Abstract
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha antagonist has been proven to have benefit for rheumatologic diseases. Because TNF-alpha is not only an important mediator of inflammation in human body, but plays many physiologic roles, it can cause unique adverse effects or complications related to these functions. Adverse effects involving neurological systems, such as Guillain-Barre syndrome, Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy, multifocal motor neuropathy with conduction blocks (MMNCB), distal symmetric polyneuropathy, and small fibers neuropathy have been previously reported. However, only several cases of infliximab-associated MMNCB are reported. We report a case of MMNCB which developed while treating spondyloarthropathy with infliximab.
Go to : 
References
1. Pestronk A. Multifocal motor neuropathy: diagnosis and treatment. Neurology. 1998; 51(6 Suppl 5):S22–4.

2. Meuth SG, Kleinschnitz C. Multifocal motor neuropathy: update on clinical characteristics, pathophysiological concepts and therapeutic options. Eur Neurol. 2010; 63:193–204.

3. Baraliakos X, Braun J. Anti-TNF-alpha therapy with infliximab in spondyloarthritides. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2010; 6:9–19.
4. Braun J, Baraliakos X. Treatment of ankylosing spondylitis and other spondyloarthritides. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2009; 21:324–34.

5. Stübgen JP. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonists and neuropathy. Muscle Nerve. 2008; 37:281–92.
6. Rodriguez-Escalera C, Belzunegui J, Lopez-Dominguez L, Gonzalez C, Figueroa M. Multifocal motor neuropathy with conduction block in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis on infliximab therapy. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005; 44:132–3.

7. Paolazzi G, Peccatori S, Cavatorta FP, Morini A. A case of spontaneously recovering multifocal motor neuropathy with conduction blocks (MMNCB) during anti-TNF alpha therapy for ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Rheumatol. 2009; 28:993–5.

8. Mohan N, Edwards ET, Cupps TR, Oliverio PJ, Sandberg G, Crayton H, et al. Demyelination occurring during an- ti-tumor necrosis factor alpha therapy for inflammatory arthritides. Arthritis Rheum. 2001; 44:2862–9.
9. Kotyla PJ, Sliwinska-Kotyla B, Kucharz EJ. Treatment with infliximab may contribute to the development of peripheral neuropathy among the patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2007; 26:1595–6.

10. Day R. Adverse reactions to TNF-alpha inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2002; 359:540–1.
11. Barber CE, Lee P, Steinhart AH, Lazarou J. Multifocal motor neuropathy with conduction block following treatment with infliximab. J Rheumatol. 2010; 37:1778–80.

12. Cocito D, Bergamasco B, Tavella A, Poglio F, Paolasso I, Costa P, et al. Multifocal motor neuropathy during treatment with infliximab. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2005; 10:386–7.

13. Cope A, Ettinger R, McDevitt H. The role of TNF alpha and related cytokines in the development and function of the autoreactive T-cell repertoire. Res Immunol. 1997; 148:307–12.
14. McCluskey L, Feinberg D, Cantor C, Bird S. "Pseudo- conduction block" in vasculitic neuropathy. Muscle Nerve. 1999; 22:1361–6.
Go to : 
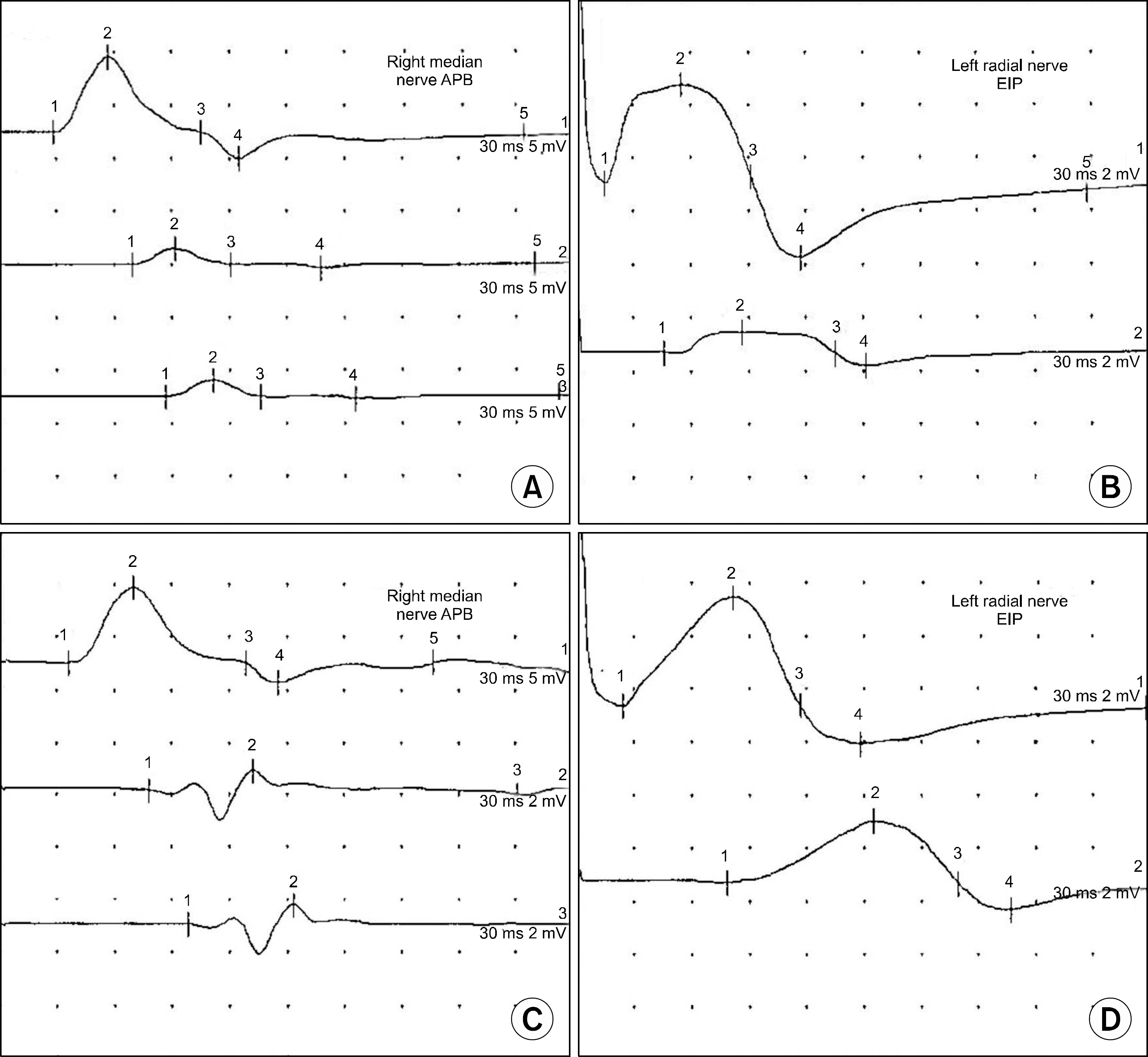 | Figure 1.Serial motor nerve conduction studies of the right median nerve and left radial nerve among the 4 months. (A, B) The first study was done at 14 days after symptom onset, muscle response after stimu-lation at the axilla is 50% reduced in amplitude and area as compared with that after more distal stimu-lation at the forearm. This fits the definition of focal motor conduction block across that nerve segment. (C, D) Four months after stopping infliximab, the conduction blocks had slightly improved in the right median nerve and left radial nerve. APB: abductor pollicis brevis, EIP: extensor indicis proprius. |
Table 1.
Nerve conduction study in the patient




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download