Abstract
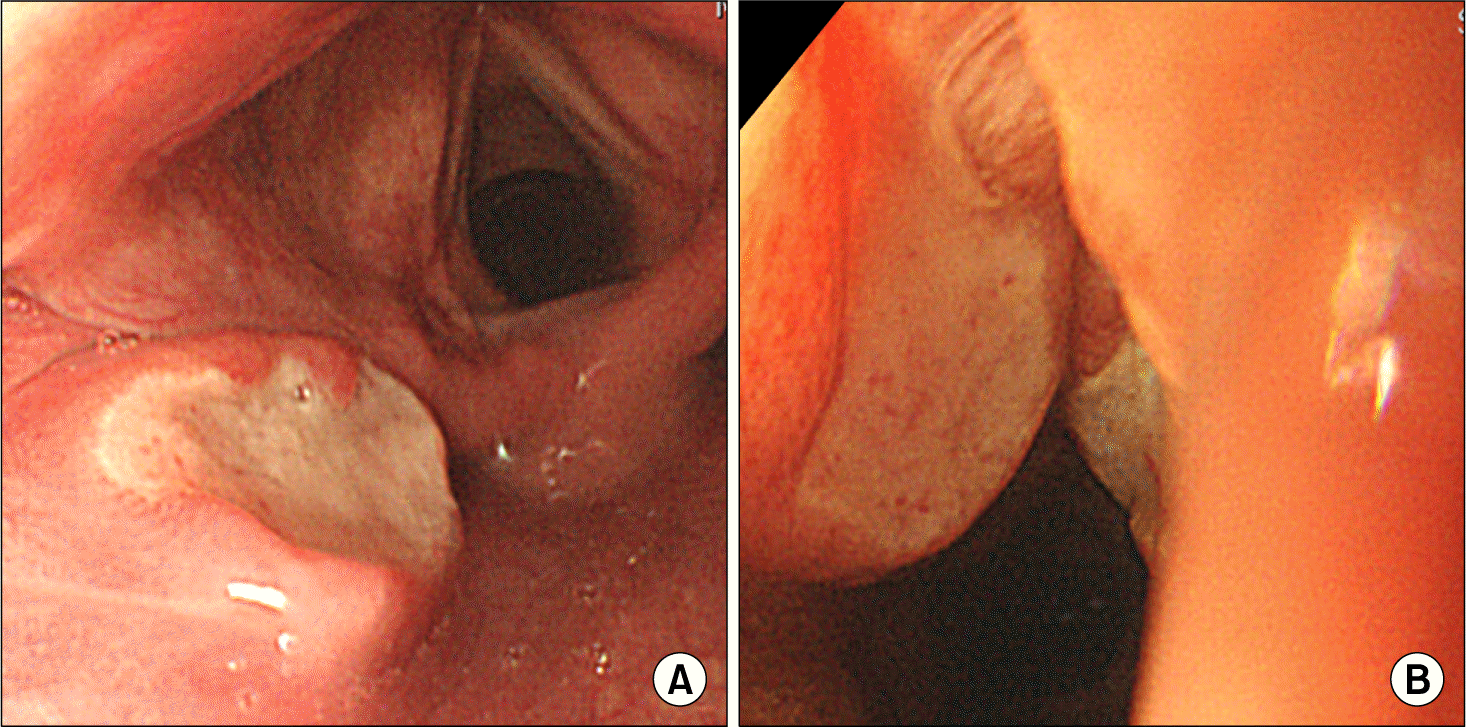
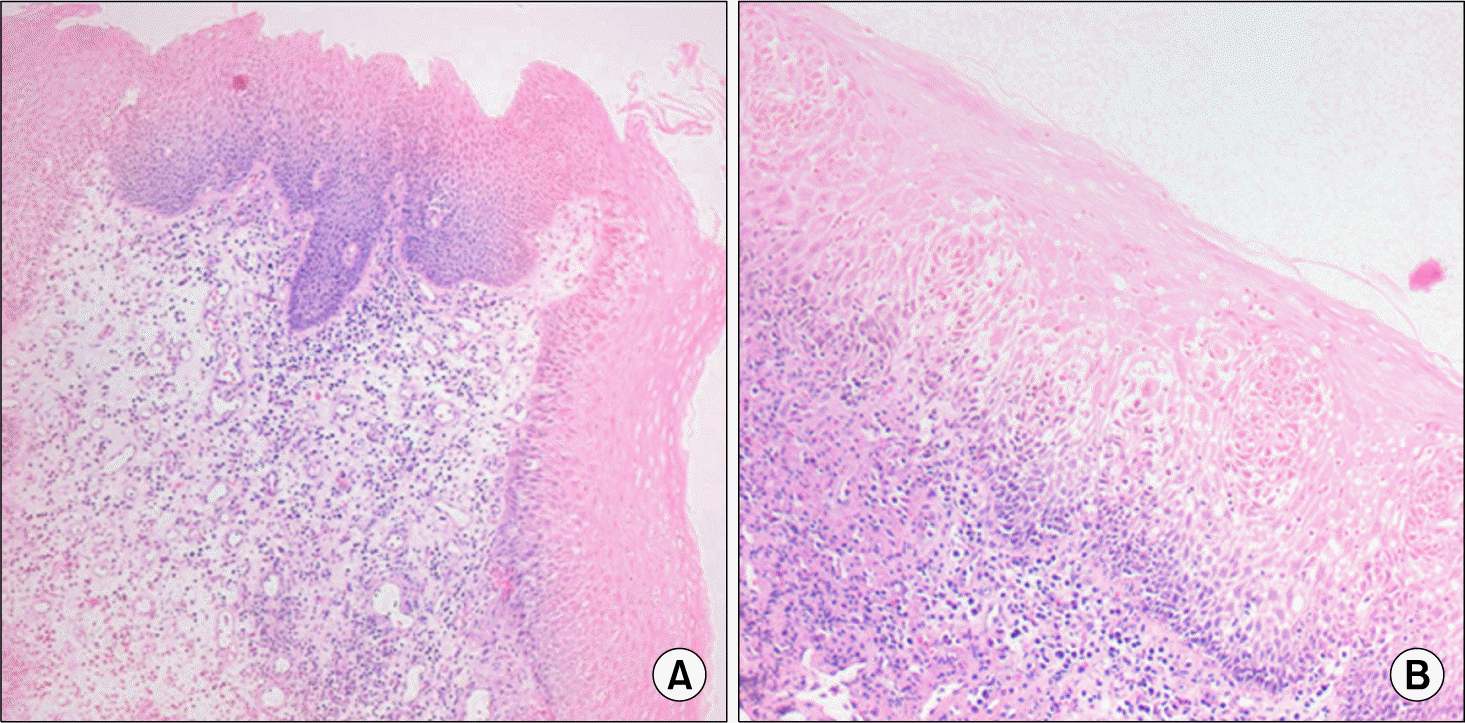
Behçet's disease is a heterogeneous disease that involves variable organ systems. Gastrointestinal Behçet's disease is rare and it generally affects the terminal ileum with propagation toward the cecum and ascending colon. Therefore, esophageal ulcer associated with Behçet's disease has not been reported frequently. We report an unusual case of Behçet's disease associated with both esophageal and pharyngeal ulcers. A 64-year-old man was admitted for an evaluation of pharyngeal and substernal discomfort sustained for 3 months. He had no underlying chronic disease; however, he suffered from recurrent oral and genital ulcers for 20 years and had folliculitis-like skin lesions on the face, scalp and trunk. He was diagnosed with Behçet's dis ease and gastroesophageal fiberscopy revealed deep ulcers on both the pharynx and upper esophagus. Esophagopharyngeal ulcers were successfully treated with prednisolone, colchicines, dapsone, and sulfasalazine.
REFERENCES
1. Yasuo M, Miyabayashi H, Okano T, Aoki H, Ichikawa K, Hirose Y. Successful treatment with corticosteroid in a case of Behç et's syndrome with multiple esophageal ulcerations. Intern Med. 2003; 42:696–9.
2. Yi SW, Cheon JH, Kim JH, Lee SK, Kim TI, Lee YC, et al. The prevalence and clinical characteristics of esophageal involvement in patients with Behç et's disease: a single center experience in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2009; 24:52–6.
3. Maruyama Y, Hisamatsu T, Matsuoka K, Naganuma M, Inoue N, Ogata H, et al. A case of intestinal Behç et's disease treated with infliximab monotherapy who successfully maintained clinical remission and complete mucosal healing for six years. Intern Med. 2012; 51:2125–9.
4. Almoznino G, Ben-Chetrit E. Infliximab for the treatment of resistant oral ulcers in Behç et's disease: a case report and review of the literature. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2007; 25(4 Suppl 45):S99–102.
5. Sakane T, Takeno M, Suzuki N, Inaba G. Behç et's disease. N Engl J Med. 1999; 341:1284–91.
6. Lehmann H, Stutte HJ, Zierott G, Schlaak M. A case of Behcet's disease with multiple intestinal ulcerations (author's transl). Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1975; 100:308–11.
7. Arma S, Habibulla KS, Price JJ, Collis JL. Dysphagia in Behç et's syndrome. Thorax. 1971; 26:155–8.
8. Mori S, Yoshihira A, Kawamura H, Takeuchi A, Hashimoto T, Inaba G. Esophageal involvement in Behcet's disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 1983; 78:548–53.
9. Yashiro K, Nagasako K, Hasegawa K, Maruyama M, Suzuki S, Obata H. Esophageal lesions in intestinal Behç et's disease. Endoscopy. 1986; 18:57–60.
10. Glosemeyer R, Deppe H, Dormann AJ, Wigginghaus B, Stolte M, Stadler R, et al. Ulcerative esophagitis and colitis as rare manifestations of Adamantiades-Behcet disease. Z Gastroenterol. 2001; 39:167–71.
11. Lorenzetti ME, Forbes IJ, Roberts-Thomson IC. Oesophageal and ileal ulceration in Behç et's disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1990; 5:714–7.
12. Ikezawa K, Kashimura H, Hassan M, Nakahara A, Yanaka A, Matsuzaki Y, et al. A case of Behç et's syndrome with esophageal involvement treated with salicylazosulfapyr-idine and prednisolone. Endoscopy. 1998; 30:S52–3.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download