Abstract
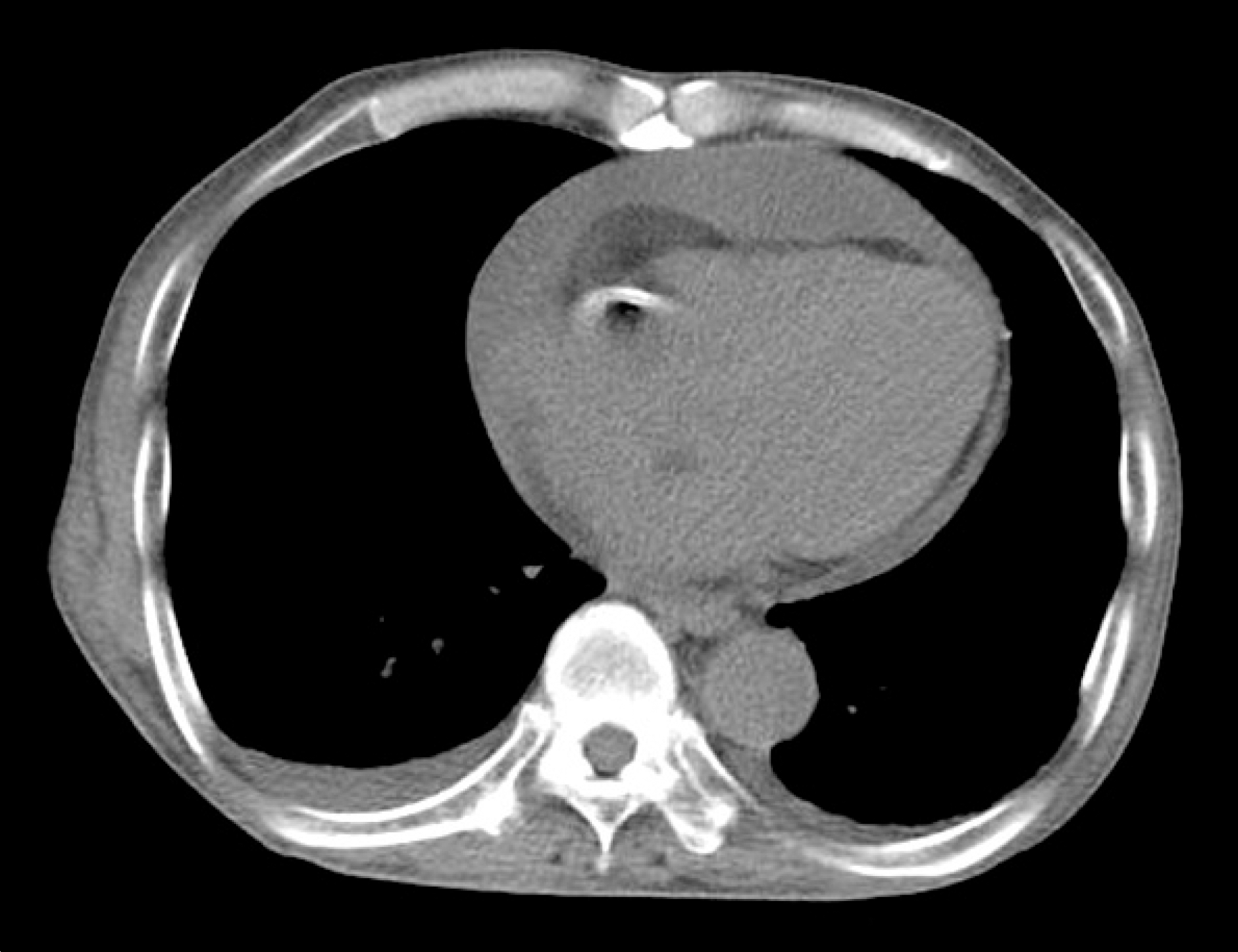
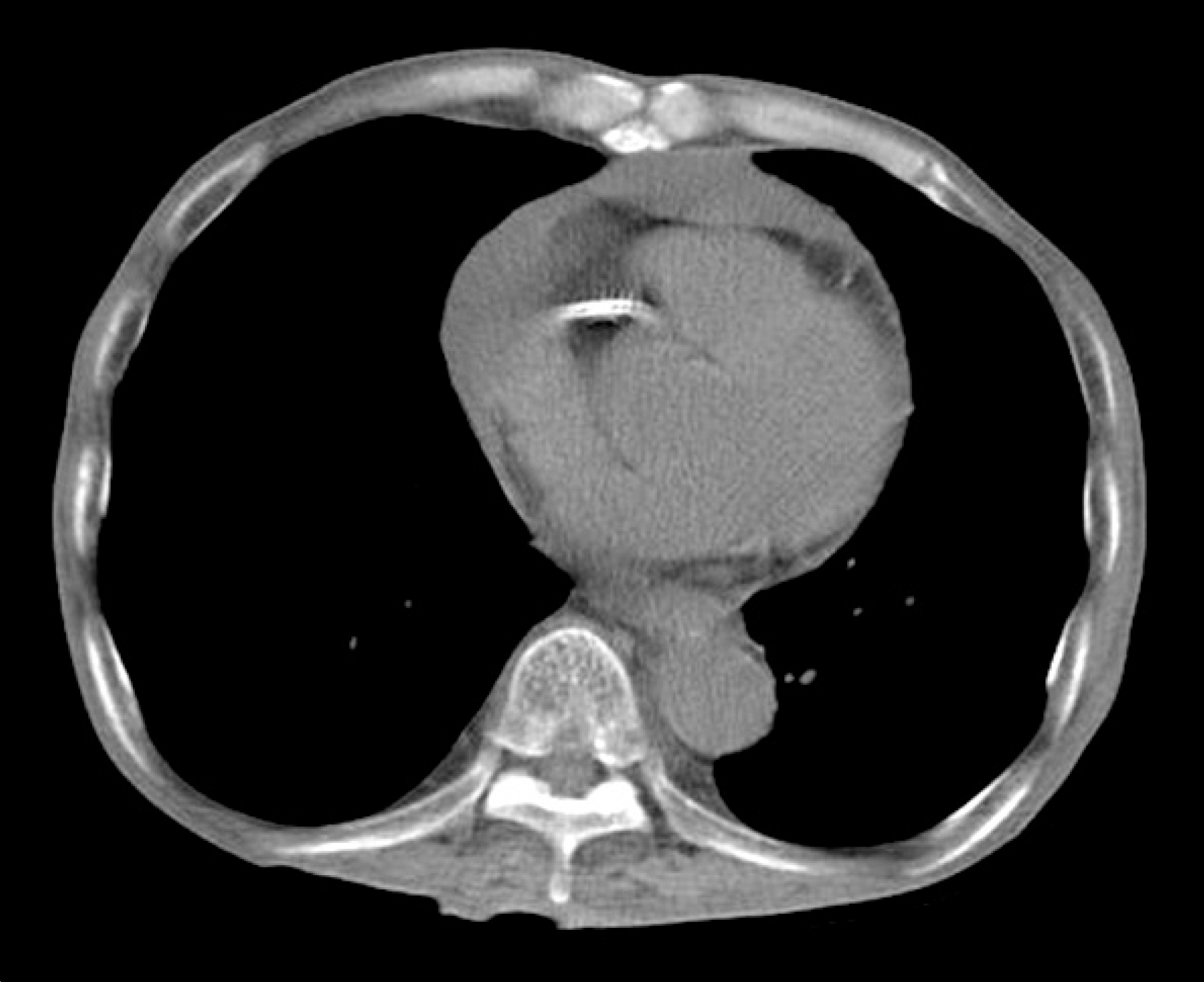
Drug-induced lupus erythematosus is defined as a lupus-like syndrome related to continuous drug exposure which resolves after discontinuation of the offending drug. Here we report a case of a 70-year-old man who developed drug-induced lupus erythematosus after receiving angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor medication for unstable angina pectoris, for 5 years. He was hospitalized with ar-thralgia, edema, and newly developed pleural effusion. The serum analysis revealed an elevated level of antinuclear antibody and antihistone antibody. After discontinuation of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor and receiving a course of prednisolone treatment, his symptoms and pleural effusion improved. To the best of our knowledge, this is, the first case report of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor-induced systemic lupus erythematosus in Korea.
References
2. Chen M, Crowson AN, Woofter M, Luca MB, Magro CM. Docetaxel (taxotere) induced subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus: report of 4 cases. J Rheumatol. 2004; 31:818–20.
4. Hoffman BJ. Sensitivity to sulfadiazine resembling acute disseminated lupus erythematosus. Arch Dermatol Syph. 1945; 51:190–2.

5. Antonov D, Kazandjieva J, Etugov D, Gospodinov D, Tsankov N. Drug-induced lupus erythematosus. Clin Dermatol. 2004; 22:157–66.

6. Oh SR, Cho M, Ryu HS, Lee JH, Cho HJ, Choi MK, et al. A Case of Isoniazid Induced Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2007; 14:431–5.

7. Park CO, Goo J, Ahn SK. A case of propylthiouracil-induced lupus erythematosus. Korean J Dermatol. 2006; 44:467–9.
9. Lee SL, CHase PH. Drug-induced systemic lupus erythematosus: a critical review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1975; 5:83–103.
10. Vedove CD, Del Giglio M, Schena D, Girolomoni G. Drug-induced lupus erythematosus. Arch Dermatol Res. 2009; 301:99–105.

11. Rubin RL, Waga S. Antihistone antibodies in SLE. J Rheumatol. 1987; 14:118.
12. Park PW, Kim TY. Antinuclear antibodies in patients on medication with cardiovascular drugs and antihypergly-cemic agents. J Lab Med Qual Assur. 2002; 24:215–20.
13. Kallenberg CG, Hoorntje SJ, Smit AJ, Weening JJ, Donker AJ, Hoedemaeker PH, et al. Antinuclear and anti-native DNA antibodies during captopril treatment. Acta Med Scand. 1982; 211:297–300.

14. di Fazano CS, Bertin P. The pharmacological management of drug-induced rheumatic disorders. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2001; 2:1623–31.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download