Abstract
Objective
To examine the mechanism for the inhibited differentiation of osteoclasts in rheumatoid arthritis synovial CD14+ osteoclast precursors, the different expressions of the osteoclastogenesis-related genes in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovial fluid CD14+ osteoclast precursors were compared with those of normal peripheral blood (PB) CD14+ osteoclast precursors.
Conclusion
The expression of the osteoclastogenesis-re-lated genes in RA synovial CD14+ osteoclast precursors is different from that of the normal PB CD14+ osteoclast precursors. These results suggest that the different expression of osteoclastogenesis-related genes might be involved in the altered osteoclastogenesis in RA synovial osteoclast precursors.
References
1. Han X, Kawai T, Taubman MA. Interference with immune-cell-mediated bone resorption in periodontal disease. Periodontol 2000. 2007; 45:76–94.
2. Takayanagi H. Osteoimmunology: shared mechanisms and crosstalk between the immune and bone systems. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007; 7:292–304.
3. Teitelbaum SL. Osteoclasts; culprits in inflammatory osteolysis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006; 8:201.
4. Walsh NC, Crotti TN, Goldring SR, Gravallese EM. Rheumatic diseases: the effects of inflammation on bone. Immunol Rev. 2005; 208:228–51.
5. Ji JD, Tassiulas I, Park-Min KH, Aydin A, Mecklenbrauker I, Tarakhovsky A, et al. Inhibition of interleukin 10 signaling after Fc receptor ligation and during rheumatoid arthritis. J Exp Med. 2003; 197:1573–83.
6. Park-Min KH, Ji JD, Antoniv T, Reid AC, Silver RB, Humphrey MB, et al. IL-10 suppresses calcium-mediated costimulation of receptor activator NF-kappa B signaling during human osteoclast differentiation by inhibiting TREM-2 expression. J Immunol. 2009; 183:2444–55.
7. Aoki K, Didomenico E, Sims NA, Mukhopadhyay K, Neff L, Houghton A, et al. The tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 is a negative regulator of osteoclastogenesis and osteoclast resorbing activity: increased resorption and osteopenia in me(v)/me(v) mutant mice. Bone. 1999; 25:261–7.
8. Kim K, Kim JH, Lee J, Jin HM, Kook H, Kim KK, et al. MafB negatively regulates RANKL-mediated osteoclast differentiation. Blood. 2007; 109:3253–9.
9. Kim K, Lee J, Kim JH, Jin HM, Zhou B, Lee SY, et al. Protein inhibitor of activated STAT 3 modulates osteoclastogenesis by down-regulation of NFATc1 and osteoclast-associated receptor. J Immunol. 2007; 178:5588–94.
10. Lari R, Fleetwood AJ, Kitchener PD, Cook AD, Pavasovic D, Hertzog PJ, et al. Macrophage lineage phenotypes and osteoclastogenesis–complexity in the control by GM-CSF and TGF-beta. Bone. 2007; 40:323–36.
11. Lee J, Kim K, Kim JH, Jin HM, Choi HK, Lee SH, et al. Id helix-loop-helix proteins negatively regulate TRANCE- mediated osteoclast differentiation. Blood. 2006; 107:2686–93.
12. Mori Y, Tsuji S, Inui M, Sakamoto Y, Endo S, Ito Y, et al. Inhibitory immunoglobulin-like receptors LILRB and PIR-B negatively regulate osteoclast development. J Immunol. 2008; 181:4742–51.
13. Takayanagi H, Kim S, Matsuo K, Suzuki H, Suzuki T, Sato K, et al. RANKL maintains bone homeostasis through c-Fos-dependent induction of interferon-beta. Nature. 2002; 416:744–9.
14. Takayanagi H, Ogasawara K, Hida S, Chiba T, Murata S, Sato K, et al. T-cell-mediated regulation of osteoclastogenesis by signalling crosstalk between RANKL and IFN-gamma. Nature. 2000; 408:600–5.
15. Takeshita S, Namba N, Zhao JJ, Jiang Y, Genant HK, Silva MJ, et al. SHIP-deficient mice are severely osteo-porotic due to increased numbers of hyper-resorptive osteoclasts. Nat Med. 2002; 8:943–9.
16. Wei S, Wang MW, Teitelbaum SL, Ross FP. Interleukin- 4 reversibly inhibits osteoclastogenesis via inhibition of NF-kappa B and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277:6622–30.
17. Haringman JJ, Gerlag DM, Zwinderman AH, Smeets TJ, Kraan MC, Baeten D, et al. Synovial tissue macrophages: a sensitive biomarker for response to treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005; 64:834–8.
18. Herrak P, Görtz B, Hayer S, Redlich K, Reiter E, Gasser J, et al. Zoledronic acid protects against local and systemic bone loss in tumor necrosis factor-mediated arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004; 50:2327–37.
19. Kinne RW, Stuhlmüller B, Burmester GR. Cells of the synovium in rheumatoid arthritis. Macrophages. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007; 9:224.
20. Smink JJ, Bégay V, Schoenmaker T, Sterneck E, de Vries TJ, Leutz A. Transcription factor C/EBPbeta isoform ratio regulates osteoclastogenesis through MafB. EMBO J. 2009; 28:1769–81.
21. Conaway HH, Persson E, Halén M, Granholm S, Svensson O, Pettersson U, et al. Retinoids inhibit differentiation of hematopoietic osteoclast progenitors. FASEB J. 2009; 23:3526–38.
22. Jacquin C, Koczon-Jaremko B, Aguila HL, Leng L, Bucala R, Kuchel GA, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor inhibits osteoclastogenesis. Bone. 2009; 45:640–9.
23. Oshima S, Onodera S, Amizuka N, Li M, Irie K, Watanabe S, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor-deficient mice are resistant to ovariectomy-induced bone loss. FEBS Lett. 2006; 580:1251–6.
24. Kurowska-Stolarska M, Distler JH, Jüngel A, Rudnicka W, Neumann E, Pap T, et al. Inhibitor of DNA binding/differentiation 2 induced by hypoxia promotes synovial fibroblast-dependent osteoclastogenesis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009; 60:3663–75.
25. Ji JD, Park-Min KH, Shen Z, Fajardo RJ, Goldring SR, McHugh KP, et al. Inhibition of RANK expression and osteoclastogenesis by TLRs and IFN-gamma in human osteoclast precursors. J Immunol. 2009; 183:7223–33.
Figure 1.
Healthy volunteer PB and RA synovial CD14+ cells were cultured with M-CSF (20 ng/mL) for 2 days, and then with RANKL (40 ng/mL) and M-CSF (20 ng/mL) for an additional 6, 9 or 12 days. The cells were stained for TRAP expression. TRAP-positive multinucleated (>3 nuclei/cell) cells were counted as osteoclasts. ∗p<0.05 versus RA 6 days.
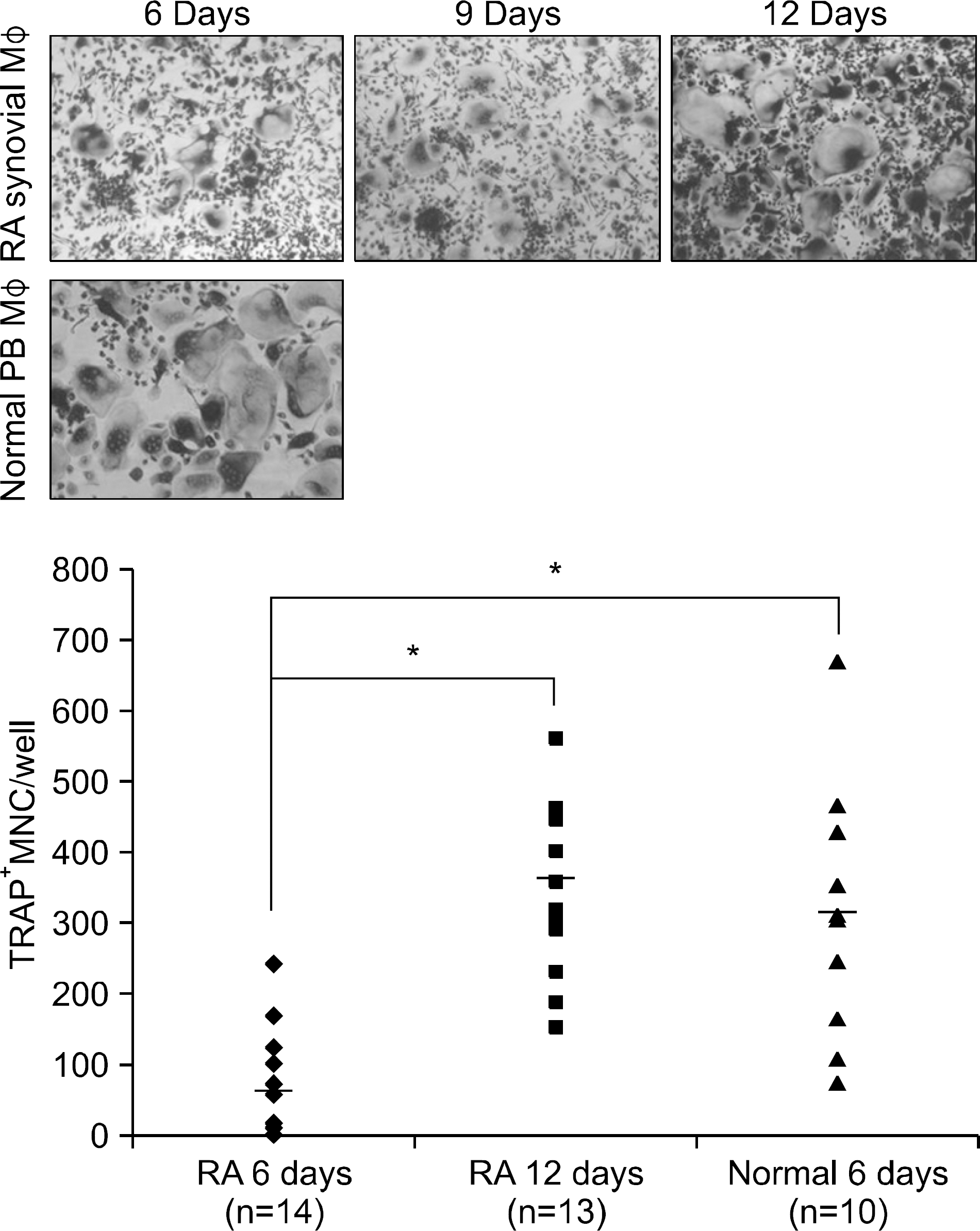
Figure 2.
The array data for gene expression was validated by performing quantitative real-time PCR in Healthy volunteer PB and RA synovial CD14+ cells. ∗p<0.05 versus Healthy volunteer PB.
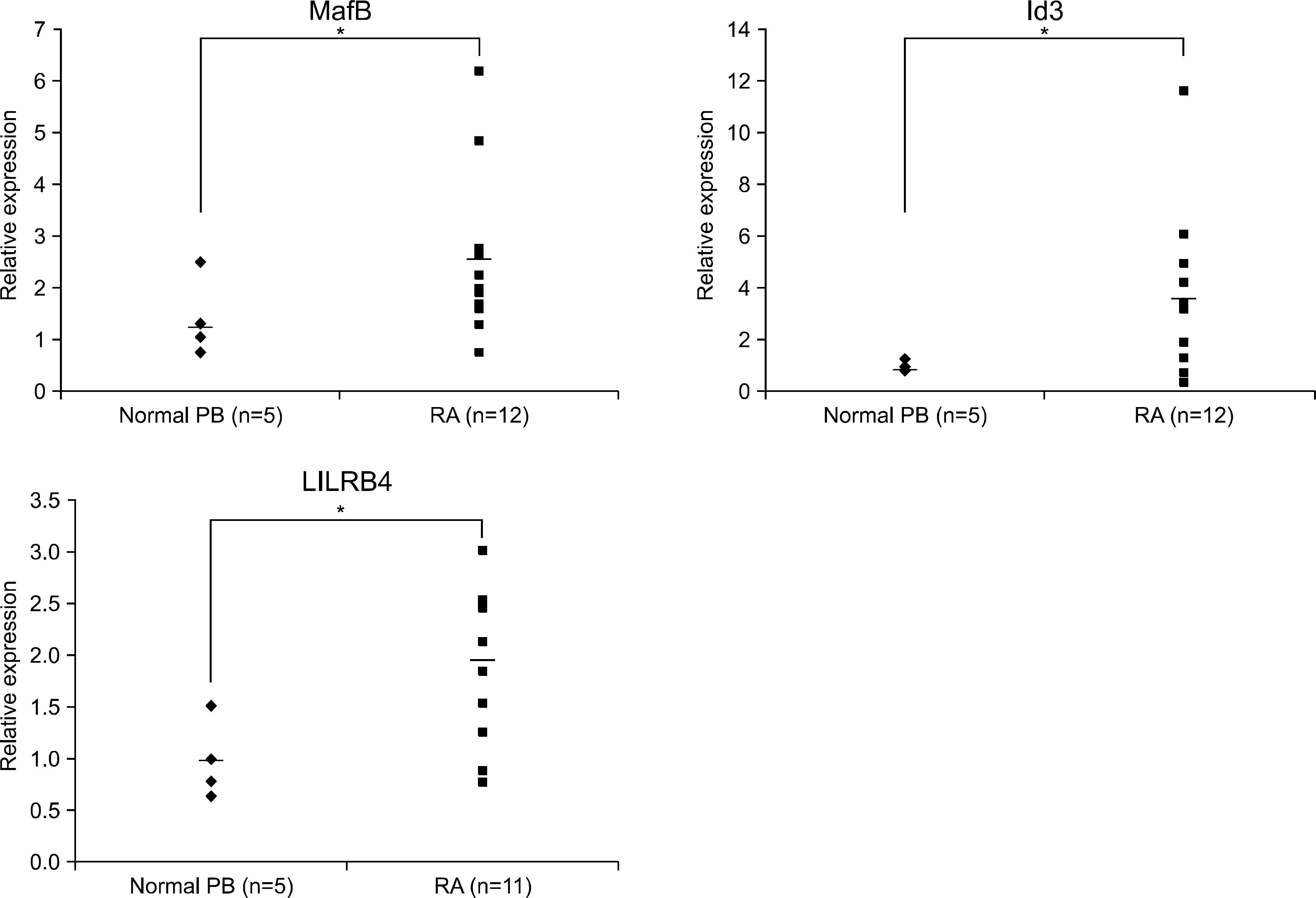
Table 1.
Differentially expressed mRNAs in the RA synovi CD14+ cells compared to that of the normal PB CD14+ cel (Cytokines and chemokines involved in osteoclastogenesis)
| Gene name | Osteoclast differentiation | Fold change | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| BMP2 | Stimulation | ND | ND |
| CCL2 (MCP-1)∗ | Stimulation | 8.5 | 0.02 |
| CCL3 (MIP-1α) | Stimulation | 1.89 | 0.4 |
| CCL4 (MIP-1β) | Stimulation | ND | ND |
| CX3CL1 | Stimulation | ND | ND |
| CXCL10 | Stimulation | 2.98 | 0.29 |
| CXCL11 | Inhibition | ND | ND |
| CXCL12 | Stimulation | 2.98 | 0.29 |
| GM-CSF | Inhibition/Stimulation | ND | ND |
| IFNα | Inhibition | ND | ND |
| IFNβ | Inhibition | ND | ND |
| IFNg | Inhibition | ND | ND |
| IL-10 | Inhibition | −1.13 | 0.68 |
| IL-12A | Inhibition | ND | ND |
| IL-12B | Inhibition | ND | ND |
| IL-17A | Stimulation | ND | ND |
| IL-18 | Inhibition | −1.13 | 0.74 |
| IL-1β | Inhibition/Stimulation | 1.07 | 1 |
| IL-27 | Inhibition | −1.09 | 0.82 |
| IL-32∗ | Stimulation | 3.04 | 0.05 |
| IL-4 | Inhibition | ND | ND |
| IL-6 | Stimulation | ND | ND |
| MIF∗ | Inhibition | 2.34 | 0.04 |
| TGFβ | Inhibition/Stimulation | ND | ND |
| TNFα | Stimulation | 1.43 | 0.63 |
| TNFSF11A (RANKL) | Stimulation | ND | ND |
Table 2.
Differentially expressed mRNAs in the RA synovia CD14+ cells compared to that of the normal PB CD14+ cell (Receptors and membrane factors involved in osteoclastogenesis
| Gene name | Osteoclast differentiation | Fold change | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| ATP6v0d2 | Positive | ND | ND |
| CSF1R∗ | Positive | 1.77 | 0.01 |
| FCER1G (FcRγ) | Positive | −1.03 | 0.99 |
| ITGAM (CD11b) | Positive | 1.28 | 0.22 |
| ITGB3 (CD61) | Positive | ND | ND |
| LILRB1 | Negative | 1.33 | 0.11 |
| LILRB3 | Negative | 1.14 | 0.67 |
| LILRB4∗ | Negative | 2.87 | 0 |
| MSR1 (SR-A)∗ | Positive | 4.84 | 0 |
| OSCAR | Positive | −1.21 | 0.71 |
| Plexin-A1 | Positive | 2.16 | 0.13 |
| TM7SF4 (DC STAMP) | Positive | ND | ND |
| TNFR11A (RANK) | Positive | ND | ND |
| TREM2∗ | Positive | 1.59 | 0.04 |
| TYROBP (DAP12) | Positive | −1.29 | 0.54 |
Table 3.
Differentially expressed mRNAs in the RA synovial CD14+ cells compared to that of the normal PB CD14+ cells (Intracellular molecules involved in osteoclastogenesis))
| Gene name Osteo | oclast differentia | tion Fold change | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bcl-2∗ | Positive | 2.83 | 0.01 |
| Btk | Positive | −1.37 | 0.36 |
| C/EBPβ | Negative | 1.39 | 0.38 |
| CaMKIV | Positive | ND | ND |
| c-Fos | Positive | −1.86 | 0.06 |
| c-Jun | Positive | 1.29 | 0.54 |
| DYRK1A | Negative | ND | ND |
| FOSL1 (Fra-1) | Positive | ND | ND |
| Gab2 | Positive | −1.29 | 0.24 |
| Id1 | Negative | ND | ND |
| Id2 | Negative | 1.34 | 0.56 |
| Id3 | Negative | 2.59 | 0.06 |
| IKBKB (IKK-β) | Positive | ND | ND |
| MafB∗ | Negative | 2.63 | 0.01 |
| MITF | Positive | 1.38 | 0.29 |
| NFATc1 | Positive | −1.01 | 1 |
| NFKB1 (NFκ B p50) | Positive | 1.38 | 0.15 |
| NFKB2 (NFκ B p52) | Positive | −1.02 | 0.99 |
| MAP3K14 (NIK) | Positive | −1.19 | 0.21 |
| PIAS3 | Negative | −1.08 | 0.39 |
| PLCγ2 | Positive | −1.13 | 0.09 |
| PU.1 | Positive | 1.02 | 0.97 |
| INPP5D (SHIP)∗ | Negative | −1.67 | 0.01 |
| PTPN6 (SHP-1) | Negative | ND | ND |
| SOCS1 | Positive | 1.76 | 0.14 |
| SOCS3 | Positive | 1.07 | 0.74 |
| STAT1 | Negative | 1.49 | 0.49 |
| Syk | Positive | 1.08 | 0.8 |
| MAP3K7 (TAK1) | Positive | 1.18 | 0.36 |
| Tec | Positive | 1.08 | 0.22 |
| TRAF6 | Positive | 1.06 | 0.54 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download