Abstract
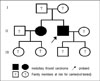
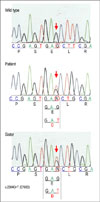
medullary carcinomas. Here, the case of a 42 years-old man with a familial medullary thyroid carcinoma, confirmed by the detection of a RET proto-oncogene mutation at exon 13 on codon 768 from a GAG (Glu) to a GAT (Asp), is described. The patient underwent a total thyroidectomy and modified radical neck dissection. His sister was found to have the same mutant gene.
Figures and Tables
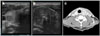 | Fig. 2Thyroid ultrasonography; (A) 1×1 cm sized hypoechoic lesion in Rt gland, (B) 2.6×2.7×3.6 cm sized hypoehoic lesion with internal calcification in Lt gland. Neck CT; (C) Multiple lymph node metastasis in Lt level III |
References
1. Brandi ML, Gagel RF, Angeli A, Bilezikian JP, Beck-Peccoz P, Bordi C, Conte-Devolx B, Falchetti A, Gheri RG, Libroia A, Lips CJ, Lombardi G, Mannelli M, Pacini F, Ponder BA, Raue F, Skogseid B, Tanburrano G, Ghakker RV, Thompson NW, Tomassetti P, Tonelli F, Wells SA Jr, Marx SJ. Guidelines for diagnosis and therapy of MEN type I and type 2. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001. 86:5658–5671.
3. Marsh DJ, Learoyd DL, Robinson BG. Medullary thyroid carcinoma: Recent advancers and managemnet update. Thyroid. 1995. 5:407–424.
4. Kebebew E, Ituarte PH, Siperstein AE, Duth QY, Clark OH. Medullary thyroid carcinoma: clinical characteristics, treatment, prognostic factor, and a comparison of staging systems. Cancer. 2000. 88:1139–1148.
5. Lee MS, Hwang DY, Kim YH, Chung JH, Oh YS, Lee MK, Kim KW. Mutations of ret proto-oncogene in 3 Korean families with MEN 2A: clinical use of new restriction sites for genetic diagnosis. Endocr J. 1998. 45:555–561.
7. Kim IJ, Kang HC, Park JH, Ku JL, Lee JS, Kwon HJ, Yoon KA, Heo SC, Yang KA, Cho BY, Kim SY, Oh SK, Youn YK, Park DJ, Lee MS, Lee KW, Park JG. RET Oligonucleotide Microarray for the Detection of RET Mutations in Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2 Syndromes. Clinical Cancer Research. 2002. 8:457–463.
10. Chung YJ, Kim HH, Kim HJ, Min YK, Lee MS, Lee MK, Kim KW, Ki CS, Kim JW, Chung JH. RET proto-oncogene mutations are restricted to codon 634 and 618 in Korean families with multiple endocrine neoplasia 2A. Thyroid. 2004. 14:813–818.
11. Nam JH, Choi YS, Park H. A Family of Mutiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2A Associated with a C634W Mutation in RET Proto-oncogene. 2005. 166.
13. Bae SJ, Kim Y, Chung YJ, Min YK, Lee MS, Lee MK, Kim KW, Ki CS, Chung JH. First Identification of the D631Y Germline Mutation in the RET Protooncogene in a Patient with Multiple Ednocrine Neoplasia 2A. 2005. 139.
18. Lee KD, Mun HS, Kim JY, Chung H, Choi SH, Ha NW, Uchino S. Analysis of RET Gene Point Mutations in a Family with Familial Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma. Korean J Otolaryngol-Head Neck Sur. 2004. 47:904–910.
19. Machenes A, Gimm O, Hinze R, Hoppner W, Boehm BO, Dralle H. Genotype-Phenotype Correlations in Hereditary Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: Oncological Features and Biochemical Properties. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001. 86:1104–1109.
20. Boccia LM, Green JS, Joyce C, Eng C, Taylor SA, Mulligan LM. Mutation of RET codon 768 is associated with the FMTC phenotype. Clin Genet. 1997. 51:81–85.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download