Abstract
Background
The aim of this study was to examine the association between the common polymorphisms of the adiponectin gene (ACDC) and the intima-media thickness (IMT) of the common carotid arteries in type 2 diabetic patients.
Methods
The B mode ultrasound examination of carotid artery was performed on 133 type 2 diabetic patients. The carotid IMT was calculated using the Intimascope computer program. The SNP45 and SNP276 of the ACDC were examined.
Results
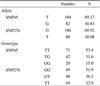
There was no significant difference in the carotid IMT among the SNP45 genotypes (0.66 ±0.18 mm for TT, 0.71±0.12 mm for TG and 0.64±0.15 mm for GG, P=NS). Subjects carrying the SNP276 GG genotype had a markedly lower serum adiponectin concentration than those carrying the TT genotype (3.35±2.00 µg/mL vs. 4.98±2.24 µg/mL, P=0.029) The carotid IMT was significantly higher in patients with the SNP276 GG genotype than those with the TT genotype (0.70±0.17 mm vs. 0.59±0.13 mm, P=0.032). Patients with the +45GG/+276GG genotype combination showed significantly higher mean carotid IMT than the other genotype combinations (0.78±0.09 mm vs. 0.71±0.15 mm, P=0.013)
Figures and Tables
Table 2
Clinical and Biochemical Characteristics of the Subjects according to the Adiponectin Genotypes at Position 45

Table 3
Clinical and Biochemical Characteristics of the Subjects according to the Adiponectin Genotypes at Position 276

Table 4
Clinical Characteristics of the Subjects according to the Carrying Status of the Adiponectin 45/276 Genotype Combination

References
1. Ouchi N, Kihara S, Arita Y, Maeda K, Kuriyama H, Okamoto Y, Hotta K, Nishida M, Takahashi M, Nakamura T, Yamashita S, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y. Novel modulator for endothelial adhesion molecules; adipocyte-derived plasma protein adiponectin. Circulation. 1999. 100:2473–2476.
2. Weyer C, Funahashi T, Tanaka S, Hotta K, Matsuzawa Y, Pratley RE, Tataranni PA. Hypoadiponectinemia in obesity and type 2 diabetes: close association with insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001. 86:1930–1935.
3. Pellme F, Smith U, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y, Brekke H, Wiklund O, Taskinen MR, Jansson PA. Circulating adiponectin levels are reduced in nonobese but insulin-resistant first-degree relatives of type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes. 2003. 52:1182–1186.
4. Hotta K, Funahashi T, Arita Y, Takahashi M, Matsuda M, Okamoto Y, Iwahashi H, Kuriyama H, Ouchi N, Maeda K, Nishida M, Kihara S, Sakai N, Nakajima T, Hasegawa K, Muraguchi M, Ohmoto Y, Nakamura T, Yamashita S, Hanafusa T, Matsuzawa Y. Plasma concentrations of a novel, adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in type 2 diabetic patients. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000. 20:1595–1599.
5. Ouchi N, Kihara S, Arita Y, Okamoto Y, Maeda K, Kuriyama H, Hotta K, Nishida M, Takahashi M, Muraguchi M, Ohmoto Y, Nakamura T, Yamashita S, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y. Adiponectin, an adipocyte-derived plasma protein, inhibits endothelial NF-NF-êB signaling through a cAMPdependent pathway. Circulation. 2000. 102:1296–1301.
6. Ouchi N, Kihara S, Arita Y, Nishida M, Matsuyama A, Okamoto Y, Ishigami M, Kuriyama H, Kishida K, Nishizawa H, Hotta K, Muraguchi M, Ohmoto Y, Yamashita S, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y. Adipocyte-derived plasma protein, adiponectin, suppresses lipid accumulation and class A scavenger receptor expression in human monocyte-derived macrophages. Circulation. 2001. 103:1057–1063.
7. Saito K, Tobe T, Minoshima S, Asakawa S, Sumiya J, Yoda M, Nakano Y, Shimizu N, Tomita M. Organization of the gene for gelatin-binding protein (GBP28). Gene. 1999. 229:67–73.
8. Menzaghi C, Ercolino T, Di Paola R, Berg AH, Warram JH, Scherer PE, Trischitta V, Doria A. A Haplotype at the adiponectin locus is associated with obesity and other features of the insulin resistance syndrome. Diabetes. 2002. 51:2306–2312.
9. Hara K, Boutin P, Mori Y, Tobe K, Dina C, Yasuda K, Yamauchi T, Otabe S, Okada T, Eto K, Kadowaki H, Hagura R, Akanuma Y, Yazaki Y, Nagai R, Taniyama M, Matsubara K, Yoda M, Nakano Y, Tomita M, Kimura S, Ito C, Froguel P, Kadowaki T. Genetic variation in the gene encoding adiponectin is associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes in the Japanese population. Diabetes. 2002. 51:536–540.
10. Wong M, Edelstein J, Wollman J, Bond MG. Ultrasonic-pathological comparison of the human arterial wall: verification of intima-media thickness. Arterioscler Thromb. 1993. 13:482–486.
11. Burke GL, Evans GW, Riley WA, Sharret AR, Howard G, Barnes RW, Rosamond W, Crow RS, Rautaharju PM, Heiss G. Arterial wall thickness is associated with prevalent cardiovascular disease in middle-aged adults: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Stroke. 1995. 26:386–391.
12. OLeary DH, Polak JF, Kronmal RA, Manolio TA, Burke GL, Wolfson SK Jr. the Cardiovascular Health Study Collaborative Research Group. Carotid-artery intima and media thickness as a risk factor for myocardial infarction and stroke in older adults. N Engl J Med. 1999. 340:14–22.
13. Yamasaki Y, Kawamori Y, Matsushima H, Nishizawa H, Kodama M, Kajimoto Y, Morishima T, Kamada T. Atherosclerosis in carotid artery of young IDDM patients monitored by ultrasound high-resolution B-mode imaging. Diabetes. 1994. 43:634–639.
14. World Health Organization. Part 1: Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellutis. Report of a WHO Consultation. 1999. Geneva: World Health Organization;WHO/NCD/NCS/99.2.
15. Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem. 1972. 18:499–502.
16. Matthews DR, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: Insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985. 28:412–419.
17. Pignoli P, Tremoli E, Poli A, Oreste P, Paoletti R. Intimal plus medial thickness of the arterial wall: a direct measurement with ultrasound imaging. Circulation. 1986. 74:1399–1406.
18. Yamasaki Y, Kawamori R, Matsushima H, Nishizawa H, Kodama M, Kubota M, Kajimoto Y, Kamada T. A symptomatic hyperglycemia is associated with increased intimal plus medial thickness of the carotid artery. Diabetologia. 1995. 38:585–591.
19. Giral P, Pithois-Merli I, Filitti V, Levenson J, Plainfosse MC, Mainardi C, Simon AC. Risk factors and early extracoronary atherosclerosis plaques detected by three site ultrasound imaging in hypercholesterolemic men. Arch Intern Med. 1991. 151:950–956.
20. Bruckert E, Giral P, Salloum J, Kahn JF, Dairou F, Truffert J, Reverdy V, Thomas D, Evans J, Grosgogeat Y. Carotid stenosis is a powerful predictor of a positive exercise electrocardiogram in a large hyperlipidemic population. Atherosclerosis. 1992. 92:105–114.
21. Giral P, Bruckert E, Dairou F, Boubrit K, Drobinski G, Chapman J, Beuder I, Turpin G. Usefulness in predicting coronary artery disease by ultrasonic evaluation of the carotid arteries in asymptomatic hypercholesterolemic patients with positive exercise stress tests. Am J Cardiol. 1999. 84:14–17.
22. Humphries S, Morgan L. Genetic risk factors for stroke and carotid atherosclerosis: insights into pathophysiology from candidate gene approaches. Lancet Neurol. 2004. 3:227–235.
23. Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Waki H, Imai Y, Shimozawa N, Hioki K, Uchida S, Ito Y, Takakuwa K, Matsui J, Takata M, Eto K, Terauchi Y, Komeda K, Tsunoda M, Murakami K, Ohnishi Y, Naitoh T, Yamamura K, Ueyama Y, Froguel P, Kimura S, Nagai R, Kadowaki T. Globular adiponectin protected ob/ob mice from diabetes and ApoE-deficient mice from atherosclerosis. J Biol Chem. 2003. 278:2461–2468.
24. Stumvoll M, Tschritter O, Fritsche A, Strager H, Renn W, Weisser M, Machicao F, Haring H. Association of the TG polymorphism in adiponectin (exon 2) with obesity and insulin sensitivity: interaction with family history of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2002. 51:37–41.
25. Takahashi M, Arita Y, Yamagata K, Matsukawa Y, Okutomi K, Horie M, Shimomura I, Hotta K, Kuriyama H, Kihara S, Nakamura T, Yamashita S, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y. Genomic structure and mutations in adipose-specific gene, adiponectin. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2000. 24:861–868.
26. Kondo H, Shimomura I, Matsukawa Y, Kumada M, Takahashi M, Matsuda M, Ouchi N, Kihara S, Kawamoto T, Sumitsuji S, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y. Association of adiponectin mutation with type 2 diabetes: a candidate gene for the insulin resistance syndrome. Diabetes. 2002. 51:2325–2328.
27. Vasseur F, Helbecque N, Dina C, Lobbens S, Delannoy V, Gaget S, Boutin P, Vaxillaire M, Lepretre F, Dupont S, Hara K, Clement K, Bihain B, Kadowaki T, Froguel P. Single-nucleotide polymorphism haplotypes in the both proximal promoter and exon 3 of the APM1 gene modulate adipocyte-secreted adiponectin hormone levels and contribute to the genetic risk for type 2 diabetes in French Caucasians. Hum Mol Genet. 2002. 11:2607–2614.
28. Bacci S, Menzaghi C, Ercolino T, Ma X, Rauseo A, Salvemini L, Vigna C, Fanelli R, Di Mario U, Doria A, Trischitta V. The +276 G/T Single Nucleotide Polymorphism of the Adiponectin Gene Is Associated With Coronary Artery Disease in Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Diabetes Care. 2004. 27:2015–2020.
29. Kubota N, Terauchi Y, Yamauchi T, Kubota T, Moroi M, Matsui J, Eto K, Yamashita T, Kamon J, Satoh H, Yano W, Froguel P, Nagai R, Kimura S, Kadowaki T, Noda T. Disruption of adiponectin causes insulin resistance and neointimal formation. J Biol Chem. 2002. 277:25863–25866.
30. Matsuda M, Shimomura I, Sata M, Arita Y, Nishida M, Maeda N, Kumada M, Okamoto Y, Nagaretani H, Nishizawa H, Kishida K, Komuro R, Ouchi N, Kihara S, Nagai R, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y. Role of adiponectin in preventing vascular stenosis: the missing link of adipovascular axis. J Biol Chem. 2002. 277:37487–37491.
31. Okamoto Y, Arita Y, Nishida M, Muraguchi M, Ouchi N, Takahashi M, Igura T, Inui Y, Kihara S, Nakamura T, Yamashita S, Miyagawa J, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y. An adipocyte-derived plasma protein, adiponectin, adheres to injured vascular walls. Horm Metab Res. 2000. 32:47–50.
32. Matsuda M, Kawasaki F, Yamada K, Kanda Y, Saito M, Eto M, Matsuki M, Kaku K. Impact of adiposity and plasma adipocytokines on diabetic angiopathies in Japanese Type 2 diabetic subjects. Diabetic Medicine. 2004. 21:881–888.
33. Jansson PA, Pellmé F, Hammarstedt A, Sandqvist M, Brekke H, Caidahl K, Forsberg M, Volkmann R, Carvalho E, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y, Wiklund O, Yang X, Taskinen MR, Smith U. A novel cellular marker of insulin resistance and early atherosclerosis in humans is related to impaired fat cell differentiation and low adiponectin. FASEB J. 2003. 17:1434–1440.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download