Abstract
Background
The prevalence of diabetes is steadily increasing in Korea. The increase in number of people with diabetes would ultimately result in premature death, poor quality of life, and increasing economic burden. However, in our country, researches regarding on the quality of diabetes management are lacking. This study was conducted in 2005 using National Health Insurance Database to know the current status of diabetes management in Korea.
Methods
We have randomly selected 3,902 subjects out of 2,503,754 subjects who had claims with diagnosis of diabetes between January 2003 to December 2003 by using two staged cluster sampling method. Field survey with review of medical records and telephone survey was conducted with standardized record forms developed by Korean Diabetes Association; Task Force Team For Basic Statistical Study of Korean Diabetes Mellitus.
Results
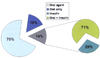
The age of diabetic subjects was 58.1 ± 12.6 years and the duration of diabetes was 6.2 ± 5.5 years. Hypertension was present in 54% of diabetic subjects. Among those with hypertension, 59% were controlled with blood pressure below 140/90 mmHg, but only 19% were controlled with blood pressure below 130/80 mmHg. Hyperlipidemia was present in 29% of diabetic subjects. Only 38% of those with hyperlipidemia were controlled with LDL-cholesterol below 100 mg/dL. For glycemic control, only 40% of diabetic subjects achieved the goal of HbA1c less than 7%, which was suggested by ADA.
References
2. Park Y, Lee H, Koh CS, Min H, Yoo K, Kim Y, Shin Y. Prevalence of diabetes and IGT in Yonchon County, South Korea. Diabetes Care. 1995. 18:545–548.
3. Kim SM, Lee JS, Lee J, Na JK, Han JH, Yoon DK, Baik SH, Choi DS, Choi KM. Prevalence of diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in Korea: Korean National Health and Nutrition Survey 2001. Diabetes Care. 2006. 29:226–231.
6. Amos AF, McCarty DJ, Zimmet P. The rising global burden of diabetes and its complications: estimates and projections to the year 2010. Diabet Med. 1997. 14:Suppl 5. S1–S85.
8. http://www.nso.go.kr/. 2006. assessed on November 24.
9. National Diabetes Surveillance System: National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. 2006. assessed on November 24.
http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/statistics/.
11. Rhee SY, Kim YS, Oh SJ, Choi WH, Park JE, Jeong WJ. Diabcare Asia 2001-Korea: Country Report on Outcome Data and Analysis. Korean J Intern Med. 2005. 20:48–54.
14. Stratton IM, Adler AI, Neil HA. Association of glycemia and macrovascular and microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes: prospective observational study. BMJ. 2000. 321:405–412.
15. UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Tight blood pressure control and risk of macrovascular and microvascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes: UKPDS38. BMJ. 1998. 317:703–713.
16. Gaede P, Vedel P, Lasen N. Multifactorial intervention and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2003. 348:383–393.
17. Chuang LM, Tsai ST, Huang BY, Tai TY. Diabcare_Asia 1998 Study Group. The status of diabetes control in Asia-a cross-sectional survey of 24,317 patients with diabetes mellitus in 1998. Diabet Med. 2002. 19:978–985.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download