Abstract
Purpose
It has been attempted to support mother of premature infants by providing information of premature infant care using e-learning because premature infants need continuous care from birth to after discharge.
Methods
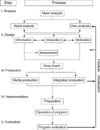
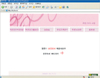
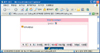
The e-Learning Program for mother of premature was developed with Xpert, Namo web editor, Adobe Photoshop, and PowerPoint and applied for 4 weeks from 4 to 30 September 2006.
Results
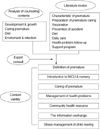
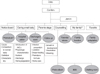
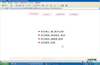
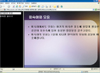
1) We found that the contents of information which premature infants' need when being in the hospital and after discharge were the definition of a premature infant, orientation of NICU, care of premature infants, care of premature infants' common diseases, the connection of healthcare resources, exchange of information, and the management of rearing stress. 2) The program content consisted of cause of premature birth, comparison to full-term baby, physiology character, orientation of NICU, common health problems, follow up care, infection control, feeding, normal development physically and mentally, weaning method, and vaccination.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Ahn YM, Kim JH. Comparison of maternal selfesteem, postpartal depression, and family function in mothers of normal and of low birth-weight infants. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2003. 33:580–590.

2. Blackburn S. Problems of preterm infant after discharge. JOGNN. 1995. 24(1):43–49.
3. Brooten D, Gennaro S, Knapp H, Brown LP, York R. Clinical specialist pre- and postdischarge teaching of parents of very low birth weight infants. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs. 1988. 18:316–322.

4. Chae SM. Development and evaluation of transitional care program for low birth weight infants and mothers. 2001. Seoul: Yonsei University;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
5. Choi YB. Effects of information via e-mail on parental attachment behavior of a premature infant. 2005. Seoul: Yonsei University;Unpublished master's thesis.
6. Chun BC. E-health and internet in medicine-a strategic perspective. J Korean Med Assoc. 2002. 45(1):4–16.

7. Drake E. Discharge teaching needs of parents in the NICU. Neonatal Netw. 1995. 14(1):49–53.
8. Gupton A, Heaman M. Learning needs of hospitalized Women at risk for preterm birth. Appl Nurs Res. 1994. 7:118–124.

9. Han KJ. Development of a home-based nursing intervention mothering program for low-birth-weight infants. J Korean Acad Home Healthc Nurse. 2001. 8(1):5–24.
10. Jang YS. Development of model for a prematures' health promotion center which is integrated with school, hospital and primary health center. 2004. Kwangju: Junnam National University;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
11. Jo WJ, Lee CJ. Study of developing a internet support program for cooperating teachers. J Korean Teacher Education. 2002. 19(2):57–79.
12. Jotzo M, Poets CF. Helping parents cope with the trauma of premature birth: an evaluation of a trauma-preventive psychological intervention. Pediatrics. 2005. 115:915–919.

13. Jun KJ, Yoon SJ, Go KS. Assessment of the public health program of health center for premature and congenital anomaly infants. J Korean Soc Matern Child Health. 2002. 5:199–214.
14. Jung HK. Hemodialysis nursing education program using Web-based learning system. Nurs Query. 2000. 9(1):146–166.
15. Keller J, Burkman E. Fleming M, Levie WH, editors. Motivation principles. Instructional message design. 1993. Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey: Educational Technology Publications.
16. Kim JS. Development and evaluation of the web-based program for maternal role support of the primiparas. 2005. Seoul: Seoul National University;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
17. Kim JY. Effect of massage program on premature infants' growth and on the mothering role confidence and satisfaction. 2004. Kwangju: Junnam National University;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
18. Kim SO. Survey for health care needs of premature baby at home. 2001. Seoul: Yonsei University;Unpublished master's thesis.
19. Klein M, Stem L. Low birth weight and the battered child syndrome. Am J Dis Child. 1971. 122(1):15–18.

20. Korean National Statistical Office. Birth and death data for 2005. 2006.
21. Ku BN, Kim MY. Maternal role confidence. Kungbuk J Nurs Sci. 2002. 6(1):39–56.
22. Kwon HK. Affect of discharge education program for mothers of premature infants on maternal role confidence and parenting stress. 2006. Kangnung: Kwandong University;Unpublished master's thesis.
23. Lee DH, editor. Problem and solution by low delivery. Subject of the 18th Fall conference in the Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health. 2005. 83–89.
24. Lee IH. Development of model for a prematures' health promotion center which is integrated with school, hospital and primary health center. Technology. 2004. 33:105–116.
25. Lee SH, Ji SA. A study on experience of the mother of premature infant in NICU. Chung-Ang J Nurs. 2001. 5(2):45–53.
26. McKim ED. The difficult first week at home with a premature infant. Public Health Nurs. 1993. 10(2):89–96.

27. Melnyk BM, Alpert-Gillis L, Feinstein NF, Fairbanks E, Schultz-Czarniak J, Hust D, et al. Improving cognitive development of low-birth-weight premature infants with the COPE program: a pilot study of the benefit of early NICU intervention with mothers. Res Nurs Health. 2001. 24:373–389.

28. Moore M, Kearsley G. Distance Education-A systems view. 1996. Boston: Wadsworth Publishing Company.
29. Na IJ. Web-based edcation. 2005. Seoul: Kwahakkyoksa Publising.
30. Park JH, Lee SW, editors. Infants' health problem by birth rate decrease. Paper presented at the 17th Spring conference of the Korean Society of Maternal and Child Health. 2005.
31. Park SJ, Lee MJ, Hong YH, Kim SY, Yoo EJ. The development of educational multimedia for mothers of premature infants. Annual Bulletin of The Bum-Suk Academic Scholarship Foundation. 2003. 7:127–135.
32. Park WS. Premature infants follow-up program. J Korean Pediatr Assoc. 2003. 46:319–325.
33. Shin YH. Current status of korean premature infant care and its prospective. Korean J Child Health Nurs. 2003. 9(1):96–106.
34. Song AS. Effect of supportive care for mothers of premature infants on anxiety and confidence of baby care after discharge. 2005. Kwangju: Junnam National University;Unpublished master's thesis.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download