Abstract
Malignant insulinomas are very rare endocrine tumours with a variable clinical course. Here, a case of a malignant insulinoma, resected from the tail of the pancreas 10 years previously, which was found to have hepatic metastasis, is reported. A pancreatic mass, without evidence of metastasis, has been found using an abdominal CT scan and intra-operative ultrasonography 10 years previously. Recently, the patient has suffered from dizziness, sweating and an altered mentality. Hyperinsulinemia was diagnosed from the biochemical laboratory finding. An abdominal CT scan and intra-operative abdominal sonography showed multiple hepatic metastasis, without local recurrence in pancreas. Therefore, a partial hepatic segmentectomy was performed. Immunohistochemical staining of the postoperative specimen was strongly positive for insulin. The postoperative biochemical response was normalized, and the patient experienced no further hypoglycemic symptom.
Figures and Tables
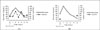 | Fig. 172 hours-fasting test after 75 g oral glucose loading. (A) 10 years ago. (B) The recent result. |
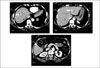 | Fig. 2Abdominal CT shows two bull's eye masses in the liver with central arterial enhancement and peripheral thick ring in right anterior and left lateral segment (arrows in A and B). There was no abnormal mass in the pancreas (C). |
 | Fig. 3Somatostatin scintigraphy shows normal uptake of liver, kidneys, large intestine at 24 hour image. Hepatic masses at abdominal CT were not synchronized with uptake of liver at scintigraphy. |
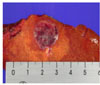 | Fig. 4The gross pathologic finding of the malignant insulinoma metastasized to the liver. The one tumor measuring 2.2 × 2 × 1.5 cm is located in the resected liver. |
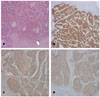 | Fig. 5(A) Section discloses portions of liver showing two foci of islet cell tumor with satellite nodules of microscopic sizes (arrow). Liver parenchyme shows mild fatty change and chronic inflammatory cell infiltration. (B)-(D) Sections disclose portions of liver showing islet cell tumor with positive immunohistochemical stain of insulin (B), Chromograninin (C), and Synaptophysin (D). |
References
1. Boden G. Glucagonomas and insulinomas. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1989. 18:831–845.
2. Fajans SS, Winik AI. Insulin-producing islet cell tumors. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 1989. 18:45–60.
3. Adrian S, David H, Richard D. Radio-frequency ablation for symptom control in a patient with metastatic pancreatic insulinoma. Clin Endocrinol. 2002. 56:557–559.
4. Hirshberg B, Cochran C, Skarulis MC, Libutti SK, Alexander HR, Wood BJ, Chang R, Kleiner DE, Gorden P. Malignant insulinoma: Spectrum of unusual clinical features. Cancer. 2005. 104:264–272.
6. Service FJ. Hypoglycemic disorders. N Engl J Med. 1995. 332:1144–1152.
7. Moller DE, Flier JS. Insulin resistance mechanisms, syndromes and implications. N Engl J Med. 1991. 325:938–955.
8. Danforth DN, Gorden P, Brennan MF. Metastatic insulin secreting carcinoma of the pancreas: Clinical course and the role of surgery. Surgery. 1984. 96:1027–1040.
9. Service FJ, McMahon MM, O'Brien PC, Ballard DJ. Functioning insulinoma incidence, recurrence, and long-term survival of patients: A 60-year study. Mayo Clin Proc. 1991. 66:711–719.
10. Boettger TC, Weber W, Beyer J, Junginger T. Value of tumor localization in patients with insulinoma. World J Surg. 1990. 14:107–114.
11. Kvols LK, Brown ML, O'Connor MK. Evaluation of a radiolabeled somatostatin analog in the detection and localization of carcinoid and islet cell tumors. Radiology. 1993. 187:129–133.
12. Modlin IM, Cornelium E, Lawton GP. Use of an isotopic somatostatin probe to image gut endocrine tumors. Arch Surg. 1995. 130:367–373.
13. Krenning EP, Dwekkeboom DJ, Bakker WH. Somatostatin receptor scintigraphy with [111In-DTPA-D-Phe1]-and [123I-Tyr3]-octreotide: The Rotterdam experience with more than 1000 patients. Eur J Nucl Med. 1993. 20:716–731.
14. Modlin IM, Tang LH. Approaches to the diagnosis of gut neuroendocrine tumors: the last word. Gastroenterology. 1997. 112:583–590.
15. Sarmiento JM, Que FG, Grant CS, Thompson GB, Farnell MB, Nagorney DM. Concurrent resections of pancreatic islet cell cancers with synchronous hepatic metastases: outcomes of an aggressive approach. Surgery. 2002. 132:976–982.
16. Grama D, Eriksson B, Martensson H, Cedermark B, Ahren B, Kristofferson A, Rastad J, Oberg K, Akerstrom G. Clinical characteristics, treatment and survival in patients with pancreatic tumors causing hormonal syndromes. World J Surg. 1992. 16:632–639.
17. McEntee GP, Nagorney DM, Kvols LK. Cytoreductive hepatic surgery for neuroendocrine tumors. Surgery. 1990. 108:1091–1096.
18. Que F, Nagorney D, Batts K. Hepatic resection for metastatic neuroendocrine carcinomas. Am J Surg. 1995. 169:36–42.
19. Schutt M, Lorch H, Kruger S, Klingenberg RD, Peters A, Klein HH. Recurrent hypoglycemia caused by malignant insulinoma: chemoembolization as a therapeutic option. Med Klin (Munich). 2001. 96:632–636.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download