Abstract
Retropharyngeal calcific tendinitis, also known as calcific tendinitis of the longus colli muscle, was first described by Hartley in 1964. It is caused by deposition of calcium hydroxyapatite crystals in the longus colli muscles from C1 to C3. Retropharyngeal calcific tendinitis is diagnosed ra-diologically by the detection of amorphous calcification and prevertebral soft tissue swelling. Twelve cases of retro-pharnygeal calcific tendinitis have been reported in the Korean literature, but no cases with ankylosing spondylitis. In this case, we report an unusual case of retropharyngeal calcific tendinitis with ankylosing spondylitis.
References
1. Hartley J. Acute cervical pain associated with retropharyngeal calcium deposit. A case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1964; 46:1753–4.
2. Chung T, Rebello R, Gooden EA. Retropharyngeal calcific tendinitis: case report and review of literature. Emerg Radiol. 2005; 11:375–80.

3. Bladt O, Vanhoenacker R, Bevernage C, Van Orshoven M, Van Hoe L, D'Haenens P. Acute calcific prevertebral tendinitis. JBR-BTR. 2008; 91:158–9.
4. Offiah CE, Hall E. Acute calcific tendinitis of the longus colli muscle: spectrum of CT appearances and anatomical correlation. Br J Radiol. 2009; 82:e117–21.

5. Southwell K, Hornibrook J, O'Neill-Kerr D. Acute longus colli calcific tendonitis causing neck pain and dysphagia. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008; 138:405–6.

6. Smith RV, Rinaldi J, Hood DR, Troost T. Hydroxyapatite deposition disease: an uncommon cause of acute odynophagia. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1996; 114:321–3.

7. Lyo IU, Kim Y, Yu HK, Ahn SK. Acute calcific retropharyngeal tendinitis - case report -. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2003; 33:317–9.
8. Lee IS, Kim SW, Kim SY, Kim BR, Lim JH, Lee J, et al. Acute retropharyngeal calcific tendinitis: two cases reports. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2009; 33:718–22.
9. Hyun SY, Shin SY, Kim JS. Calcific tendinitis of the longus colli muscle in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. J Korean Rheumatism Association. 2010; 17:66–70.

10. Park SY, Jin W, Lee SH, Park JS, Yang DM, Ryu KN. Acute retropharyngeal calcific tendinitis: a case report with unusual location of calcification. Skeletal Radiol. 2010; 39:817–20.

11. Shin DE, Ahn CS, Choi JP. The acute calcific prevertebral tendinitis: report of two cases. Asian Spine J. 2010; 4:123–7.

12. Song KJ, Lee KB. Acute calcific tendinitis of the longus colli muscle in the cervical spine. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2010; 45:486–9.

13. Lee CH, Huh SH, Jin SM, Lee SH. 3 Cases of acute retropharyngeal calcific tendinitis misconceived as acute retropharyngeal abscess. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2011; 54:411–4.

Figure 2.
(A) Sagittal non-enhan-ced CT of the neck and (B) axial images show amorphous calcific lesion (arrow) anterior to C1∼2.
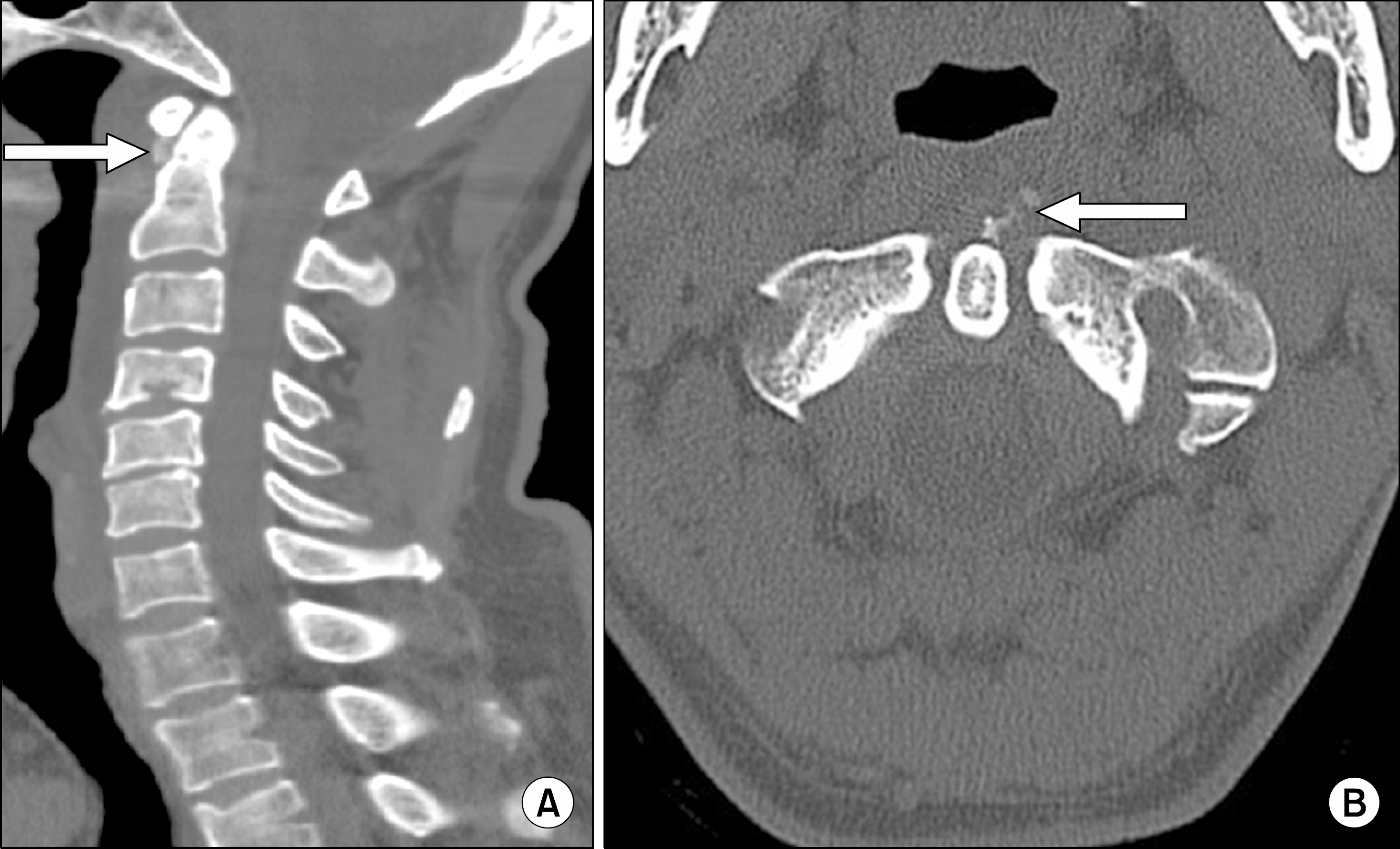
Figure 3.
(A) MRI T2 sagittal image shows prominent swelling (arrow) of left side longus colli muscle insertion near the anterior arch of atlas with possible calcific tendinitis involving the longus colli muscles. (B) MRI T2 axial image shows low signal intensity (arrow) in the anterolateral space of the vertebra.

Table 1.
Summary of patients with retropharyngeal calcific tendinitisin in Korea




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download