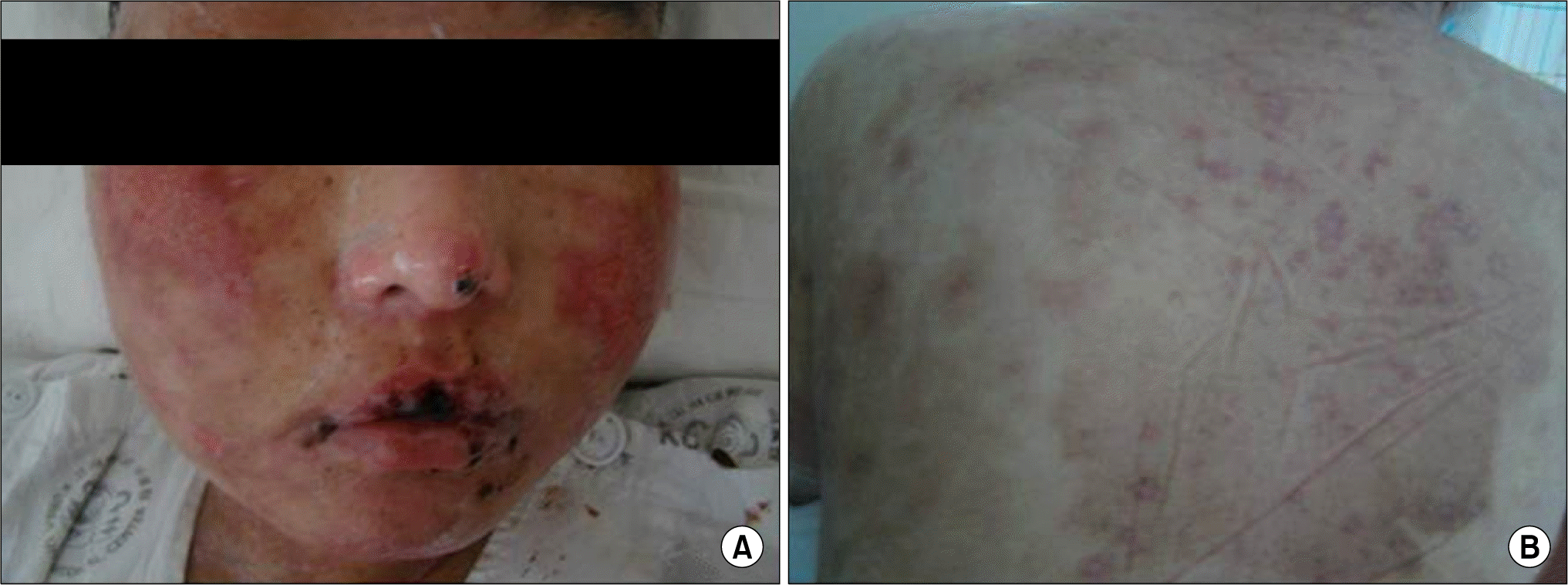
Figure 1.
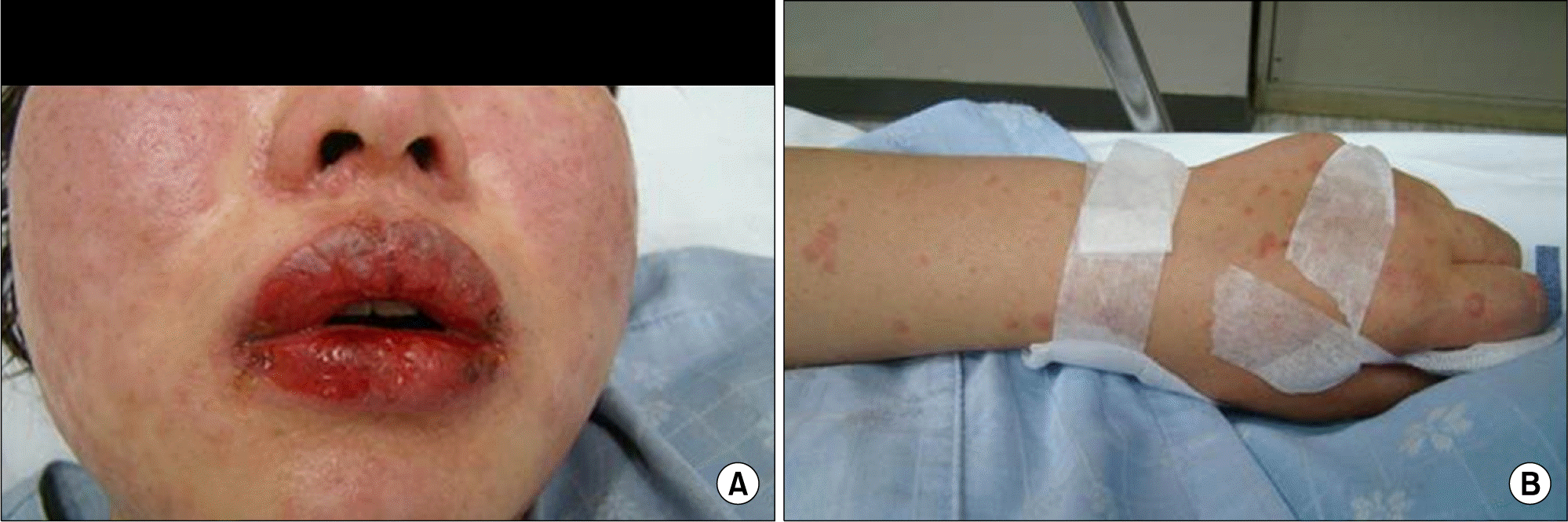
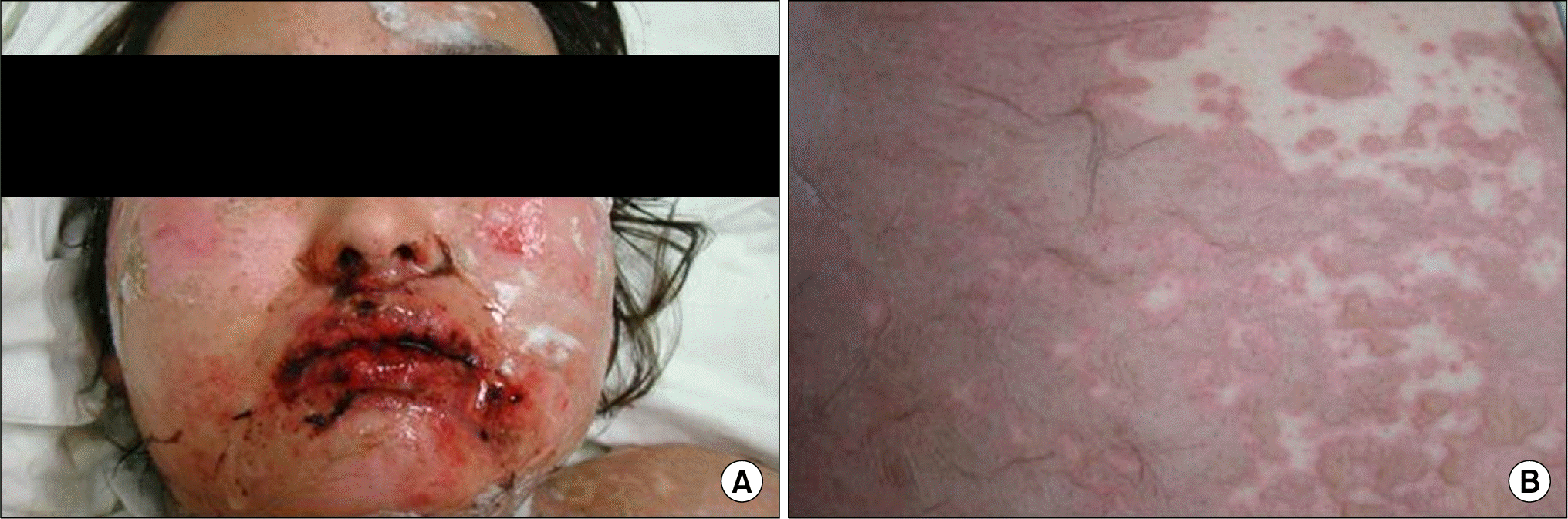
Day 1, The patient had diffuse erythema of the face, erosion of the lips and oral mucosa, and erythematous macules and multiple clear, small, fluid-filled vesicles on her extremities.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download