Abstract
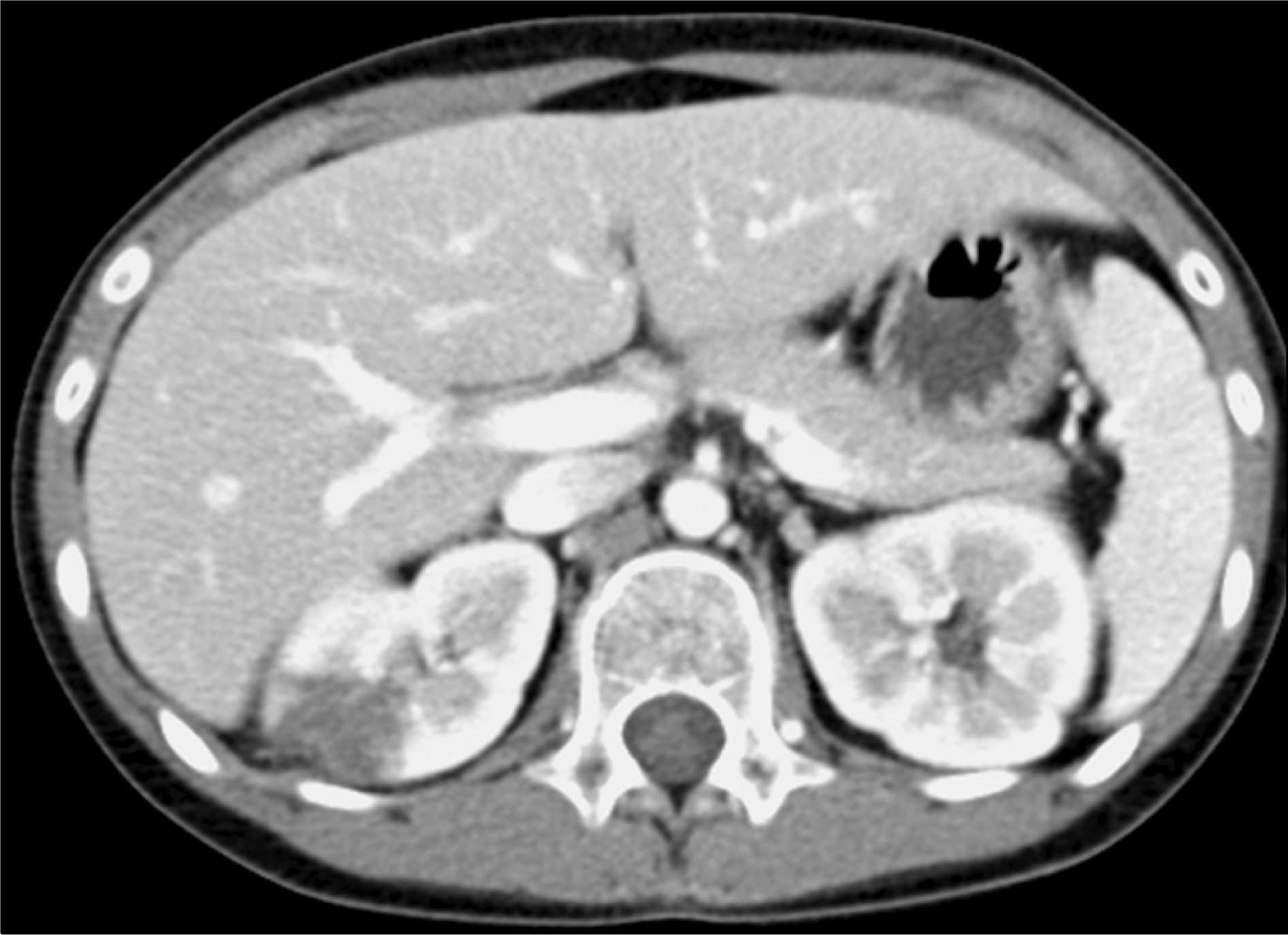
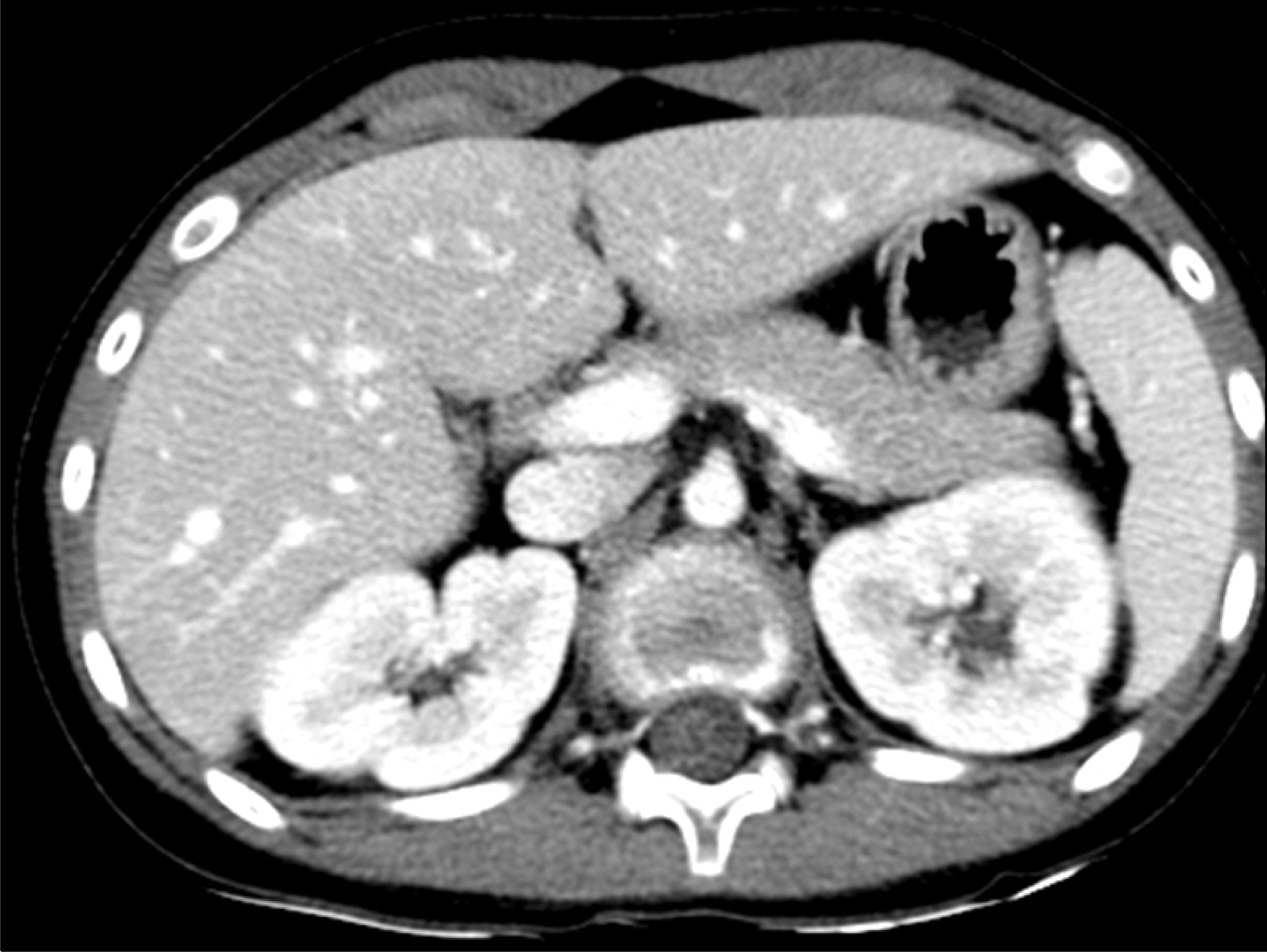
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease affecting multiple organ systems, and is characterized by the deposition of immune complexes and a large array of autoantibodies. Thrombosis is a relatively frequent and serious complication of SLE; however, renal infarction in young patients with antiphospholipid anti-body-negative lupus has rarely been reported, and no pediatric case has been reported in Korea. A 12-year-old female patient was presented to our hospital with a 3-day history of nausea, vomiting, and right flank pain. She was diagnosed with SLE and lupus nephritis two years ago and was treated with corticosteroids and hydroxychloroquine, azathioprine. Abdominal computed tomography (CT) showed renal infarction in the upper pole of the right kidney. Subcutaneous low molecular weight heparin was started, and warfarin was also started simultaneously and continued for 3 months. After 3 months, only minimal atrophic changes were seen on the abdominal CT. She is doing well by maintaining oral anticoagulant therapy and is being followed up regularly through outpatient clinic visits.
REFERENCES
1. Bourgault M, Grimbert P, Verret C, Pourrat J, Herody M, Halimi JM, et al. Acute renal infarction: a case series. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013; 8:392–8.

2. Suwabe H, Moriuchi J, Hoshina Y, Iwata Y, Ichikawa Y, Arimori S. Renal and cerebral infarctions in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus without antiphospholipid antibodies. Ryumachi. 1993; 33:335–40.
3. den Heijer M, Koster T, Blom HJ, Bos GM, Briet E, Reitsma PH, et al. Hyperhomocysteinemia as a risk factor for deep-vein thrombosis. N Engl J Med. 1996; 334:759–62.

4. Danowski A, de Azevedo MN, de Souza Papi JA, Petri M. Determinants of risk for venous and arterial thrombosis in primary antiphospholipid syndrome and in antiphospholipid syndrome with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 2009; 36:1195–9.

5. Brouwer JL, Bijl M, Veeger NJ, Kluin-Nelemans HC, van der Meer J. The contribution of inherited and acquired thrombophilic defects, alone or combined with antiphospholipid antibodies, to venous and arterial thromboembolism in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Blood. 2004; 104:143–8.

6. Espinosa G, Cervera R, Font J, Reverter JC, Shoenfeld Y. Mechanisms of thrombosis in the antiphospholipid syndrome. Inmunologí a. 2003; 22:53–62.
7. De Stefano V, Martinelli I, Mannucci PM, Paciaroni K, Chiusolo P, Casorelli I, et al. The risk of recurrent deep venous thrombosis among heterozygous carriers of both factor V Leiden and the G20210A prothrombin mutation. N Engl J Med. 1999; 341:801–6.

9. Calvo-Alén J, Toloza SM, Fernández M, Bastian HM, Fessler BJ, Roseman JM, et al. LUMINA Study Group. Systemic lupus erythematosus in a multiethnic US cohort (LUMINA). XXV. Smoking, older age, disease activity, lupus anticoagulant, and glucocorticoid dose as risk factors for the occurrence of venous thrombosis in lupus patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 52:2060–8.

10. Erkan D, Yazici Y, Peterson MG, Sammaritano L, Lockshin MD. A cross-sectional study of clinical thrombotic risk factors and preventive treatments in antiphospholipid syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2002; 41:924–9.

11. Sisó A, Ramos-Casals M, Bové A, Brito-Zerón P, Soria N, Muñoz S, et al. Previous antimalarial therapy in patients diagnosed with lupus nephritis: influence on outcomes and survival. Lupus. 2008; 17:281–8.

12. Kang DG, Kim BS, Jang EH, Shin SY, Kim J. Renal Artery Thrombosis in a Patient with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus without Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome: A Case Study. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2009; 16:248–52.

13. Tsugawa K, Tanaka H, Kudo M, Nakahata T, Ito E. Renal artery thrombosis in a pediatric case of systemic lupus erythematosus without antiphospholipid antibodies. Pediatr Nephrol. 2005; 20:1648–50.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download