Abstract
Behcet's disease (BD) is a rare, multisystemic disorder characterized by vasculitis. Although renal involvement rarely coexists with BD, several types of renal involvements have been reported: amyloidosis, glomerulonephritis and vascular involvement. Herein, we report a rare case of BD complicated with IgA nephropathy (IgAN). A 42-year-old woman visited the hospital due to joint pains and painful subcutaneous nodules. Based on her medical history of recurrent orogenital ulcers, arthritis, enteral ulcers, erythema nodosum-like skin lesions, and a positive pathergy test, we diagnosed her with BD. To evaluate proteinuria, we performed a renal biopsy. The patient was diagnosed with BD complicated with IgAN, and treated with a low dosage of steroid, colchicine, as well as angiotensin II type I receptor blockers. Although renal involvement in BD is rare, it is important to periodically perform renal function assessments in patients with BD involving abnormal urine results.
Go to : 
References
1. Yazici H, Fresko I, Yurdakul S. Behç et's syndrome: disease manifestations, management, and advances in treatment. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2007; 3:148–55.
2. Hashimoto T, Toya Y, Kihara M, Yabana M, Inayama Y, Tanaka K, et al. Behç et's disease complicated by IgA nephropathy with nephrotic syndrome. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2008; 12:224–7.
3. Akpolat T, Akkoyunlu M, Akpolat I, Dilek M, Odabas AR, Ozen S. Renal Behç et's disease: a cumulative analysis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2002; 31:317–37.
4. Akpolat T, Dilek M, Aksu K, Keser G, Toprak O, Cirit M, et al. Renal Behç et's disease: an update. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2008; 38:241–8.
5. Hemmen T, Perez-Canto A, Distler A, Offermann G, Braun J. IgA nephropathy in a patient with Behç et's syndrome–case report and review of literature. Br J Rheumatol. 1997; 36:696–9.
6. Haas M. Histologic subclassification of IgA nephropathy: a clinicopathologic study of 244 cases. Am J Kidney Dis. 1997; 29:829–42.

7. Working Group of the International IgA Nephropathy Network and the Renal Pathology Society. Roberts IS, Cook HT, Troyanov S, Alpers CE, Amore A, et al. The Oxford classification of IgA nephropathy: pathology defi-nitions, correlations, and reproducibility. Kidney Int. 2009; 76:546–56.

8. Altay M, Secilmis S, Unverdi S, Ceri M, Duranay M. Behcet's disease and IgA nephropathy. Rheumatol Int. 2012; 32:2227–9.

10. Yurdakul S, Yazici H. Behç et's syndrome. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2008; 22:793–809.
11. Tomino Y, Sakai H. Special Study Group (IgA Nephropathy) on Progressive Glomerular Disease. Clinical guidelines for immunoglobulin A (IgA) nephropathy in Japan, second version. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2003; 7:93–7.

12. Fernandes PF, Júnior GB, Barros FA, Sousa DC, Franco LM, Patrocínio RM. Behcet's disease and IgA nephropathy: report of this association in a patient from Brazil and literature review. Invest Clin. 2006; 47:405–11.
13. Akutsu Y, Itami N, Tanaka M, Kusunoki Y, Tochimaru H, Takekoshi Y. IgA nephritis in Behç et's disease: case report and review of the literature. Clin Nephrol. 1990; 34:52–5.
14. Suemitsu T, Saga T, Inui A, Ariizumi M, Shogi E, Sato H. A ciclosporin A responsive case of Behç et's disease associated with IgA nephropathy. Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 1993; 35:189–94.
15. Furukawa T, Hisao O, Furuta S, Shigematsu H. Henoch-Schö nlein purpura with nephritis in a patient with Behç et's disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 1989; 13:497–500.
Go to : 
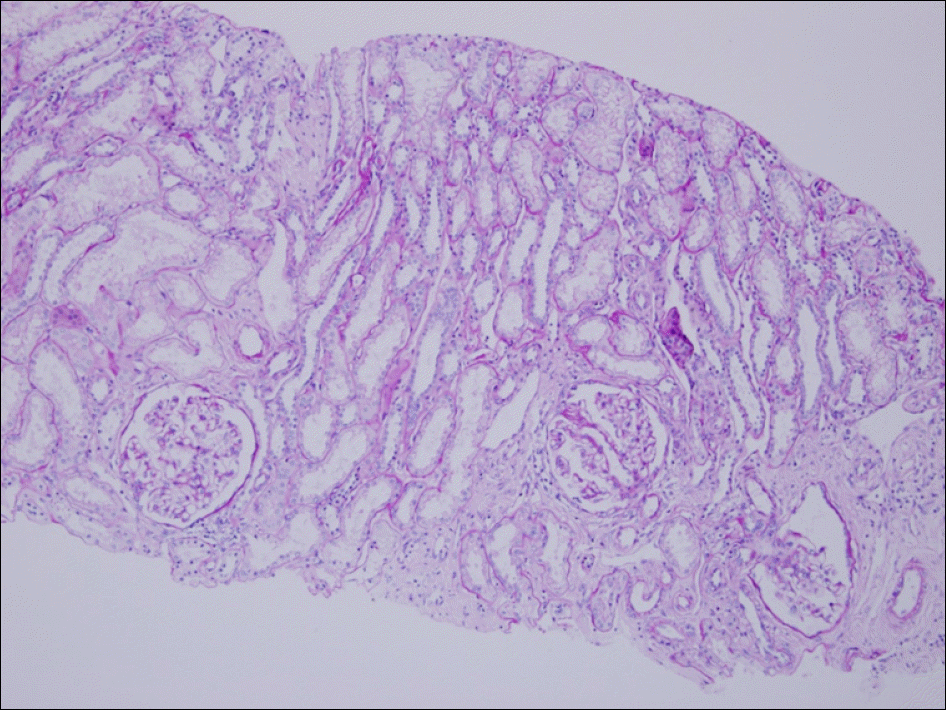 | Figure 1.Each glomerulus was mildly increased in size and focally increased in mesangial cellularity (PAS, ×100). |
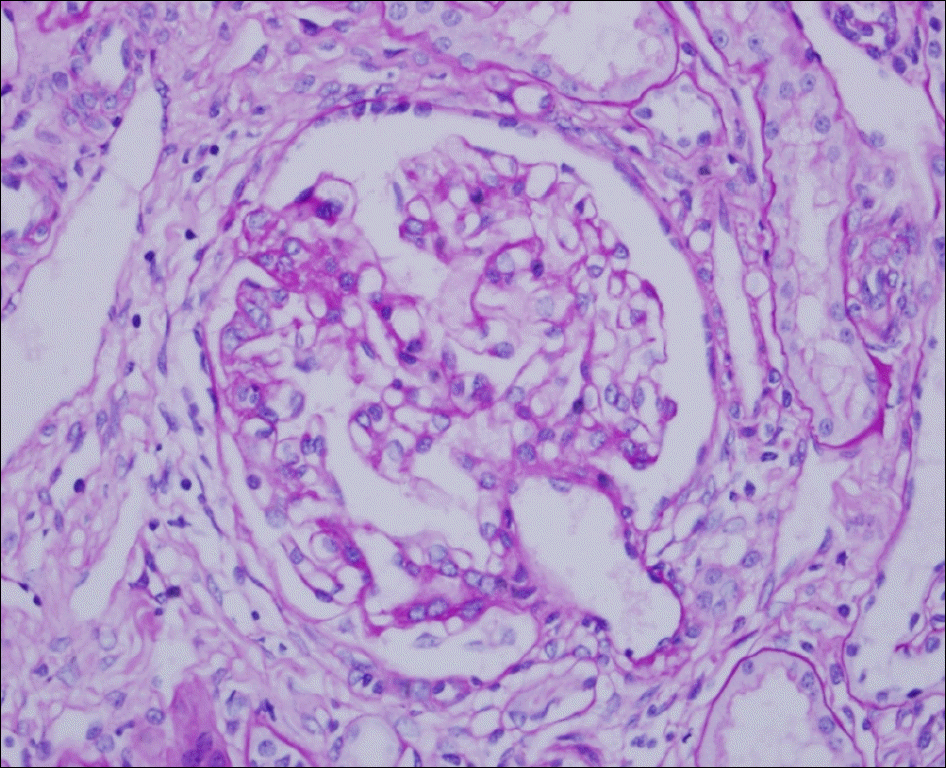 | Figure 2.Light microscopic finding of renal biopsy. A focus of segmental mesangial expansion by mild mesangial hypercellu-larity is seen with Bowman's adhesion (PAS, ×400). |
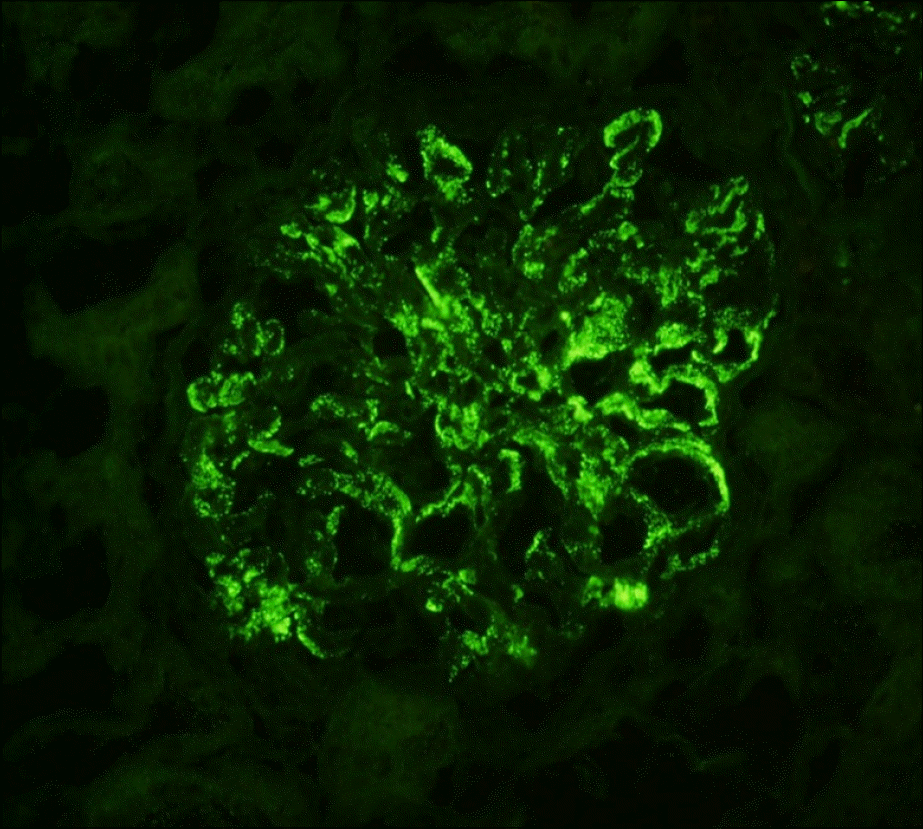 | Figure 3.Immunofluorescent finding. Strong positive staining of IgA is noted in the mesangium and focal peripheral capillary loops (DIF for IgA, ×400). |
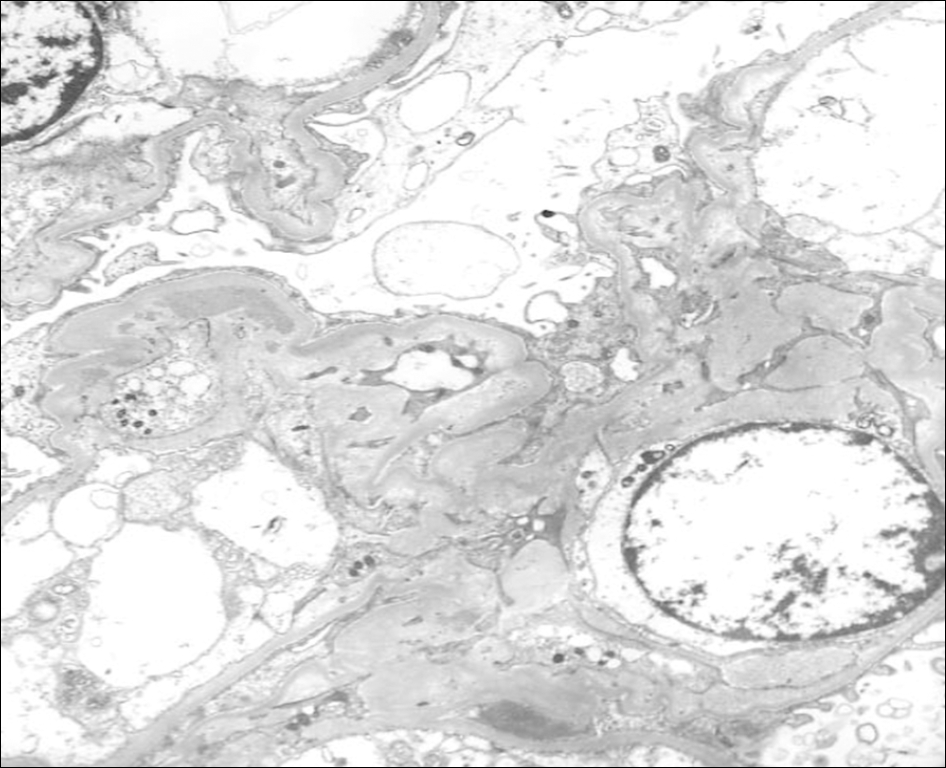 | Figure 4.Ultrastructural finding. Multiple mesangial electron dense deposits are presentedin the mesangial region with suben-dothelial mesangial interposition (original magnification, ×2,500). |
Table 1.
Reported cases of IgA nephropathy associated with Behcet's disease




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download