Abstract
McCune-Albright syndrome (MAS) is a sporadic disease that's characterized by polyostotic fibrous dysplasia, cafe-au-lait pigmentation of the skin, and multiple endocrinopathies, including sexual precocity, hyperthyroidism, acromegaly, and hypercortisolism. Recent evidence has shown that the clinical manifestations are caused by a postzygotic activating missense mutation in the gene coding for the α-subunit of Gs protein that stimulates c-AMP formation in the affected tissues. Substitution of the Arg201 residue in Gsα with cysteine or histidine have been identified in many MAS patients and Arg201 to Gly or Leu mutations have also been recently identified. We identified the Arg201 to His mutation in the gene encoding Gsα in the thyroid tissue from a 36-year-old man who was suffering with polyostotic fibrous dysplasia and hyperthyroidism.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
Simple X-ray. A, Chest X-ray: There is a clavicular fracture of right. B, Skull: There is a diffuse thickening of occipital bone. C, Left humerus: There is a osteolytic lesion and cortical bone thinning of mid-portion.

Fig. 2
A, Brain CT: Multifocal mixed lytic or sclerotic lesions of the skull base are shown. B, Lumbar spine MRI: Compression fracture is seen in the lumbar spine.
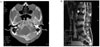
Fig. 3
Bone scan. It shows increased bony uptakes at occipital bone, low cervical spine, left first, third, eighth, eleventh ribs, and right fifth rib, left scapula, left humerus, left elbow, left carpal bones and fingers. Also there are suspicious small foci of increased uptakes at thoracic and lumbar spines.

Fig. 4
Thyroid scan. There are enlarged left lobe and irregular areas of photon deficiency in right lobe.

References
1. McCune DJ. Ostitis fibrosa cystica: The case of a nine year old girl who also exhibits precocious puberty, multiple pigmentation of the skin and hyperthyroidism. Am J Dis Child. 1936. 52:743–747.
2. Lee PA, Dop CV, Migeon CJ. McCune-Albright syndrome, long-term follow-up. JAMA. 1986. 256:2980–2984.
4. Weinstein LS, Yu S, Warner DR, Liu J. Endocrine manifestations of stimulatory G Protein α-subunit mutations and the role of genomic imprinting. Endocr Rev. 2001. 22:675–705.
5. Weinstein LS, Liu J, Sakamoto A, Xie T, Chen M. Minireview: GNAS: Normal and Abnormal Functions. Endocrinology. 2004. 145:5459–5464.
6. Song HD, Chen FL, Shi WJ, Wang S, Zhang Q, Hu RM, Chen JL. A novel, complex heterozygous mutation within Gsα gene in patient with McCune- Albright syndrome. Endocrine. 2002. 18:121–128.
9. Lumbroso S, Paris F, Sultan C. Activating Gsα mutations: Analysis of 113 patients with signs of McCune-Albright syndrome-A European collaborative study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004. 89:2107–2113.
10. Mastorakos G, Mitsiades NS, Doufas AG, Koutras DA. Hyperthyroidism in McCune-Albright syndrome with a review of thyroid abnormalities sixty years after the first report. Thyroid. 1997. 7:433–439.
11. Haruihiko I, Koji S, Keiichi K, Junta T. McCune-Albright syndrome associated with non-autoimmune type of hyperthyroidism with development of thyrotoxicosis crisis. Horm Res. 2000. 53:256–259.
12. Di Candia SD, Weber G, Mora S, Pellegrin MD, Chiumello G. Early fractures and occult hyperthyroidism: McCune-Albright syndrome? Horm Res. 2001. 56:58–62.
13. Landis CA, Masters SB, Spada A, Pace AM, Bourne HR, Vallar L. GTPase inhibiting mutations activate the alpha chain of Gs and stimulate adenylyl cyclase in human pituitary tumours. Nature. 1989. 340:692–696.
14. Riminucci M, Fisher LW, Majolagbe A, Corsi A, Lala R, Sanctis CD, Robey PG, Bianco P. A novel GNAS1 mutation, R201G, in McCune-Albright syndrome. J Bone Miner Res. 1999. 14:1987–1989.
15. Liens D, Delmas PD, Meunier PJ. Long-term effects of intravenous pamidronate in fibrous dysplasia of bone. Lancet. 1994. 343:953–954.
16. Chapurlat RD, Delmas PD, Meunier D, Meunier PJ. Long-term effects of intravenous pamidronate in fibrous dysplasia of bone. J Bone Miner Res. 1997. 12:1746–1752.
17. Plotkin H, Rauch F, Zeitlin L, Munns C, Travers R, Glorieux FH. Effect of pamidronate treatment in children with polyostotic fibrous dysplasia of bone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003. 88:4569–4575.
18. Weinstein RS. Long-term aminobisphosphonate treatment of fibrous dysplasia: Spectacular increase in bone density. J Bone Miner Res. 1997. 12:1314–1315.
19. Kitagawa Y, Tamai K, Ito H. Oral alendronate treatment for polyostotic fibrous dysplasia: a case report. J Orthop Sci. 2004. 9:521–525.
20. Yamamoto T, Ozono K, Shima M, Yoshikawa H, Okada S. Alendronate and pharmacological doses of 1 α OHD3 therapy in a patient with McCune-Albright syndrome and accompanying hypophosphatemia. J Bone Miner Metab. 2002. 20:170–173.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download