Abstract
Dermatomyositis (DM) is an idiopathic inflammatory myopathy, characterized by inflammation of the proximal skeletal muscles and typical skin manifestations, which results in symmetric muscle weakness. A 43-year-old man was presented with skin rash and left leg weakness, and he had a history of poliomyelitis. Initially, he was diagnosed as having post-polio syndrome (PPS) due to unilateral muscle weakness and a result of an the electromyography (EMG), which had shown patterns of PPS. After 4 months with conservative therapy for PPS, weakness of bilateral upper arms had developed and skin rashes on his entire body had aggravated and progressed. He was diagnosed as having dermatomyositis, based on elevated muscle enzyme levels, typical skin rashes, and typical EMG findings, which indicated muscle disease. When a patient with previous poliomyelitis has a newly developed muscle weakness or pain, we should consider various possible causes other than PPS.
REFERENCES
1. Zong M, Lundberg IE. Pathogenesis, classification and treatment of inflammatory myopathies. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017; 297–306.

2. Chung JH, Seo PG. Clinical manifestations of dermatomyositis. Korean J Dermatol. 2002; 40:258–65.
3. Bohan A, Peter JB. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1975; 292:403–7.
5. Miller FW. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Goldman L, Andrew IS, editors. Goldman's Cecil medicine. 24th ed.p. 1716–20. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier;2012.

8. Dalakas MC. Polymyositis, dermatomyositis and in-clusion-body myositis. N Engl J Med. 1991; 325:1487–98.

Figure 1.
Skin lesions show (A) erythema and edema in both upper eyelids (Heliotrope rash), and (B) raised violaceous rashes or papules in dorsal surfaces of metacarpophalangeal and interphalangeal joints (Gottron's papules).
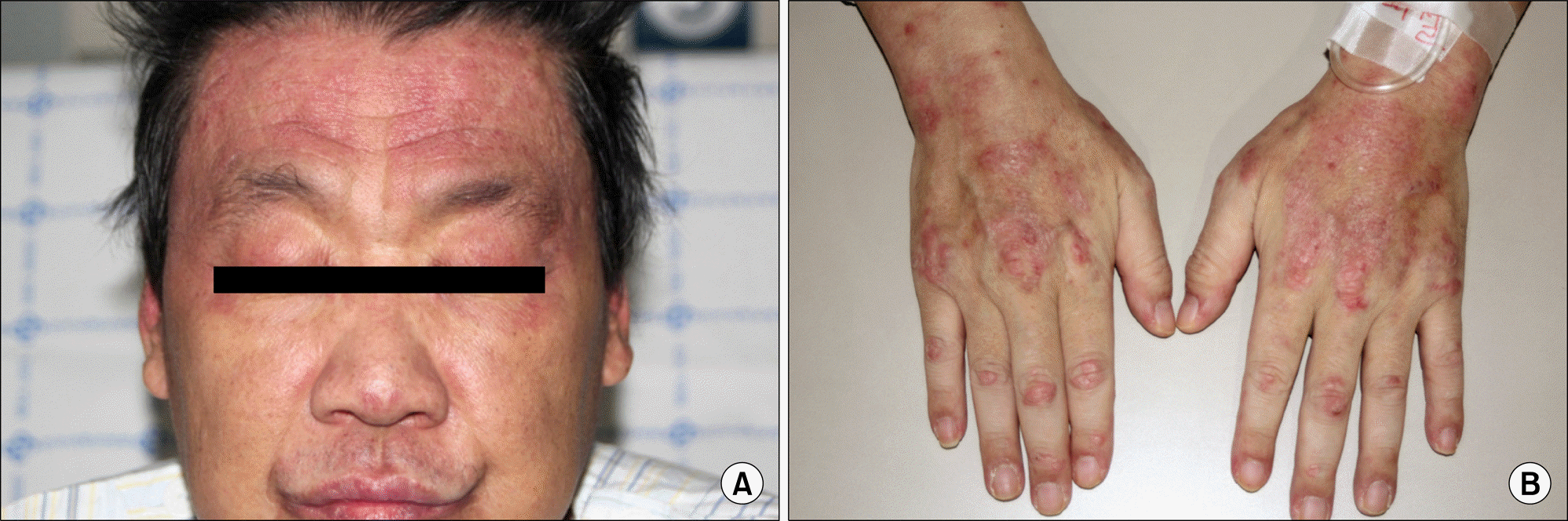
Figure 2.
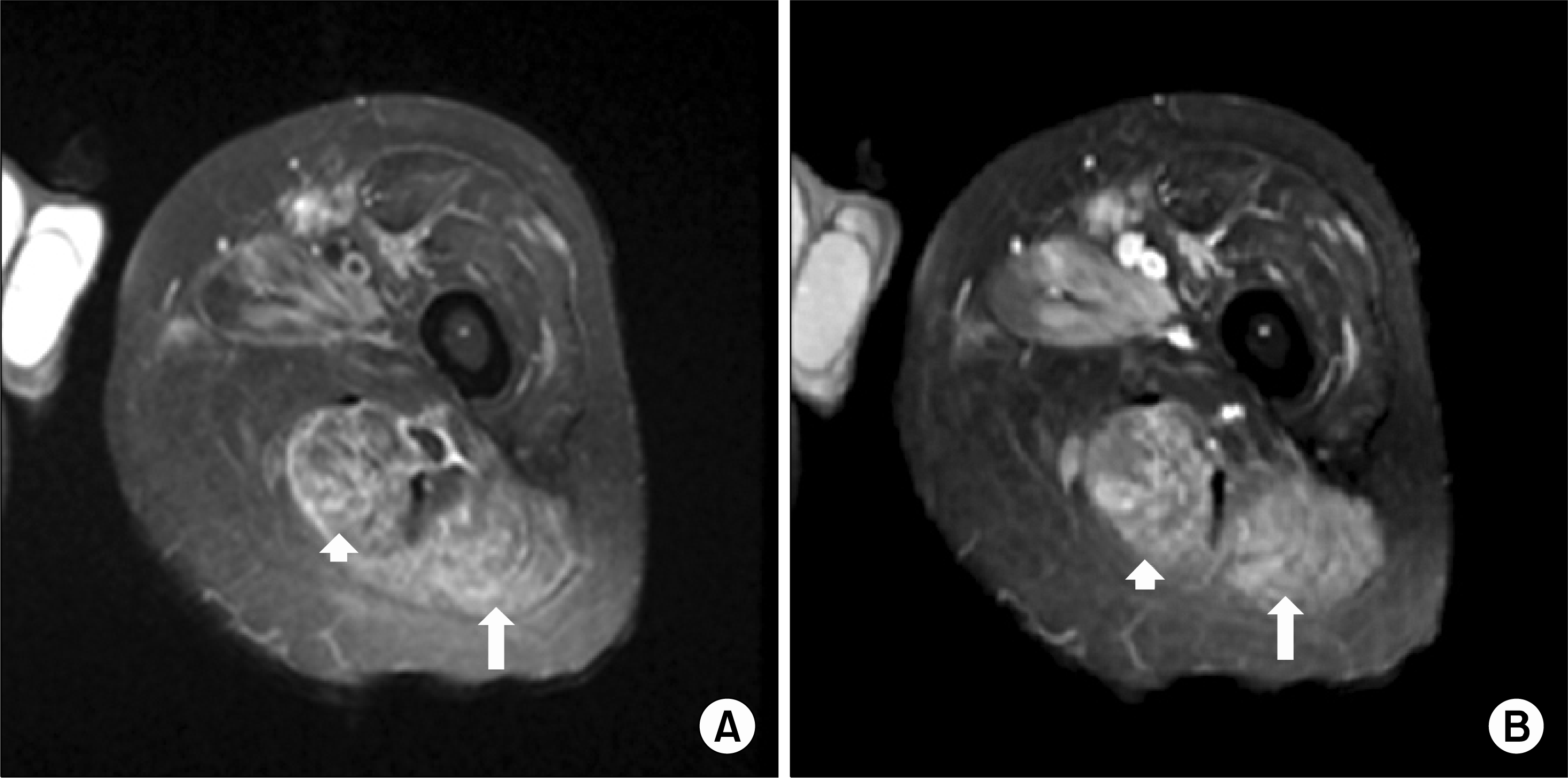
(A) Axial T2-weighted spin-echo MR image shows edema in the left thigh musculature, prominently in the semitendinous muscle (short arrow) and gluteus maximus (long arrow). (B) Axial T1-weighted spin-echo contrast MR image shows diffuse enhancement in the left semitendinous muscle and gluteus maximus with deep fascia enhancement.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download