Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationships among quality of sleep, depression, late-life function and disability in community-dwelling older women with urinary incontinence.
Methods
A stratified random sampling method was conducted to recruit participants from May 10 to August 17, 2007. Data were collected by questionnaires, which were constructed to include lower urinary tract symptoms, quality of sleep, depression, and late-life function and disability in 128 community-dwelling older women.
Results
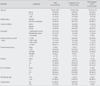
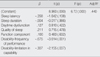
The major findings of this study were as follow: 1) 56.3% of participants belonged to urinary incontinence group. 2) There were significant relationships between depression and sleep latency, sleep duration, daytime dysfunction, quality of sleep, function component, frequency dimension, and limitation dimension. 3) Depression was significantly associated with frequency dimension, limitation dimension in capability which explained 44% of variance in depression.
Conclusion
These results may contribute to a better understanding of sleep quality, depression, late-life function and disability in the community-dwelling older women with urinary incontinence. Therefore, health programs for prompting older women's health should be planned based on results of the study.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Abrams P, Cardozo L, Fall M, Griffiths D, Rosier P, Ulmsten U, et al. The standardisation of terminology in lower urinary tract function: Report from the standardisation sub-committeeof the International Continence Society. Urology. 2003. 61:37–49.
2. Anger JT, Saigal CS, Litwin MS. Urologic Diseases of America Project. The prevalence of urinary incontinence among community dwelling adult women: Results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. The Journal of Urology. 2006. 175:601–604.

3. Buysse DJ, Reynolds CF 3rd, Monk TH, Berman SR, Kupfer DJ. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: A new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Research. 1989. 28:193–213.

4. Choo MS, Ku JH, Oh SJ, Lee KS, Paick JS, Seo JT, et al. Prevalence of urinary incontinence in Korean women: An epidemiologic survey. International Urogynecology Journal and Pelvic Floor Dysfunction. 2007. 18:1309–1315.
5. Dawson C, Whitfield H. ABC of urology. Bladder outflow obstruction. British Medical Journal. 1996. 312:767–770.

6. Haley SM, Jette AM, Coster WJ, Kooyoomjian JT, Levenson S, Heeren T, et al. Late life function and disability instrument: II. Development and evaluation of the function component. The Journals of Gerontology. 2002. 57:M217–M222. Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences.

7. Jackson S, Donovan J, Brookes S, Eckford S, Swithinbank L, Abrams P. The Bristol Female Low Urinary Tract Symptoms questionnaire: Development and psychometric testing. British Journal of Urology. 1996. 77:805–812.
8. Jette AM, Haley SM, Coster WJ, Kooyoomjian JT, Levenson S, Heeren T, et al. Late life function and disability instrument: I. Development and evaluation of the disability component. The Journals of Gerontology. 2002. 57:209–216. Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences.

9. Jung IK, Kwak DI, Joe SH, Lee HS. A study of standardization of Korean Form of Geriatric Depression Scale. Journal of Korean Geriatric Psychiatry. 1997. 1:61–72.
10. Kim JI. Prevalence of urinary incontinence and other urologic symptoms in a community residing elderly people. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2002. 32:28–39.

11. Kim KH. Study on correlation between urinary Incontinence & lower urinary tract symptom and daily life of middle-aged & elderly women in urban city. 2002. Seoul: Ewha Womans University;Unpublished master's thesis.
12. Kim KH, Park HJ, Jin YH, Kang YH, Shin KR. The correlation among quality of life, depression, and urinary incontinence of elderly women in a urban city. Journal of the Korean Geriatrics Society. 2007. 27:943–962.
13. Kim MS, Lee SH. Prevalence rate and associated factors of urinary incontinence among nursing home residents. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2008. 38:92–100.

14. Lee HJ, Jo KH. Type of college students attitude toward elderly suicide. Journal of Korean Association of Welfare for the Aged. 2006. 34:293–311.
15. Lee MJ. A study on urinary incontinence and sleep disorder, quality of life of elderly women. 2007. Seoul: Ewha Womans University;Unpublished master's thesis.
16. Lekan-Rutledge D. Urinary incontinence strategies for frail elderly women. Journal of Urological Nursing. 2004. 24:281–301.
17. MacDonald CD, Butler L. Silent no more: Elderly women's stories of living with urinary incontinence in long-term care. Journal of Gerontological Nursing. 2007. 33:14–20.

18. Melville JL, Delaney K, Newton K, Katon W. Incontinence severity and major depression in incontinent women. Obstetrics & Gynecology. 2005. 106:585–592.

19. Milsom I. The prevalence of urinary incontinence. Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica. 2000. 79:1056–1059.

20. Montgomery P, Dennis J. Physical exercise for sleep problems in adults aged 60+. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2002. 4:CD003404.

21. Oh YH, Bae HO, Kim YS. A study on physical and mental function affecting self-perceived health of older persons in Korea. Journal of the Korean Geriatrics Society. 2006. 26:461–476.
22. Park YH, Suh EE. The risk of malnutrition, depression, and the perceived health status of older adults. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2007. 37:941–948.

23. Pilcher JJ, Ginter DR, Sadowsky B. Sleep quality versus sleep quantity: Relationship between sleep and measures of health, well-being and sleepiness in college students. Journal of Psychosomatic Research. 1997. 42:583–596.
24. Segulin N, Deponte A. The evaluation of depression in the elderly: A modification of the Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS). Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics. 2007. 44:105–112.

25. Shin KL, Kim MY. The relationship between cognitive function and depression in a Korean island elderly. Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing. 2001. 3:32–41.
26. Woo KM. Effects of exercise-motivation program for the elderly women. 2003. Busan: Kosin University;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
27. Wyman JF. Treatment of urinary incontinence in men and older women: The evidence shows the efficacy of a variety of a techniques. The American Journal of Nursing. 2003. 103:Suppl. 26–35.
28. Yesavage JA, Brink TL, Rose TL, Lum O, Huang V, Adey M, et al. Development and validation of a geriatric depression screening scale: A preliminary report. Journal of Psychiatric Research. 1983. 17:37–49.

29. Youn JH. A study on IBS and stress perceived by college women and their dietary habit and sleeping quality. 2005. Seoul: Ewha Womans University;Unpublished master's thesis.
30. Yu MK. A study on the sleep in the community dwelling elderly. 2007. Seoul: Ewha Womans University;Unpublished master's thesis.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print






 XML Download
XML Download