This article has been corrected. See "Human Leukocyte Antigen-DRB1 Associations in Korean Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis" in Volume 21 on page 278.
Abstract
Objective
The aim of this study is to investigate the association of different subgroups of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (JRA) with human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class II DR alleles.
Methods
One hundred and nineteen Korean juvenile rheumatoid arthritis patients were classified as HLA-DRB1 allele. To assess the frequency, phenotype frequencies of all JRA cases and each subtypes were compared to those of 485 adult controls.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1. Grom AA, Giannini EH, Glass DN. Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and the trimolecular complex (HLA, T cell receptor, and antigen). Differences from rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994; 37:601–7.
2. Nepom B. The immunogenetics of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1991; 17:825–42.

3. Brewer EJ Jr, Bass J, Baum J, Cassidy JT, Fink C, Jacobs J, et al. Current proposed revision of JRA Criteria. JRA Criteria Subcommittee of the Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee of the American Rheumatism Section of The Arthritis Foundation. Arthritis Rheum. 1977; 20(2 Suppl):195–9.
4. Petty RE, Southwood TR, Baum J, Bhettay E, Glass DN, Manners P, et al. Revision of the proposed classification criteria for juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Durban, 1997. J Rheumatol. 1998; 25:1991–4.
5. Leak AM, Woo P. Juvenile chronic arthritis, chronic iridocyclitis, and reactivity to histones. Ann Rheum Dis. 1991; 50:653–7.

6. Glass DN, Giannini EH. Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis as a complex genetic trait. Arthritis Rheum. 1999; 42:2261–8.

7. Haas JP, Truckenbrodt H, Paul C, Hoza J, Scholz S, Albert ED. Subtypes of HLA-DRB1*03, *08, *11, *12, *13 and *14 in early onset pauciarticular juvenile chronic arthritis (EOPA) with and without iridocyclitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1994; 12(Suppl 10):S7–14.
8. Ploski R, Vinje O, Rønningen KS, Spurkland A, Sørskaar D, Vartdal F, et al. HLA class II alleles and heterogeneity of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. DRB1*0101 may define a novel subset of the disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1993; 36:465–72.
9. Garavito G, Yunis EJ, Egea E, Ramirez LA, Malagón C, Iglesias A, et al. HLA-DRB1 alleles and HLA-DRB1 shared epitopes are markers for juvenile rheumatoid arthritis subgroups in Colombian mestizos. Hum Immunol. 2004; 65:359–65.

10. Lee KW, Oh DH, Lee C, Yang SY. Allelic and hap-lotypic diversity of HLA-A, -B, -C, -DRB1, and -DQB1 genes in the Korean population. Tissue Antigens. 2005; 65:437–47.

11. Olerup O, Zetterquist H. HLA-DR typing by PCR amplification with sequence-specific primers (PCR-SSP) in 2 hours: an alternative to serological DR typing in clinical practice including donor-recipient matching in cadaveric transplantation. Tissue Antigens. 1992; 39:225–35.

12. Kam MH, Jeffery LB. Handbook of HLA-typing Techniques. p. 432. Boca Raton: CRC Press;1993.
13. Alsaeid K, Haider MZ, Kamal H, Srivastva BS, Ayoub EM. Prevalence of human leukocyte antigen (HLA) DRB1 alleles in Kuwaiti children with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Immunogenet. 2002; 29:1–5.

14. Stastny P, Fernandez-Viña M, Cerna M, Havelka S, Ivaskova E, Vavrincova P. Sequences of HLA alleles associated with arthritis in adults and children. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1993; 37:5–8.
15. Miller ML, Aaron S, Jackson J, Fraser P, Cairns L, Hoch S, et al. HLA gene frequencies in children and adults with systemic onset juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1985; 28:146–50.

16. Thomson W, Barrett JH, Donn R, Pepper L, Kennedy LJ, Ollier WE, et al. British Paediatric Rheumatology Study Group. Juvenile idiopathic arthritis classified by the ILAR criteria: HLA associations in UK patients. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2002; 41:1183–9.

17. Pratsidou-Gertsi P, Kanakoudi-Tsakalidou F, Spyropoulou M, Germenis A, Adam K, Taparkou A, et al. Nationwide collaborative study of HLA class II associations with distinct types of juvenile chronic arthritis (JCA) in Greece. Eur J Immunogenet. 1999; 26:299–310.

Go to : 
Table 1.
Number, median age at onset, percentage female for each of the JRA subgroup
| Type | Number (%) | Median age (range) | Sex: no. of female (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| All JRA | 119 (42%) | 6.6 (0.6∼15.7) | 64 (53.8%) |
| Polyarticular | 50 | 7.8 (1.9∼15) | 32 (64%) |
| RF* + | 12 | 7.8 (4.1∼13.8) | 10 (83.3%) |
| RF* – | 38 | 7.8 (1.9∼15) | 22 (57.9%) |
| Pauciarticular | 35 (29.4%) | 6.8 (0.8∼15.7) | 16 (45.7%) |
| Systemic | 34 (28.6%) | 5.7 (0.6∼13.8) | 19 (44.2%) |
Table 2.
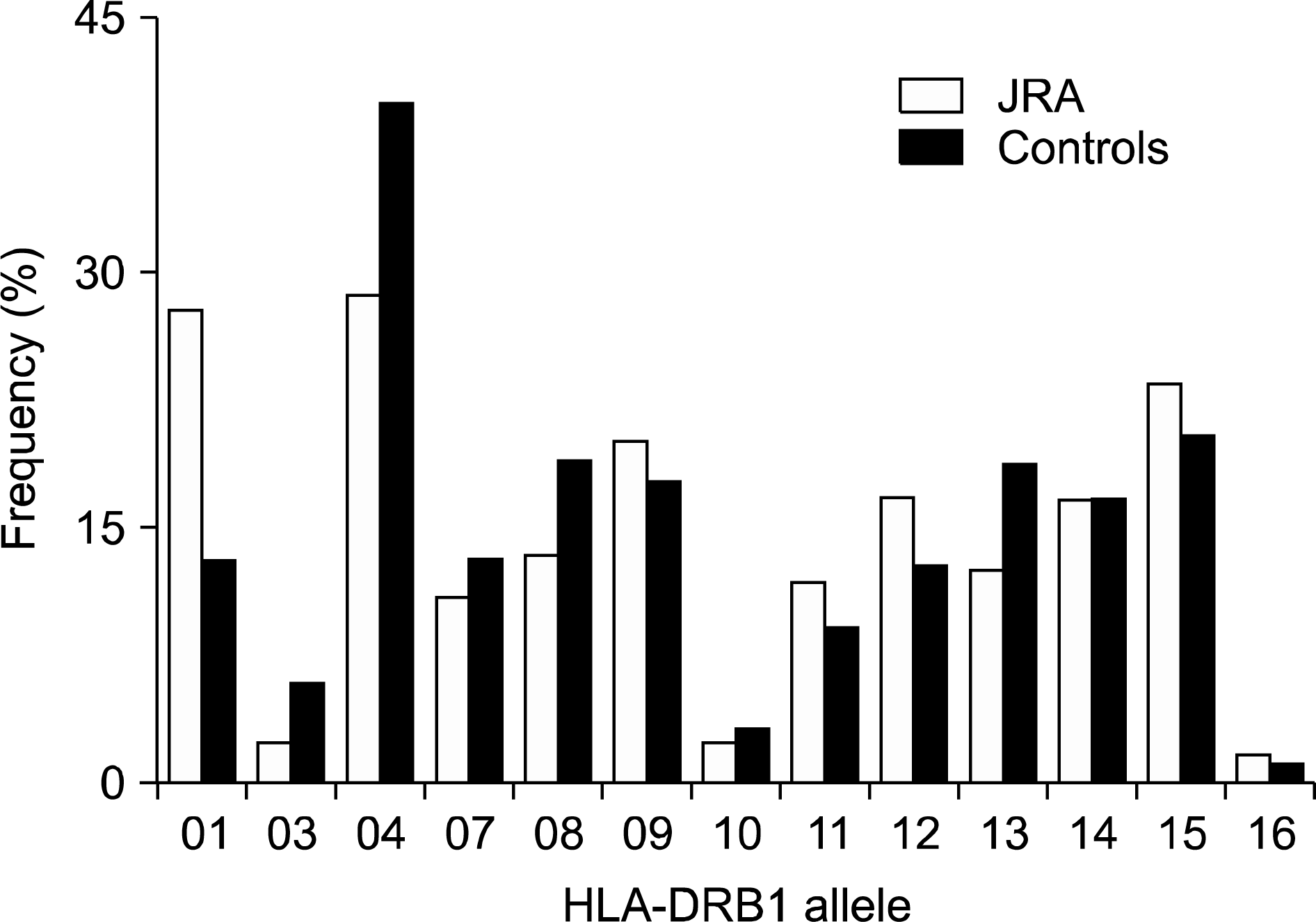
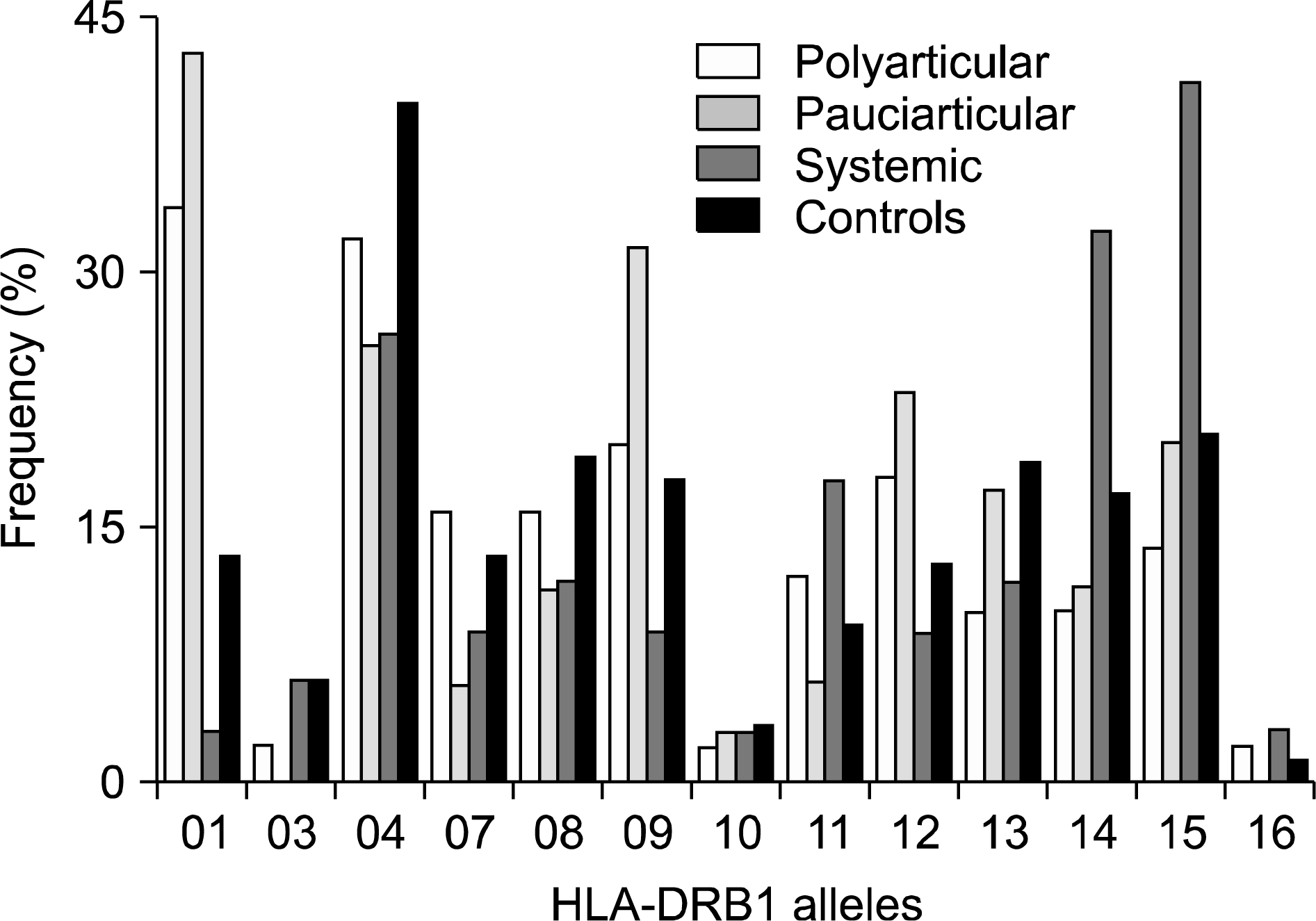
HLA-DRB1 phenotype frequencies in JRA patients, subtypes and controls
Table 3.
HLA-DRB1*01 phenotype frequency percentage and Odds ratio in each subtypes of JRA versus controls
| Subtypes | JRA* | Controls† | Odds ratio | p-value‡ | 95% C.I.§ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyarticular | 18.1% | 2.98 | <0.0001 | 1.66, 5.34 | |
| RF+ | 22.7% | 3.97 | 0.017∥ | 1.42, 11.10 | |
| RF− | 16.7% | 6.9% | 2.70 | 0.003 | 1.38, 5.26 |
| Pauciarticular | 21.7% | 3.75 | <0.0001 | 2.00, 7.00 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download