Abstract
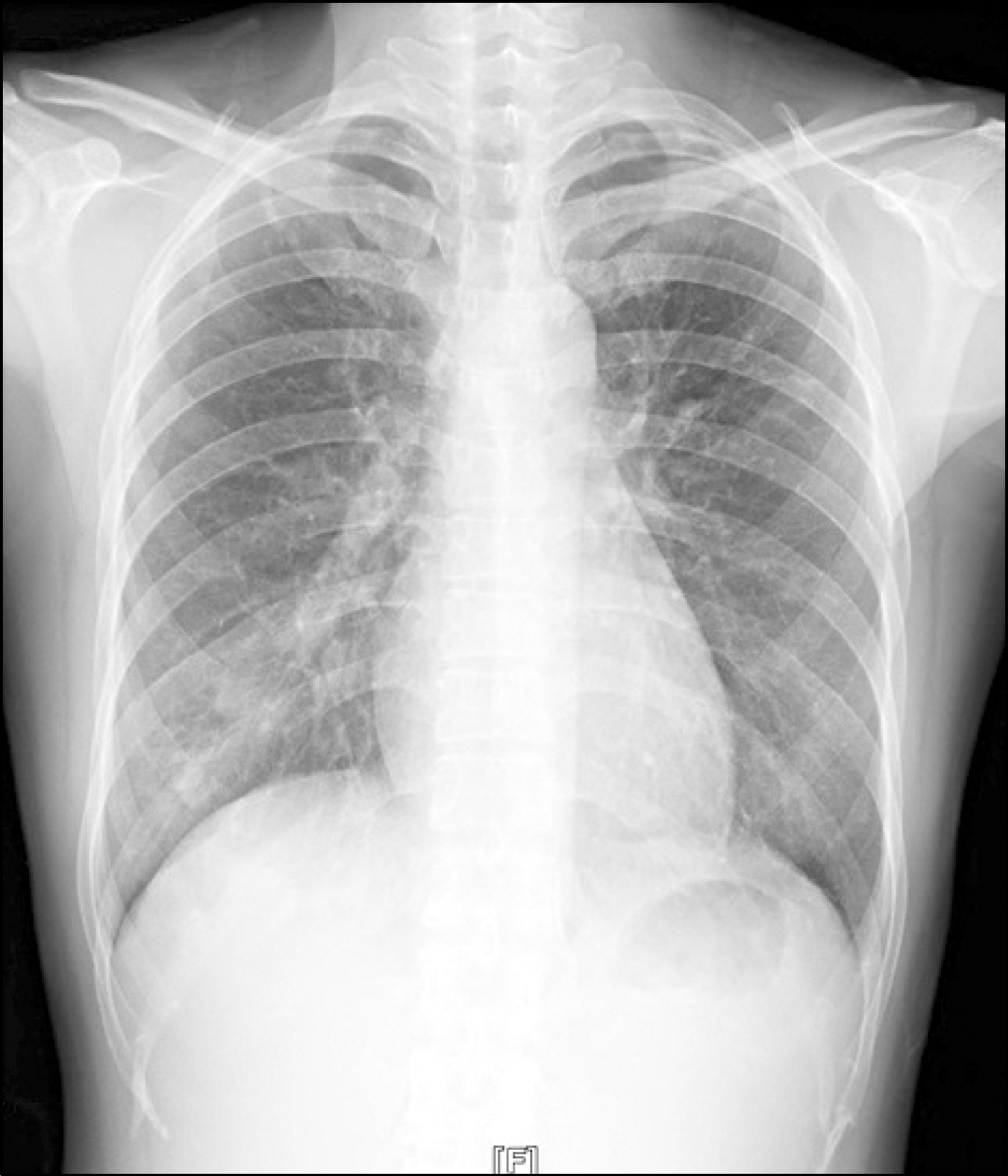
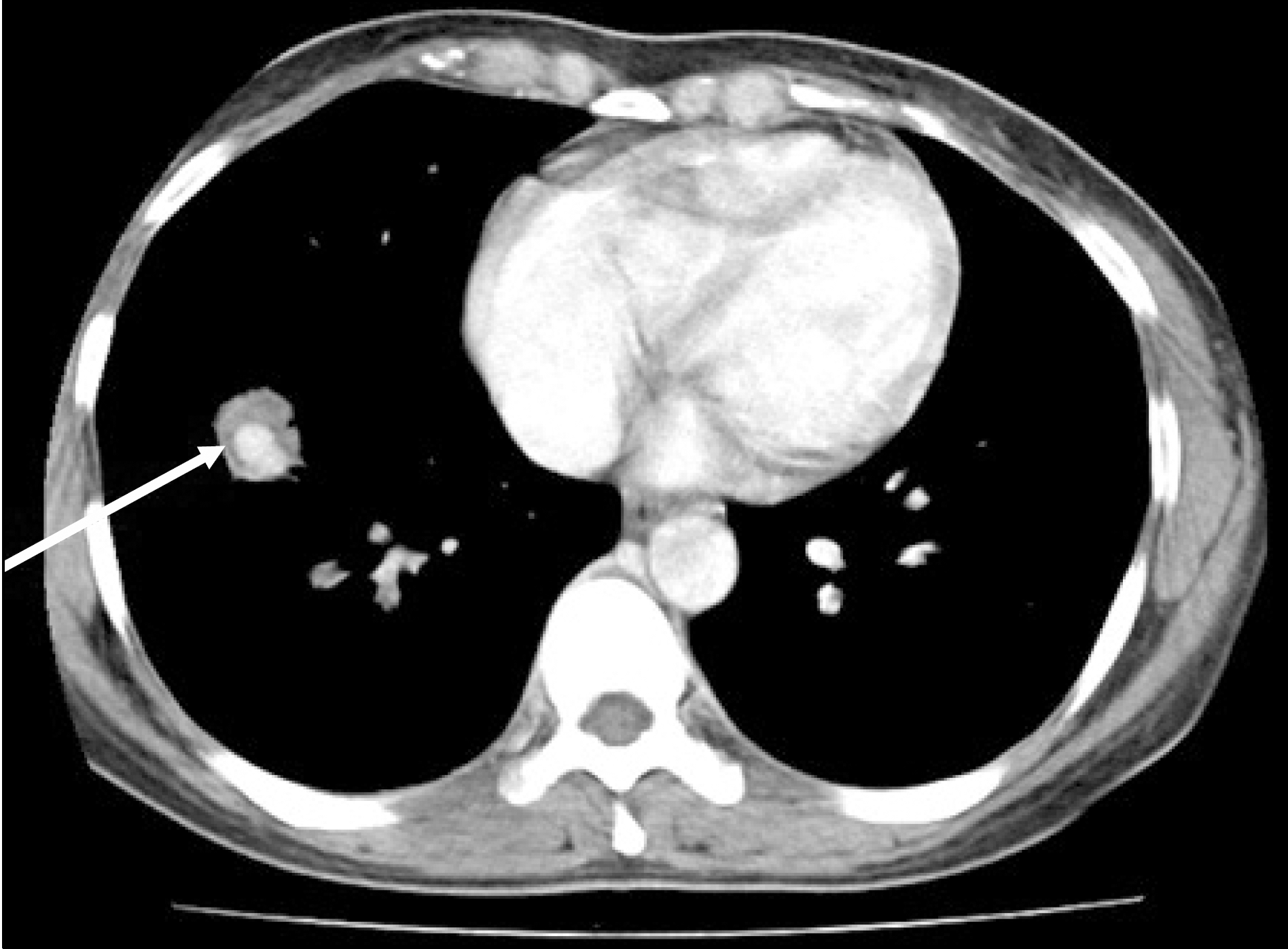
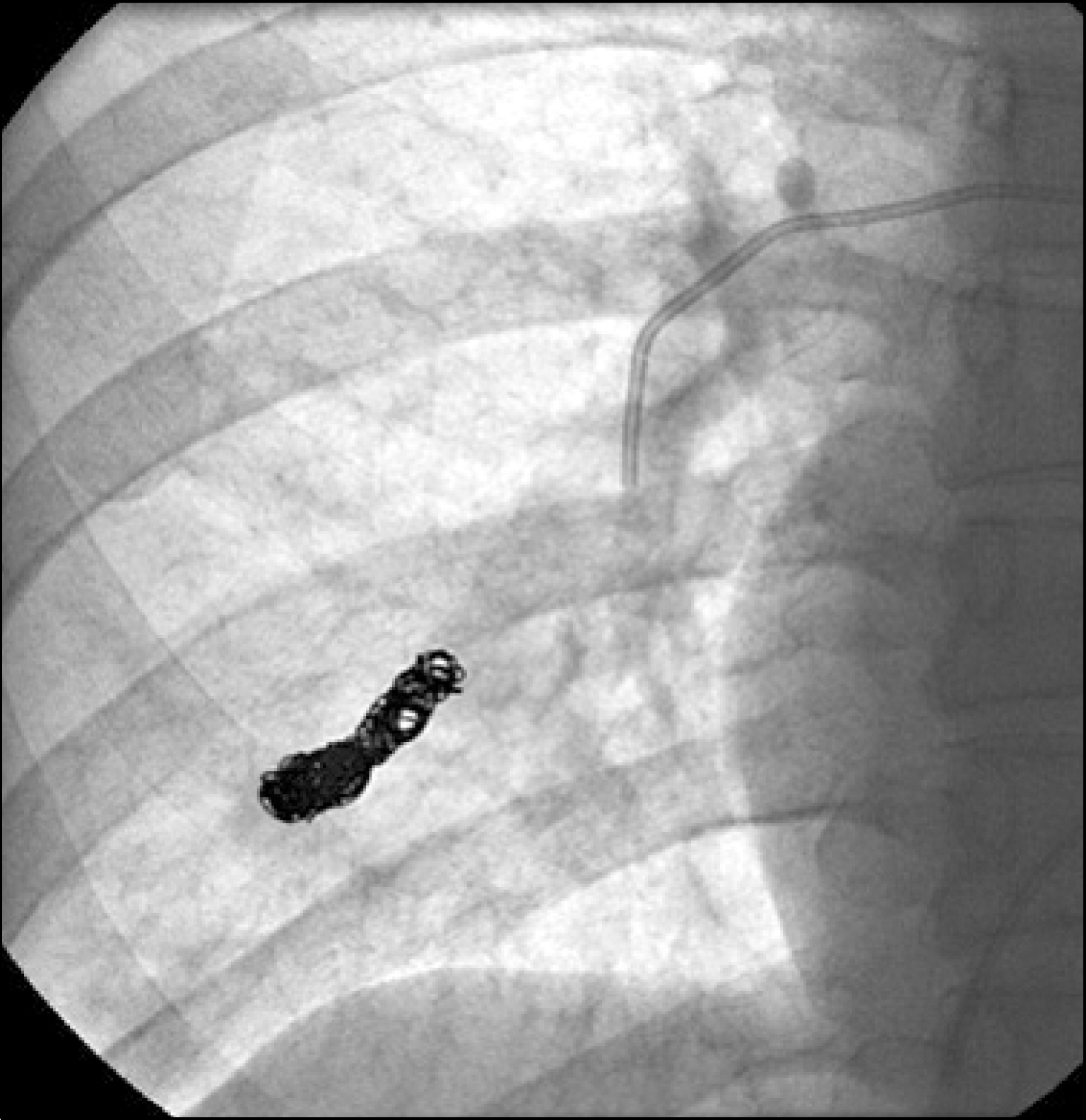
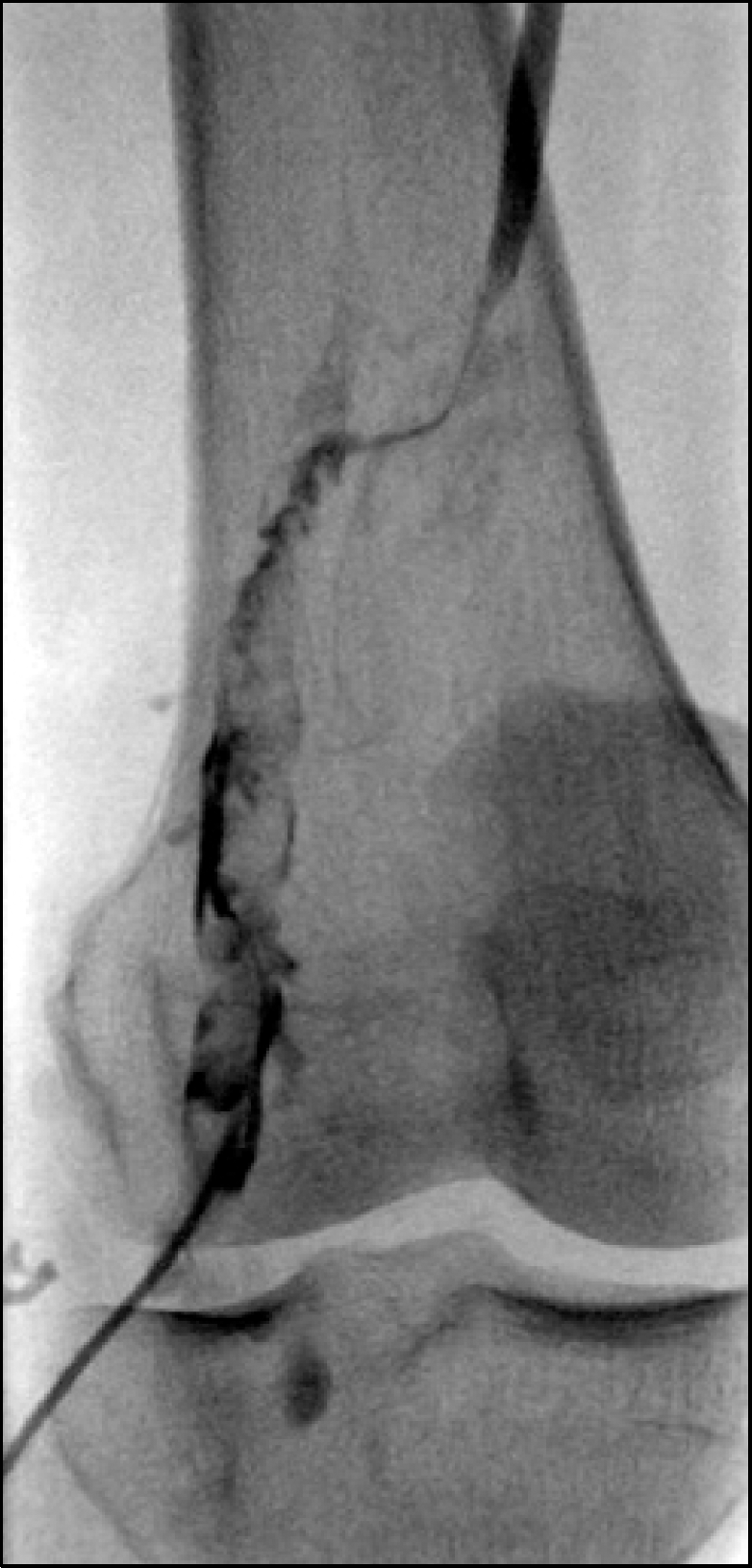
Behcet'sdisease is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by oral ulcers, genital ulcers, uveitis, and skin lesions. Furthermore, Behcet's disease can manifest as vascular lesions, such as, those of vasculitis, venous thrombosis, or thrombophlebitis or as an arterial aneurysm. Here, the authors report the case of a pulmonary artery aneurysm and deep vein thrombosis in a 41-year-old woman with a previous diagnosis of Behcet's disease. The patient presented with hemoptysis and a cough, and was found to have a bleeding pulmonary artery aneurysm at the right lower lung. Pulmonary arteriography was performed and the aneurysm was embolized with coils. As a result, hemoptysis did not subsequently recur. However, five years later, deep vein thrombosis occurred in the left leg. Left leg pain improved after the regional infusion of thromb-olytics.
References
1. Cil BE, Geyik S, Akmangit I, Cekirge S, Besbas N, Balkanci F. Embolization of a giant pulmonary artery aneurysm from Behcet disease with use of cyanoacrylate and the "bubble technique". J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2005; 16:1545–9.
2. Erkan F, Kiyan E, Tunaci A. Pulmonary complications of Behç et's disease. Clin Chest Med. 2002; 23:493–503.
3. Kim YG, Ko HK, Ko OB, Kim TS, Kim HW, Lee CK, et al. Bronchial artery embolization for massive hemoptysis in a patient with Behcet's disease. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2005; 12:311–4.
4. Kural-Seyahi E, Fresko I, Seyahi N, Ozyazgan Y, Mat C, Hamuryudan V, et al. The longterm mortality and morbidity of Behç et syndrome: a 2-decade outcome survey of 387 patients followed at a dedicated center. Medicine (Baltimore). 2003; 82:60–76.
5. Hamuryudan V, Er T, Seyahi E, Akman C, Tü zün H, Fresko I, et al. Pulmonary artery aneurysms in Behç et syndrome. Am J Med. 2004; 117:867–70.
6. Atzeni F, Sarzi-Puttini P, Doria A, Boiardi L, Pipitone N, Salvarani C. Behç et's disease and cardiovascular involvement. Lupus. 2005; 14:723–6.
7. Jean-Baptiste E. Clinical assessment and management of massive hemoptysis. Crit Care Med. 2000; 28:1642–7.

8. Tunaci M, Ozkorkmaz B, Tunaci A, Gül A, Engin G, Acunaş B. CT findings of pulmonary artery aneurysms during treatment for Behç et's disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1999; 172:729–33.
9. Lê Thi Huong D, Wechsler B, Papo T, Piette JC, Bletry O, Vitoux JM, et al. Arterial lesions in Behç et's disease. A study in 25 patients. J Rheumatol. 1995; 22:2103–13.
10. Swanson KL, Johnson CM, Prakash UB, McKusick MA, Andrews JC, Stanson AW. Bronchial artery embolization: experience with 54 patients. Chest. 2002; 121:789–95.
11. Sharafuddin MJ, Sun S, Hoballah JJ, Youness FM, Sharp WJ, Roh BS. Endovascular management of venous throm-botic and occlusive diseases of the lower extremities. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2003; 14:405–23.

12. Hatemi G, Silman A, Bang D, Bodaghi B, Chamberlain AM, Gul A, et al. Management of Behç et disease: a systematic literature review for the European League Against Rheumatism evidence-based recommendations for the management of Behç et disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009; 68:1528–34.
13. Calamia KT, Schirmer M, Melikoglu M. Major vessel involvement in Behç et's disease: an update. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011; 23:24–31.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download