Abstract
Scleroderma pathogenesis is the accumulation of ex-tracellular matrix proteins and is a relatively rare connective tissue disorder characterized by skin fibrosis, ob-literative vasculopathy, and distinct autoimmune abnormalities. However, many other clinical conditions known collectively as the scleroderma-like syndrome present with substantial skin fibrosis and may be confused with scleroderma, sometimes leading to an incorrect diagnosis. Due to this, early and correct diagnosis is very important to for appropriate treatment available for scleroderma-like syndrome. We report a rare case of scleredema mimicking systemic sclerosis with hypoalbuminemia induced by malabsorption in alcoholic chronic pancreatitis. In this case, the patient's skin sclerosis and joint contracture dramati-cally improved after high dose steroid theraphy.
References
1. Boin F, Hummers LK. Scleroderma-like fibrosing disorders. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2008; 34:199–220.

2. Cho SY, Chung JH. Pathogenesis of scleroderma. Ann Dermatol. 2007; 14:73–80.
3. Chiu NT, Lee BF, Hwang SJ, Chang JM, Liu GC, Yu HS. Protein-losing enteropathy: diagnosis with (99m) Tc-labeled human serum albumin scintigraphy. Radiology. 2001; 219:86–90.
4. DiMagno EP, Go VL, Summerskill WH. Relations between pancreatic enzyme ouputs and malabsorption in severe pancreatic insufficiency. N Engl J Med. 1973; 288:813–5.
6. Taga M, Takahashi H, Yasui H, Tsukuda H, Motoya S, Sugaya T, et al. Case of protein-losing gastroenteropathy associated with scleroderma in which central serous cho-rioretinopathy developed. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2001; 24:125–32.
7. Suzuki Y, Okamoto H, Koizumi K, Tateishi M, Hara M, Kamatani N. A case of severe acute pancreatitis, in over-lap syndrome of systemic sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus, successfully treated with plasmapheresis. Mod Rheumatol. 2006; 16:172–5.

8. Ahn SY, Park HY, Lee WS. Linear scleroderma improved by narrow Band UVB phototherapy. Korean J Dermatol. 2009; 47:494–7.
Figure 1.
Physical examination of range of motion in knee joint and sclerotic skin in lower extremities. (A) Range of motion in both knees joint was less than 90 degree. (B, C) Ill-defined, oranged-hued, pitting indurative edema of both shins and foot dorsums. (D, E) The Skin of upper thigh (A) compared normal skin of forearm (B) does not have been pinched very hard because of sclerosis.
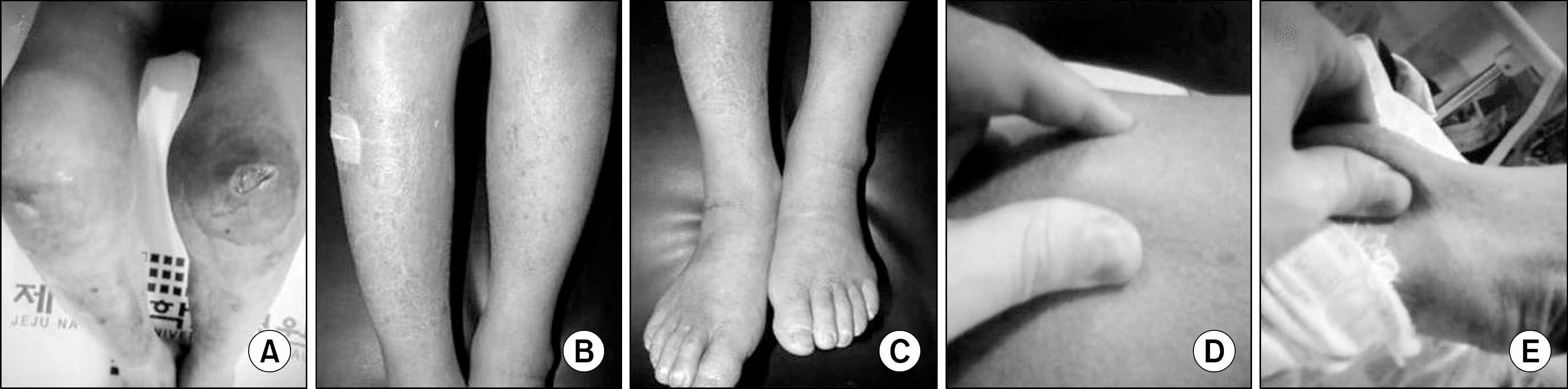
Figure 2.
(A) Enhanced Abdominal pelvic CT revealed granular calcification and generalized atrophy in the pancreas without a dilated pancreatic duct and pancreas swelling. (B) Colonoscopic finding was revealed microvesicular fat drop without mucosal lesion.
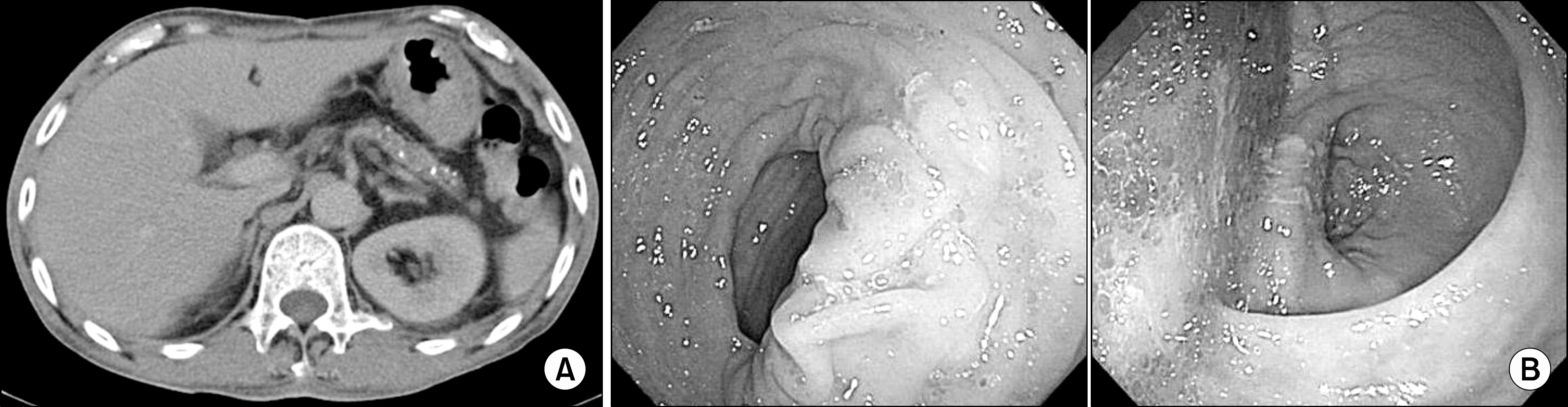
Figure 3.
Skin biopsy in Rt. lateral thigh. (A, B) Large areas of subcutaneous fat replaced by newly formed collagen which consists of thick, hyalinized hypocellular bundles (A, H&E stain, ×50), (B, H&E, ×100). (C, D) Increased thickened wavy collagen bundles in the reticular dermis without manifest inflammatory infiltrations. (C, Masson-Trichrome stain, ×50), (D, Masson's-Trichrome stain, ×100).

Figure 4.
Both knee joint cont-ractures were improved enough to be walking alone in the hospital at 19 days after admission.
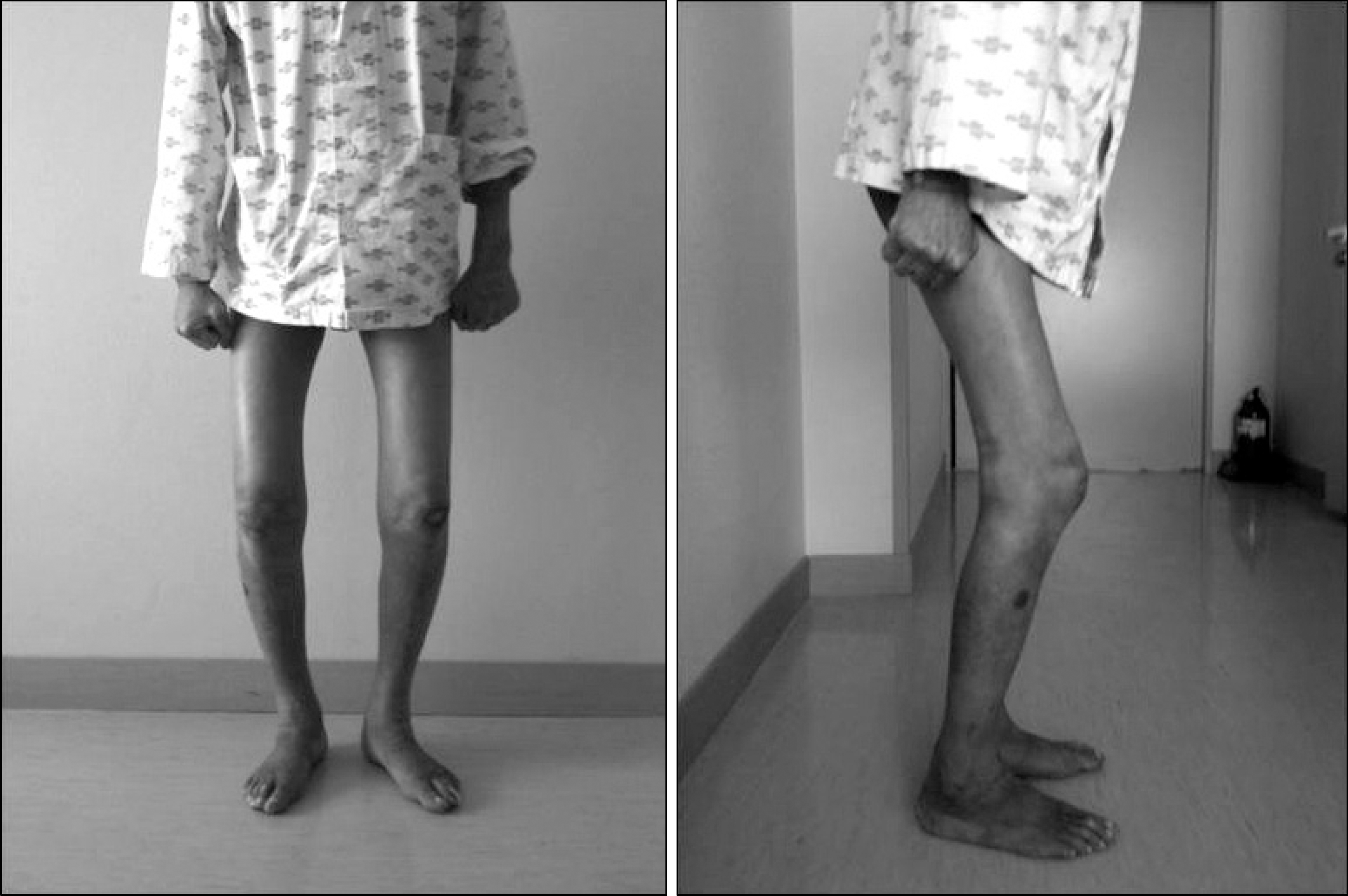
Table 1.
Differentiating features between scleroderma and scleroderma-like fibrosing disorders




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download