Abstract
Behcet's disease is a systemic vasculitis, characterized by recurrent oral aphthous ulcers, recurrent genital ulcers, skin lesion, and ocular involvement. Monoclonal antibody to the tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) is considered as a possible therapeutic approach to achieve clinical improvement, preventing relapse in Behcet's disease refractory to conventional anti-inflammatory drugs or immunosuppressive durgs. We report the use of infliximab, which is one of the TNF-α monoclonal antibodies, in a 17-year-old girl with Behcet's disease exhibiting severe mucocutaneous, ocular and neurological involvement refractory to standard treatment.
REFERENCES
1. Akman-Demir G, Serdaroglu P, Tasçi B. Clinical patterns of neurological involvement in Behç et's disease: evaluation of 200 patients. The Neuro-Behç et Study Group. Brain. 1999; 122:2171–82.
2. Arida A, Fragiadaki K, Giavri E, Sfikakis PP. Anti-TNF agents for Behç et's disease: analysis of published data on 369 patients. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2011; 41:61–70.
3. Gijtenbeek JM, van den Bent MJ, Vecht CJ. Cyclosporine neurotoxicity: a review. J Neurol. 1999; 246:339–46.

4. Hatemi G, Silman A, Bang D, Bodaghi B, Chamberlain AM, Gul A, et al. Management of Behç et disease: a systematic literature review for the European League Against Rheumatism evidence-based recommendations for the management of Behç et disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009; 68:1528–34.
5. Saenz A, Ausejo M, Shea B, Wells G, Welch V, Tugwell P. Pharmacotherapy for Behcet's syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000; CD001084.

6. Pineton de Chambrun M, Wechsler B, Geri G, Cacoub P, Saadoun D. New insights into the pathogenesis of Behç et's disease. Autoimmun Rev. 2012; 11:687–98.
7. Melikoglu M, Fresko I, Mat C, Ozyazgan Y, Gogus F, Yurdakul S, et al. Short-term trial of etanercept in Behç et's disease: a double blind, placebo controlled study. J Rheumatol. 2005; 32:98–105.
8. Ohno S, Nakamura S, Hori S, Shimakawa M, Kawashima H, Mochizuki M, et al. Efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics of multiple administration of infliximab in Behç et's disease with refractory uveoretinitis. J Rheumatol. 2004; 31:1362–8.
9. Almoznino G, Ben-Chetrit E. Infliximab for the treatment of resistant oral ulcers in Behç et's disease: a case report and review of the literature. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2007; 25(4 Suppl 45):S99–102.
10. Hassard PV, Binder SW, Nelson V, Vasiliauskas EA. Anti-tumor necrosis factor monoclonal antibody therapy for gastrointestinal Behç et's disease: a case report. Gastroenterology. 2001; 120:995–9.
11. Licata G, Pinto A, Tuttolomondo A, Banco A, Ciccia F, Ferrante A, et al. Anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody therapy for recalcitrant cerebral vasculitis in a patient with Behç et's syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003; 62:280–1.
12. Alty JE, Monaghan TM, Bamford JM. A patient with neuro-Behç et's disease is successfully treated with etanercept: further evidence for the value of TNFalpha blockade. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2007; 109:279–81.
13. Leccese P, D'Angelo S, Angela P, Coniglio G, Olivieri I. Switching to adalimumab is effective in a case of neu-ro-Behcet's disease refractory to infliximab. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2010; 28(4 Suppl 60):S102.
14. Ju JH, Kwok SK, Seo SH, Yoon CH, Kim HY, Park SH. Successful treatment of life-threatening intestinal ulcer in Behç et's disease with infliximab: rapid healing of Behç et's ulcer with infliximab. Clin Rheumatol. 2007; 26:1383–5.
15. Lee JH, Cheon JH, Jeon SW, Ye BD, Yang SK, Kim YH, et al. Efficacy of infliximab in intestinal Behç et's disease: a Korean multicenter retrospective study. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013; 19:1833–8.
Figure 1.
(A) MRI axial T1 image. Thickening of dura along left sphenoid wing is shown. (B) Coronal T1 image. Increased signal from optic canal to left lateral rectus muscle. (C, D) MRI: axial fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) image. Focal high signal intensity lesions are noted in the left temporal lobe and left frontal base, suggestive of recurrent inflammation.
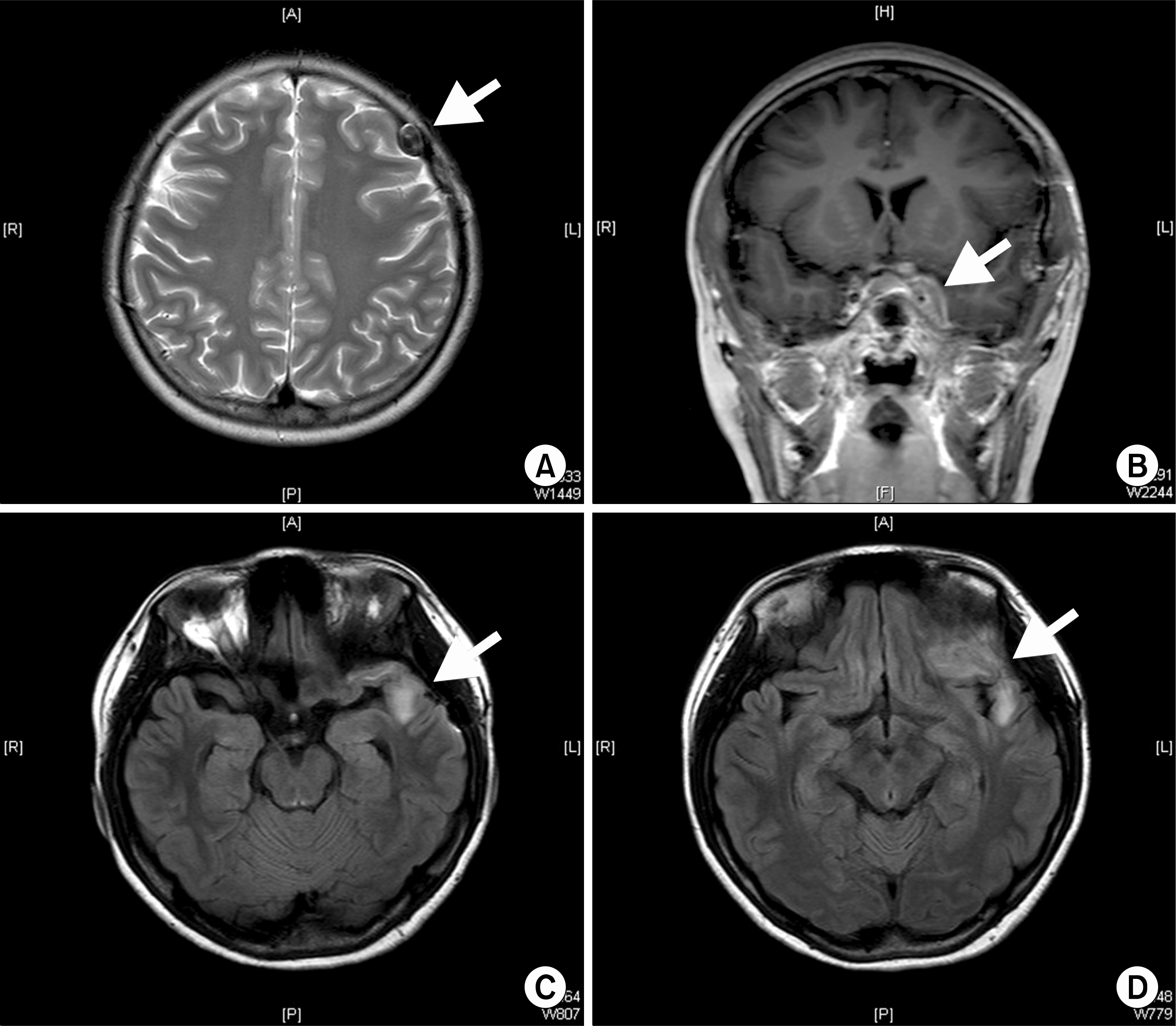
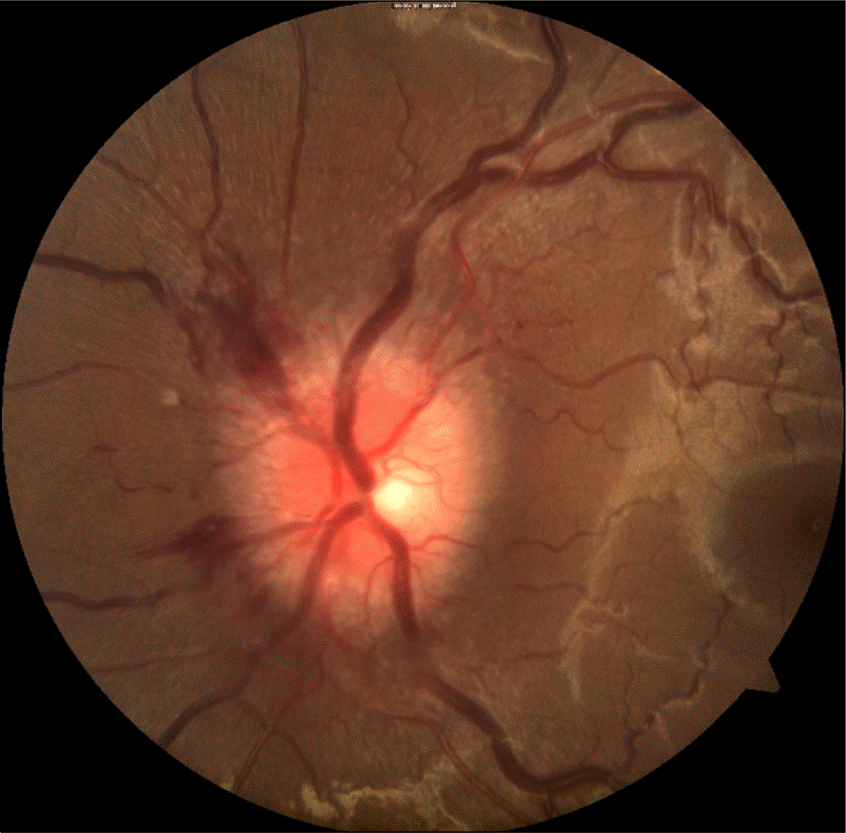
Figure 2.
Image of fundoscopy. Swelling and hyperemia of the disk, blurring of disk margin, and distended veins suggest that the patient has optic neuritis.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download