Abstract
Background
With the extension of human life span, the prevalence of diabetes in elderly population is increasing. The glycemic control is also important in elderly diabetics because the life expectancy in elderly is steadily increased. In this study, we investigated the role of family support on glycemic control in elderly type diabetic patients.
Methods
This study was conducted with 126 type 2 diabetic patients over 60 years of age who were enrolled between March and December, 2005. The data for glycemic control, family characteristics, and family support were collected by structured questionnaire, personal interview, and medical record review. We used total supportive index scores to evaluate family support. We evaluated the relationship between family support and glycemic control.
Results
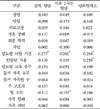
Fasting plasma glucose was positively correlated with duration of diabetes (r = 0.277, P = 0.003). Postprandial 2 hour plasma glucose was negatively correlated with monthly incomes (r = -0.357, P = 0.002), assessment support (r = -0.201, P = 0.029). Hemoglobin A1c was positively correlated with duration with diabetes (r = 0.294, P = 0.002) and insulin use (r = 0.259, P = 0.004), but it was negatively correlated with diabetic self-management education (r = -0.190, P = 0.036). Adjusted for age, sex, duration of diabetes, and monthly incomes, there were no significant associations between glycemic control and family support.
Figures and Tables
References
1. assessed on July, 2007. http://www.nso.go.kr.
2. Kim SM, Lee JS, Lee J, Na JK, Han JH, Yoon DK, Baik SH, Choi DS, Choi KM. Prevalence of diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in Korea: Korean National Health and Nutritional Survey 2001. Diabetes Care. 2006. 29:226–231.
4. Cole I, Chesla CA. Interventions for the family with diabetes. Nurs Clin North Am. 2006. 41:625–639.
5. Kaplan BH, Cassel JC, Gore S. Social support and health. Med Care. 1977. 15:47–58.
6. Kan CF. Family social support: toward a conceptual model. Adv Nurs Sci. 1988. 2:18–25.
19. La Greca AM, Bearman KJ. The diabetes social support questionnaire-family version: Evaluating adolescents' diabetes-specific support from family members. J Pediatr Psychol. 2002. 27:665–676.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print







 XML Download
XML Download