Abstract
Background
Objective
Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
 | Fig. 1The study recruitment and categorization of analyzed patients. We enrolled the patients diagnosed with hen's egg allergy by an oral food challenge at the Aichi Children's Health and Medical Center at ≤6 years of age from March 2012 to August 2015. A questionnaire was completed by the caregivers of patients from September to December 2015 regarding the timing of the introduction and discontinuation of cow's milk formula (CMF) (within the first week of life, from the first week to 1 month, and from 1 to 3 months), and the frequency of CMF ingestion (at least once daily, 2–4 days per week, ≤1 day per week). The analyzed patients were categorized into the following subgroups: exclusively breast feeding (breast-fed group); discontinued ingestion of CMF before 3 months of age (temporary group); continuous ingestion of CMF, but not daily, up to 3 months of age (nondaily group); continuous ingestion of CMF at least once daily (daily group). CMA, cow's milk allergy. |
Table 1
Baseline characteristics between excluded and analyzed patients
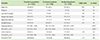
Values are presented as number (%) or median (interquartile range). Mann-Whitney U-test or chi-squate test or Fisher exact test, as appropriate for comparisons.
Family history, family history of allergic diseases; total IgE, maximum total IgE titer at <72 months of age; EW-sIgE, maximum egg white-specific IgE titer at <72 months of age; CMA, cow's milk allergy; CM-sIgE, maximum cow's milk-specific IgE titer at <72 months of age; NS, nonsignificant.
*p < 0.05, statistically significant. †Analysis for CMA patients.
Table 2
Background and the incidence of cow's milk allergy in the designated four groups according to the ingestion of cow's milk formula

NSValues are presented as number (%) or median (interquartile range). Mann-Whitney U-test or chi-square test or Fisher exact test, as appropriate for comparisons. Bonferroni correction (significance level 0.033) was performed, as appropriate, for multiple comparisons.
OR, odds ratio; family history, family history of allergic diseases; total IgE, maximum total IgE titer at <72 months of age; EW-sIgE, maximum egg white-specific IgE titer at <72 months of age; CMA, cow's milk allergy; OFC, oral food challenge; Diagnosed with OFC, diagnosed with positive cow's milk oral food challenge test result; CM-sIgE, maximum cow's milk-specific IgE titer at <72 months of age; NS, nonsignificant.
*p < 0.001. †Analysis for CMA patients.
Table 3
The multivariate logistic regression analysis of the risk factors for the development of cow's milk allergy

Values are presented as number (%).
CMA, cow's milk allergy; aOR, adjusted odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; family history, family history of allergic diseases; EW-sIgE, maximum egg white-specific IgE titer at <72 months of age; CMF, cow's milk formula; NS, nonsignificant.
*p < 0.05, statistically significant. †CMF ingestion at least once daily until first 3 months of age.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download