Abstract
Mesenchymal tumors including hemangiopericytomas, hepatocellular tumors, adrenal carcinomas, and a variety of other large tumors have been reported to produce excessive amounts of insulin-like growth factor (IGF) type II precursor, which binds weakly to insulin receptors and strongly to IGF-I receptors, leading to insulin like actions. In addition to increased IGF-II production, IGF-II bioavailability is increased due to complex alterations in circulating binding proteins.
The authors of this article diagnosed non-islet cell tumor hypoglycemia from an 81-year-old male patient suffering from repetitive fasting hypoglycemia while he has not received any treatment for pulmonary hemangiopericytoma diagnosed in the past. Moreover, this topic is getting reported as the authors have experienced a significant improvement of catamnesis by a treatment with glucocorticoid
Figures and Tables
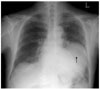
 | Fig. 2Chest CT shows a 8 cm sized huge mass lesion at the left lower lung in the arterial phase (A). Follow up CT after 11 months shows a slightly increased (11.3 cm sized) huge mass lesion at the left lower lung in the arterial phase (B). |
References
1. Zapf J. Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins and tumor hypoglycemia. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 1995. 6:37–42.
2. Daughaday WH. The pathophysiology of IGF-II hypersecretion in non-islet cell tumor hypoglycemia. Diabetes Rev. 1995. 3:62–72.
6. Larsen PR, Kronenberg HM, Melmed S, Polonsky KS. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 2003. 10th ed. Saunders;1845–1846.
7. Baxter RC, Holman SR, Corbould A, Stranks S, Ho PJ, Braund W. Regulation of the insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins by glucocorticoid and growth hormone in nonislet cell tumor hypoglycemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1995. 80:2700–2708.
8. Frystyk J, Skjaerbaek C, Dinesen B, Orskov H. Free insulin-like growth factors (IGF-I and IGF-II) in human serum. FEBS Lett. 1994. 348:185–191.
9. Baxter RC, Daughaday WH. Impaired formation of the ternary insulin-like growth factor-binding protein complex in patients with hypoglycemia due to nonislet cell tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991. 73:696–702.
10. Daughaday WH. Free insulin-like growth factor (IGF) in disorders of IGF binding protein 3 complex formation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004. 89:3–5.
11. Teale JD, Marks V. Glucocorticoid therapy suppresses abnormal secretion of big IGF-II by non-islet cell tumours inducing hypoglycaemia (NICTH). Clin Endocrinol. 1998. 49:491–498.
12. Gullo D, Sciacca L, Parrinello G, Tomaselli L, Vigneri R. Treatment of hemangiopericytoma-induced hypoglycemia with growth hormone and corticosteroids. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999. 84:1758–1759.
13. Teale JD, Wark G. The effectiveness of different treatment options for non-islet cell tumour hypoglycaemia. Clin Endocrinol. 2004. 60:457–460.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download