Abstract
Background
Peripheral neuropathy is a common complication of diabetes mellitus, contributing the greatest morbidity and mortality and impairing the quality of life. Recently the receptor of erythropoietin (Epo) was proven to be expressed in neuronal cell and recombinant human Epo (rhEpo) has been shown to have neuroprotective and neurotrophic potential in peripheral neuropathy. But there is no report about baseline Epo level in blood before rhEpo treatment with diabetic peripheral neuropathy.
Methods
From Jan. 2000 to Sep. 2006, diabetic patients were reviewed about Epo level in blood, anemia, and peripheral neuropathy in Chonbuk National University Hospital. And we compared the mean value of baseline Epo level in diabetic patients with anemia according to the peripheral neuropathy.
Results
The mean value of Epo of patients with peripheral neuropathy was lower than that of patients without peripheral neuropathy (16.3 ± 7.1 vs 26.1 ± 29.7 mU/mL, P < 0.05). There was no significance in the correlation between hemoglobin and Epo level in diabetic patients with anemia irrespective of presence of peripheral neuropathy (r = -0.02, P = 0.81).
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
The comparison of serum Epo level between anemic patients with DPN and anemic patients without DPN. DPN, Diabetic peripheral neuropathy; Epo, Erythropoietin
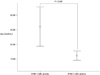
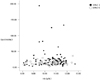
Fig. 2
The correlation between the level of serum Epo and hemoglobin in diabetic patients with anemia.
Correlation coefficient was not statistically significant irrespective of presence of DPN (r = -0.02, P = 0.81 in all patients, r = -0.046, P = 0.68 in subgroup without DPN, r = -0.003, P = 0.97 in subgroup with DPN). DPN, Diabetic peripheral neuropathy; Epo, Erythropoietin; Hb, hemoglobin.
References
1. Jelkmann W. Erythropoietin: structure, control of production, and function. Physiol Rev. 1992. 72:449–489.
2. Brines M, Cerami A. Discovering erythropoietin's extra-hematopoietic functions: biology and clinical promise. Kidney Int. 2006. 70:246–250.
3. Bianchi R, Buyukakilli B, Brines M, Savino C, Cavaletti G, Oggioni N, Lauria G, Borgna M, Lombardi R, Cimen B, Comelekoglu U, Kanik A, Tataroglu C, Cerami A, Ghezzi P. Erythropoietin both protects from and reverses experimental diabetic neuropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. 101:823–828.
4. Hassan K, Simri W, Rubenchik I, Manelis J, Gross B, Shasha SM, Kristal B. Effect of erythropoietin therapy on polyneuropathy in predialytic patients. J Nephrol. 2003. 16:121–125.
5. Parry GJ. Management of diabetic neuropathy. Am J Med. 1999. 107:27S–33S.
6. Boulton AJ, Malik RA, Arezzo JC, Sosenko JM. Diabetic somatic neuropathies. Diabetes Car. 2004. 27:1458–1486.
7. Herman WH, Kennedy L. Underdiagnosis of peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2005. 28:1480–1481.
8. Fisher JW. A quest for erythropoietin over nine decades. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1998. 38:1–20.
9. Brines M, Cerami A. Emerging biological roles for erythropoietin in the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005. 6:484–494.
11. Campana WM, Myers RR. Exogenous erythropoietin protects against dorsal root ganglion apoptosis and pain following peripheral nerve injury. Eur J Neurosci. 2003. 18:1497–1506.
12. Hanson P, Schumacker P, Debugne T, Clerin M. Evaluation of somatic and autonomic small fibers neuropathy in diabetes. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 1992. 71:44–47.
13. Jamal GA, Hansen S, Weir AI, Ballantyne JP. The neurophysiologic investigation of small fiber neuropathies. Muscle Nerve. 1987. 10:537–545.
14. Lauria G, Holland N, Hauer P, Cornblath DR, Griffin JW, McArthur JC. Epidermal innervation: changes with aging, topographic location, and in sensory neuropathy. J Neurol Sci. 1999. 164:172–178.
15. Christianson JA, Riekhof JT, Wright DE. Restorative effects of neurotrophin treatment on diabetes-induced cutaneous axon loss in mice. Exp Neurol. 2003. 179:188–199.
16. Smith AG, Ramachandran P, Tripp S, Singleton JR. Epidermal nerve innervation in impaired glucose tolerance and diabetes-associated neuropathy. Neurology. 2001. 57:1701–1704.
17. Bianchi R, Marini P, Merlini S, Fabris M, Triban C, Mussini E, Fiori MG. ATPase activity defects in alloxan-induced diabetic sciatic nerve recovered by ganglioside treatment. Diabetes. 1988. 37:1340–1345.
18. Lauria G, Sghirlanzoni A, Lombardi R, Pareyson D. Epidermal nerve fiber density in sensory ganglionopathies: clinical and neurophysiologic correlations. Muscle Nerve. 2001. 24:1034–1039.
19. McCarthy BG, Hsieh ST, Stocks A, Hauer P, Macko C, Cornblath DR, Griffin JW, McArthur JC. Cutaneous innervation in sensory neuropathies: evaluation by skin biopsy. Neurology. 1995. 45:1848–1855.
20. Campana WM, Myers RR. Erythropoietin and erythropoietin receptors in the peripheral nervous system: changes after nerve injury. FASEB J. 2001. 15:1804–1806.
21. Bachmann S, Le Hir M, Eckardt KU. Co-localization of erythropoietin mRNA and ecto-5'-nucleotidase immunoreactivity in peritubular cells of rat renal cortex indicates that fibroblasts produce erythropoietin. J Histochem Cytochem. 1993. 41:335–341.
22. Ricerca BM, Todaro L, Caputo S, Cotroneo P, Damiani P, Manto A, Pitocco D, Storti S, Ghirlanda G. Blunted erythropoietin response to anemia in type 1 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 1999. 22:647.
23. Cameron NE, Cotter MA, Maxfield EK. Anti-oxidant treatment prevents the development of peripheral nerve dysfunction in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Diabetologia. 1993. 36:299–304.
24. Feldman EL. Oxidative stress and diabetic neuropathy: a new understanding of an old problem. J Clin Invest. 2003. 111:431–433.
25. Lipton SA. Erythropoietin for neurologic protection and diabetic neuropathy. N Engl J Med. 2004. 350:2516–2517.
26. Digicaylioglu M, Lipton SA. Erythropoietin-mediated neuroprotection involves cross-talk between Jak2 and NF-kappaB signalling cascades. Nature. 2001. 412:641–647.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download