Abstract
Secondary amyloidosis is one of the most serious complications in chronic inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. The extracellular deposit of aggregates of amyloid leads to target organ dysfunction. The mainstay treatment of secondary amyloidosis is the control of underlying disease activity. Many reports have reported that TNF-α inhibitors improve clinical outcomes. Here, we encountered a 34-year-old patient with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis who developed secondary amyloidosis despite treatment with TNF-α inhibitors. We present this case and include a review of the literature.
Figures and Tables
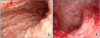 | Figure 3(A) Esophagogastroduodenoscopy, (B) Colonoscopy. (A) Severe atropic change at body and pylorus of stomach, (B) Diffuse petechiae and inflammation and spontaneous bleeding. |
References
1. Gertz MA, Kyle RA. Secondary systemic amyloidosis: response and survival in 64 patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 1991. 70:246–256.
2. Suzuki A, Ohosone Y, Obana M, Mita S, Matsuoka Y, Irimajiri S, et al. Cause of death in 81 autopsied patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1994. 21:33–36.
3. Okuda Y, Takasugi K, Oyama T, Onuma M, Oyama H. Amyloidosis in rheumatoid arthritis-clinical study of 124 histologically proven cases. Ryumachi. 1994. 34:939–946.
4. Rysavá R, Merta M, Spicka I, Tesar V. Current therapeutic possibilities in primary and secondary amyloidosis and our experience with 31 patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2003. 18:Suppl 5. v38–v40.
5. Brunt EM, Tiniakos DG. Metabolic storage diseases: amyloidosis. Clin Liver Dis. 2004. 8:915–930.
6. Röcken C, Radun D, Glasbrenner B, Malfertheiner P, Roessner A. Generalized AA-amyloidosis in a 58-yearold Caucasian woman with an 18-month history of gastrointestinal tuberculosis. Virchows Arch. 1999. 434:95–100.
7. Benson MD, Cohen AS. Serum amyloid A protein in amyloidosis, rheumatic, and enoplastic diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 1979. 22:36–42.
8. Nakamura T, Higashi S, Tomoda K, Tsukano M, Baba S. Efficacy of etanercept in patients with AA amyloidosis secondary to rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2007. 25:518–522.
9. Komatsuda A, Morita K, Ohtani H, Yamaguchi A, Miura AB. Remission of the nephrotic syndrome in a patient with renal amyloidosis due to rheumatoid arthritis treated with prednisolone and methotrexate. Am J Kidney Dis. 1998. 32:E7.
10. Kobak S, Oksel F, Kabasakal Y, Doganavsargil E. Ankylosing spondylitis-related secondary amyloidosis responded well to etanercept: a report of three patients. Clin Rheumatol. 2007. 26:2191–2194.
11. Gottenberg JE, Merle-Vincent F, Bentaberry F, Allanore Y, Berenbaum F, Fautrel B, et al. Anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha therapy in fifteen patients with AA amyloidosis secondary to inflammatory arthritides: a followup report of tolerability and efficacy. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. 48:2019–2024.
12. Thornton BD, Hoffman HM, Bhat A, Don BR. Successful treatment of renal amyloidosis due to familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome using an interleukin 1 receptor antagonist. Am J Kidney Dis. 2007. 49:477–481.
13. Narváez J, Hernández MV, Ruiz JM, Vaquero CG, Juanola X, Nollaa JM. Rituximab therapy for AA-amyloidosis secondary to rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2011. 78:101–103.
14. Régent A, Mouthon L. Anti-TNFalpha therapy in systemic autoimmune and/or inflammatory diseases. Presse Med. 2009. 38:761–773.
15. Roque R, Ramiro S, Cordeiro A, Gonçalves P, Da Canas S, Santos MJ. Development of amyloidosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis under TNF-blocking agents. Clin Rheumatol. 2011. 30:869–870.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download