Abstract
Relapsing polychondritis is an episodic, systemic inflammation of the cartilage with unknown autoimmune etiology. It leads to the destruction of cartilaginous structures of the ear, eye, nose, respiratory tract, joints, skin, and heart valve, and its presented symptoms are diverse. It can be improved mainly by corticosteroid or immunosuppressive agents. Recently, the use of biologic agents (TNF inhibitors, rituximab, tocilizumab et al) was reported from abroad. However, there is no reported case of relapsing polychondritis, which is treated by biologic agents in Korea. We report this first case of refractory relapsing polychondritis, which was improved with a treatment of Infliximab.
REFERENCES
1. Jaksch-Wartenhorst R. Polychondropathia. Wien Arch Inn Med. 1923; 6:93–100.
3. Yang H, Peng L, Jian M, Qin L. Clinical analysis of 15 patients with relapsing auricular polychondritis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2014; 271:473–6.

4. Yeo SW, Kim HR, Yoon CH, Park SN. A case of relapsing polychondritis with inner ear symptom improved by plasmaphresis. Korean Journal of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery. 2005; 48:1290–3.
5. de Barros AP, Nakamura NA, Santana Tde F, Motta JQ, Bianchi WA. Infliximab in relapsing polychondritis. Rev Bras Reumatol. 2010; 50:211–6.
6. Abdwani R, Kolethekkat AA, Al Abri R. Refractory relapsing polychondritis in a child treated with antiCD20 monoclonal antibody (rituximab): first case report. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2012; 76:1061–4.

7. McAdam LP, O'Hanlan MA, Bluestone R, Pearson CM. Relapsing polychondritis: prospective study of 23 patients and a review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 1976; 55:193–215.
8. Damiani JM, Levine HL. Relapsing polychondritis–report of ten cases. Laryngoscope. 1979; 89:929–46.
9. Martin J, Roenigk HH, Lynch W, Tingwald FR. Relapsing polychondritis treated with dapsone. Arch Dermatol. 1976; 112:1272–4.

10. Park J, Gowin KM, Schumacher HR Jr. Steroid sparing effect of methotrexate in relapsing polychondritis. J Rheumatol. 1996; 23:937–8.
Figure 1.
Photomicrograph of left auricular cartilage Biopsy. Auricular cartilage showing degeneration with vacuolization of chondrocyte, fibrosis (H&E stain, A ×100, B ×200).
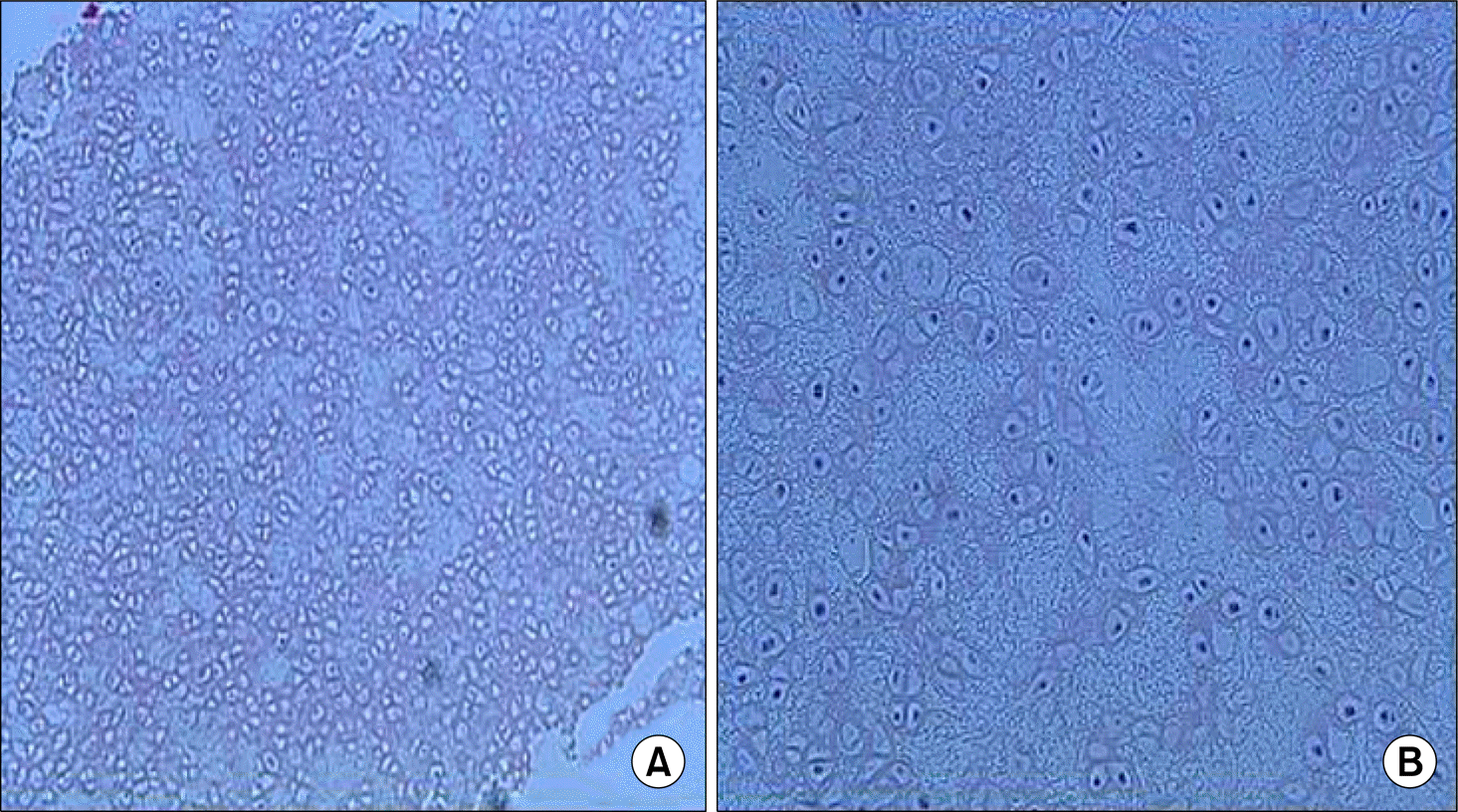
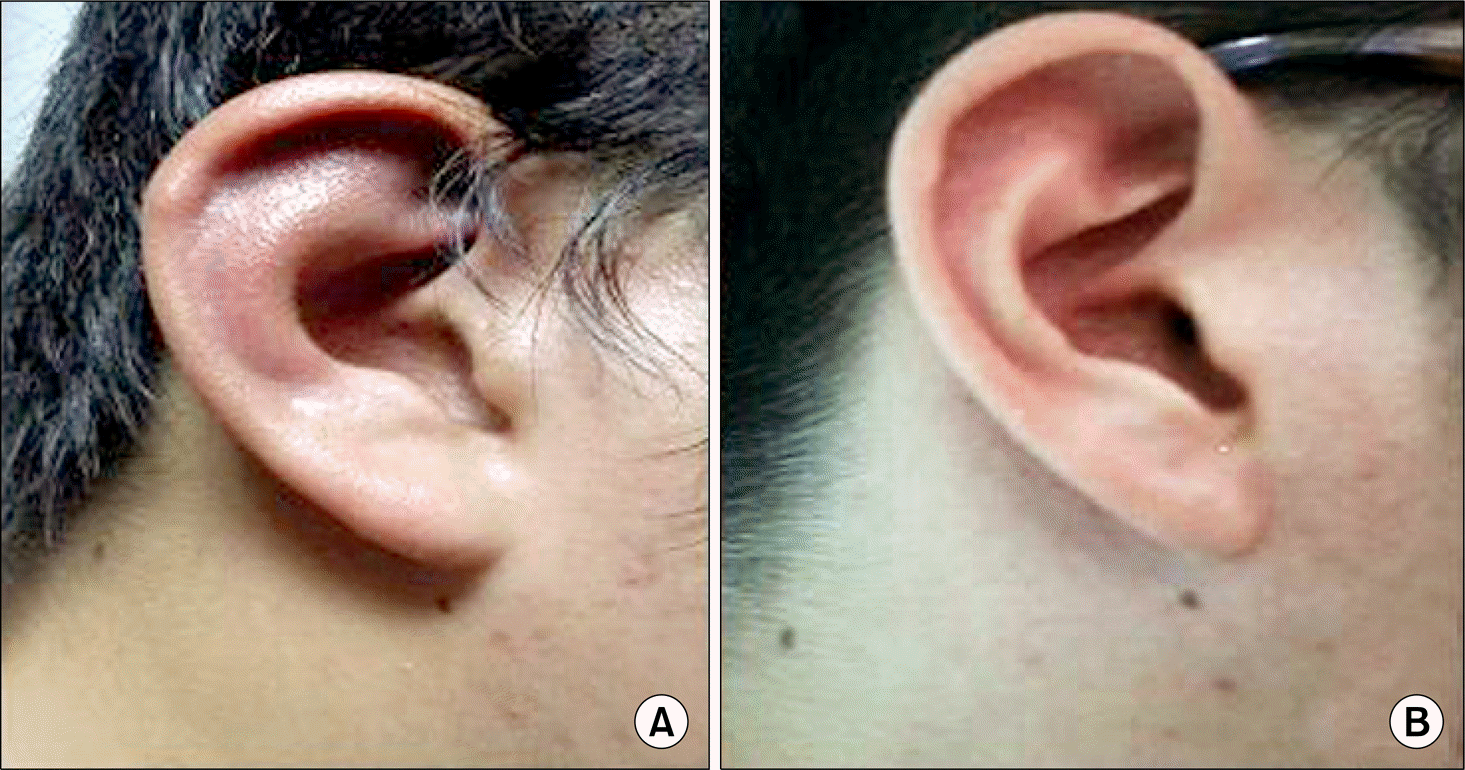
Figure 2.
Photograph of right auricle in the patient. Left photo is the patient's right ear before the infliximab infusion. It shows swelling and redness of the ear, but sparing of the earlobe (A). Rigtht photo is the patient's right ear after the infliximab infusion. It shows no swelling, redness of the ear (B).




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download