Abstract
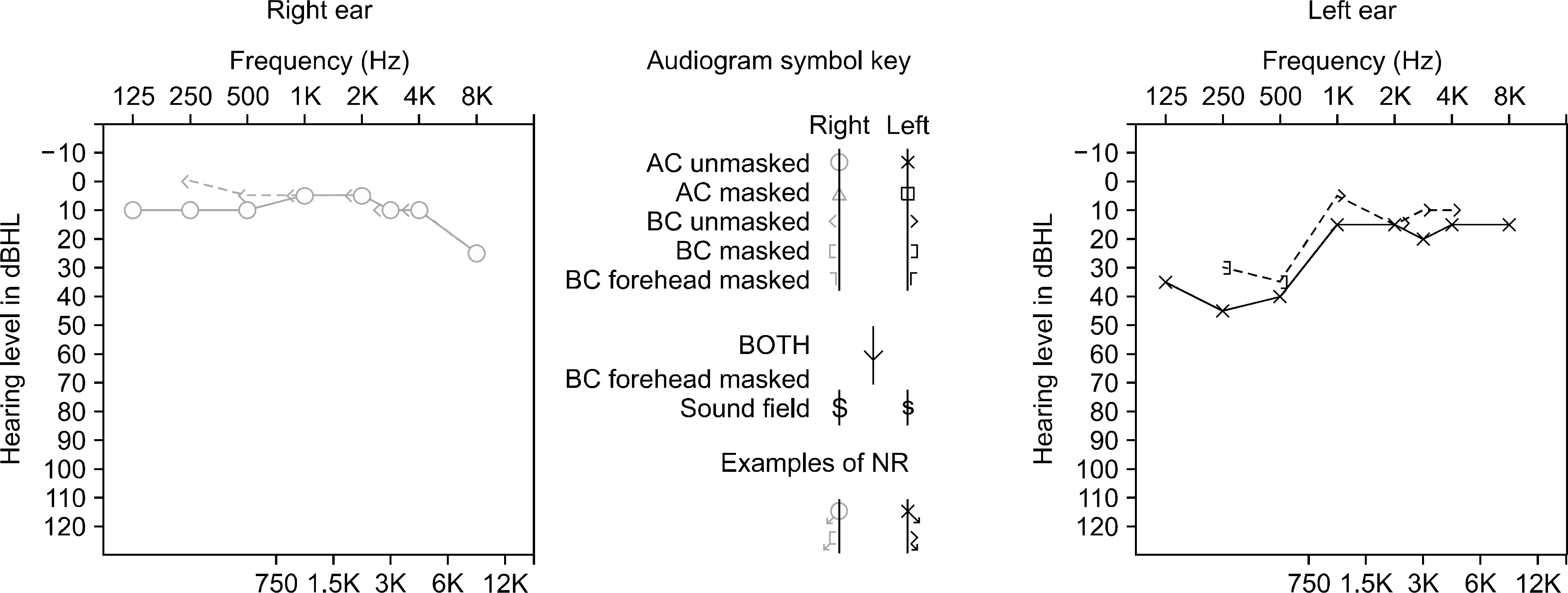
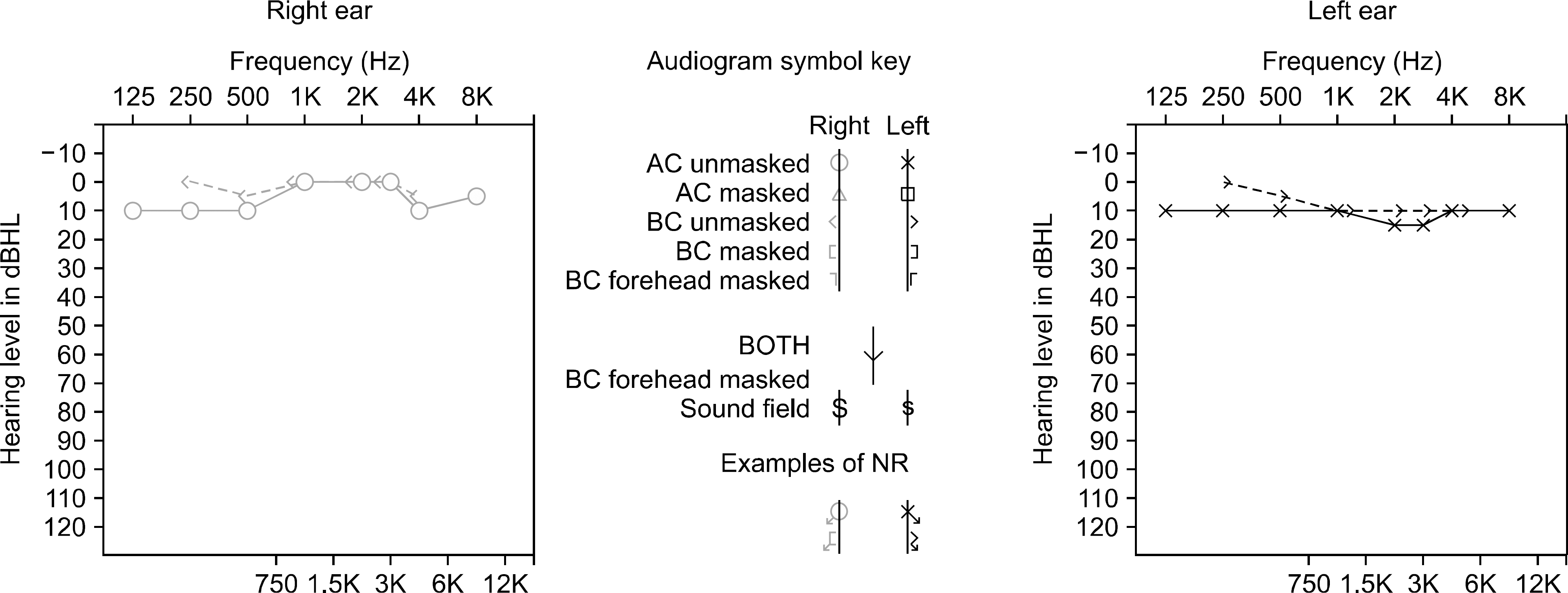
Sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) is rarely presented in patients with several immune-mediated inflammatory diseases. We report a case of sudden SNHL in a patient with axial spondyloarthritis (aSpA). A 29-year-old male with aSpA was admitted for sudden unilateral hearing loss. His aSpA symptom was stable; however, pure tone audiometry revealed that he had SNHL in the left ear at low frequency. His hearing was fully recovered with systemic and local steroid therapy. This case suggests that sudden SNHL may be an extraarticular manifestation of aSpA and thus need prompt steroid therapy in order to restore hearing.
References
1. Kuhn M, Heman-Ackah SE, Shaikh JA, Roehm PC. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a review of diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis. Trends Amplif. 2011; 15:91–105.
2. Toubi E, Ben-David J, Kessel A, Halas K, Sabo E, Luntz M. Immune-mediated disorders associated with idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2004; 113:445–9.

3. Yueh B, Shapiro N, MacLean CH, Shekelle PG. Screening and management of adult hearing loss in primary care: scientific review. JAMA. 2003; 289:1976–85.
4. Bak SK, Kim HS, Lee SH, Jung JH, Jeon JW, Park SD, et al. A case of systemic lupus erythematosus with sensorineural hearing loss. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2003; 10:433–7.
5. Lee EY, Ahn MS, Shin J, Lee CK, Cho YS, Yoo B, et al. A case of systemic lupus erythematosus presented with sensorineural hearing loss. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2001; 8:140–4.
6. Raza K, Karokis D, Wilson F, Delamere JP. Sensorineural hearing loss, iritis and ankylosing spondylitis. Br J Rheumatol. 1998; 37:1363.

7. Corapci I, Armagan O, Tascioglu F, Oner C. Sensorineural hearing loss in a patient with ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatol Int. 2004; 24:252–3.

8. Park SN, Yeo SW, Park YS, Suh BD. Immune-mediated sensorineural hearing loss in a patient with ankylosing spondylitis. Korean J Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2000; 43:663–6.
9. Rudwaleit M, van der Heijde D, Landewé R, Listing J, Akkoc N, Brandt J, et al. The development of Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part II): validation and final selection. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009; 68:777–83.

10. Savastano M, Marioni G, Bernini G, Punzi L. Tinnitus and bilateral sensorineural hearing loss: ankylosing spondylitis or a side-effect of sulphasalazine treatment? Acta Otolaryngol. 2005; 125:671–3.

11. Amor-Dorado JC, Barreira-Fernandez MP, Vazquez-Rodriguez TR, Gomez-Acebo I, Miranda-Filloy JA, Diaz de Teran T, et al. Audiovestibular manifestations in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2011; 90:99–109.

12. Adam M, Erkan AN, Arslan D, Leblebici B, Ozlü oğlu L, Nafiz Akman M. High-frequency sensorineural hearing loss in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: is it an extra-rticuler feature of disease? Rheumatol Int. 2008; 28:413–7.

13. Eryilmaz A, Dagli M, Karabulut H, Sivas Acar F, Erkol Inal E, Gocer C. Evaluation of hearing loss in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. J Laryngol Otol. 2007; 121:845–9.

14. Ajodhia JM, Dix MR. Drug-induced deafness and its treatment. Practitioner. 1976; 216:561–70.
15. Byl FM Jr. Sudden hearing loss: eight years' experience and suggested prognostic table. Laryngoscope. 1984; 94:647–61.
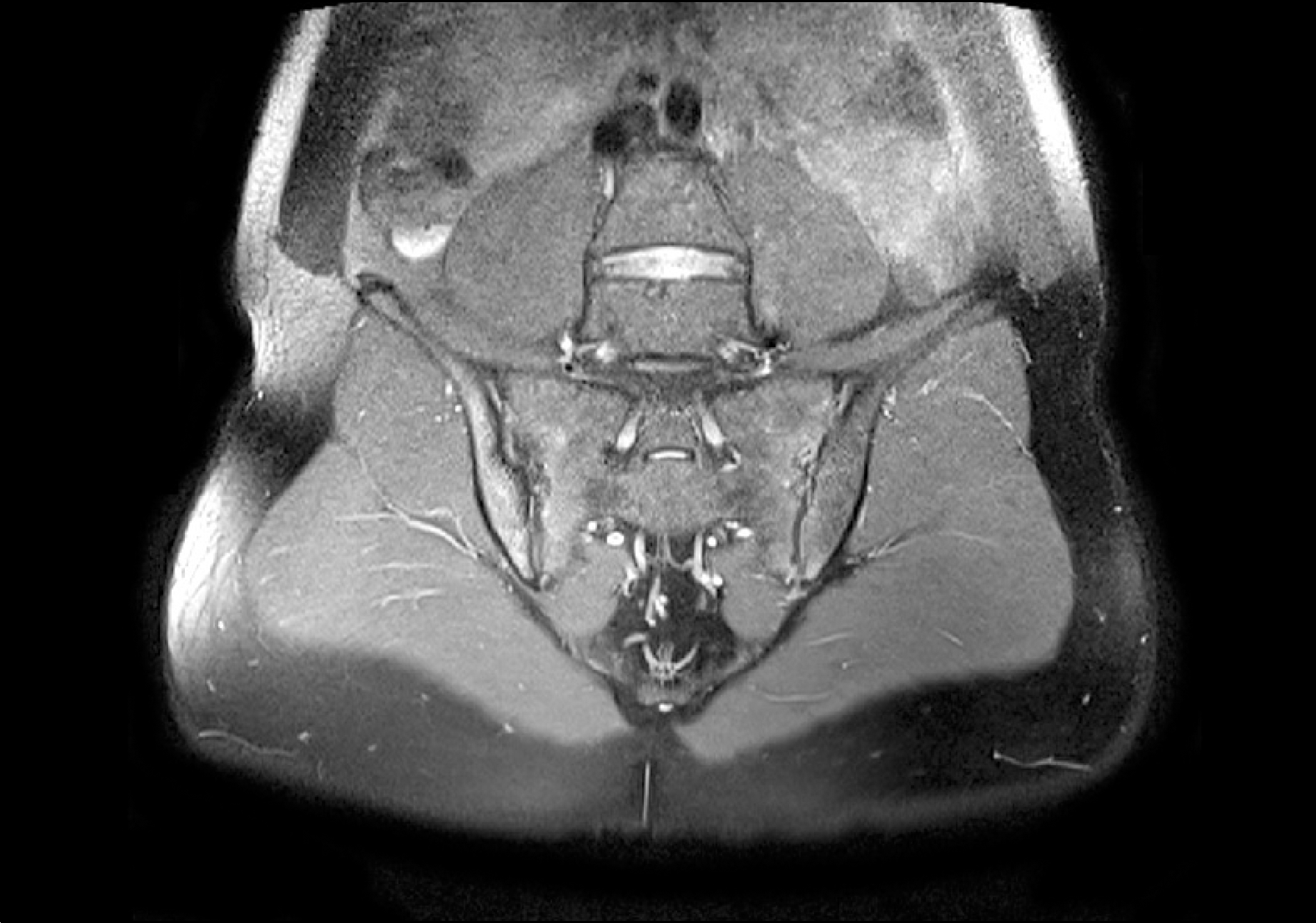
Figure 1.
Pelvic bone MRI showed subchondral bone erosions with bone marrow edema on bilateral sacroiliac joints.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download