Abstract
Magnesium sulfate (MgSO4) has been considered as an adjunct therapy for severe and life-threatening asthma exacerbation. The literature search was performed using MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane Library and Google Scholar to summarize the current state of knowledge regarding magnesium therapy in acute exacerbation of adult asthma. A total of 16 trials and 4 meta-analyses were identified. As results, intravenous MgSO4 was beneficial in severe exacerbation, but evidence for nebulized magnesium was insufficient. However, larger trials are required to draw confirmative conclusions on the efficacy. Regarding the safety concern, the risk of major toxicity appears to be very low at usual doses described in the literature. Additionally, results from 4 surveys were examined on the gaps between knowledge and practice, and on the barrier to the use of MgSO4 at emergency departments. This literature review summarized the up-to-date evidence on the issues regarding the use of MgSO4 for acute asthma. We expect more studies to be conducted for evidence making in the Asian-Pacific regions.
Magnesium sulfate (MgSO4) has been considered as an adjunct therapy for severe and life-threatening asthma exacerbation. Theoretically, magnesium can induce bronchial smooth muscle relaxation in a dose-dependent manner [1] by inhibiting calcium influx into the cytosol [2], histamine release from mast cells [3], or acetylcholine release from cholinergic nerve endings [4]. It also may increase the bronchodilator effect of β2-agonist by increasing the receptor affinity [5]. Historically, in the literature, the first description on the clinical use of magnesium for asthma was reported in 1936 [6]. In 1987, Okayama et al. [7] reported rapid bronchodilating effects of intravenous (IV) MgSO4 infusion in 10 asthma patients. In 1989, its effect was also reported for prevention of endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation in an elderly asthma patient with severe exacerbation [8].
The first randomized controlled trial (RCT) was conducted in 1989 by Skobeloff et al. [9] to investigate its efficacy. Since then, it has been examined by several RCTs and meta-analyses. At the same time, the use of nebulized MgSO4 has also gained scientific interests. Current guidelines [10-12] suggest the use of IV MgSO4 as an adjunct therapy to improve pulmonary functions and reduce hospital admission in certain patients with severe and life-threatening acute exacerbations unresponsive to initial treatments, whereas the evidence has been weaker for nebulized magnesium.
In this review, we aimed to summarize the current state of knowledge regarding the use of MgSO4 in acute exacerbation of adult asthmatics.
Population: adult asthma patients with acute exacerbation
Intervention: MgSO4 (intravenous or nebulized form)
Control: placebo
Outcome: clinical efficacy
The literature search was performed during the period September 2011 until December 2011. Articles were searched from MEDLINE, EMBASE, the Cochrane Library and Google Scholar. Search terms included the terms for asthma, exacerbation and magnesium. Additionally, manual searching the references for relevant articles was also performed on respiratory or emergency medicine journals. The search for unpublished data was not conducted. The search was limited to the last 25 years (1986 to 2011).
First, authors scanned titles, abstracts, and selected relevant articles for retrieval of full-text. Through a full-text review, final selection was made: RCTs were included if they were conducted on adult acute asthmatics and compared its efficacy with placebo. The quality of included RCTs were determined by the five point Jadad score [13]. Meta-analyses were included if they included the issues relevant to our key question. Suspected duplicates were excluded. Finally, 10 RCTs for IV MgSO4, 6 RCTs for nebulized MgSO4, and 4 meta-analyses were included. All the identified articles were originally written in English, although attempts were made to find out non-English sources including Korean and Japanese.
The following data were extracted: study design, study population (patients, or number of pooled trials), interventions, control, co-treatments, and outcomes of interest.
Articles were searched again from the same electronic databases to retrieve information on the practice status at emergency departments regarding the use of MgSO4 in acute asthma patients. This search was not limited to adult population, because studies were scarce. Finally, 4 original articles were selected.
Included RCTs were summarized in Tables 1 and 2. Overall quality of RCTs was high, having a Jadad score of 4 or 5 in 11/16 trials. The majority (13/16) of the studies were double-blinded, while two trials [14, 15] for IV and one trial [16] for nebulized MgSO4 were single-blinded. However, heterogeneity was identified for the included trials. For RCTs on IV form, there were variations in the severity of attack, definition of severity, treatment dose (2 g bolus in 6/10 trials), co-treatments (IV theophylline/aminophylline in 5/10 trials, and nebulized ipratropium in 2/10 trials), and timing to measure outcomes. As for nebulized form, there was notable heterogeneity in the treatment dose of nebulized MgSO4.
The included meta-analyses were described in Table 3. A meta-analysis by Mohammed et al. [17] was the most up-to-date and comprehensive one including most of published RCTs and also unpublished data such as conference abstracts. Three recently published RCTs [15, 18, 19], not included in the meta-analyses, had distinct points from previous trials in that the recent trials used nebulized ipratropium as one of the routine treatments.
There have been 3 meta-analyses and 2 recent RCTs. The results from the Cochrane review by Rowe et al. [20] stated that IV MgSO4 as adjunct to standard treatment was beneficial in severe acute asthma patients, both in terms of pulmonary functions and hospital admission rate. The results by Rodrigo et al. [21] were not concordant, but the number of pooled studies and patients were smaller than the Cochrane review. The recent reviews by Mohammed et al. [17] found that the efficacy was only marginal on pulmonary function (standardized mean difference (SMD) 0.25, 95% confidence interval (CI) -0.01 to 0.51), and not significant on hospital admission (relative risk (RR) 0.87, 95% CI 0.70 to 1.08). However, their analyses were not confined to severe exacerbations.
Notably, two recent RCTs used nebulized ipratropium bromide as their standard treatments. The trials by Bradshaw et al. [19] did not show additional benefit of 1.2 g IV MgSO4 even in subgroups of life-threatening exacerbation. However, the trials by Singh et al. [15] showed its positive effect on forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) % predicted (vs. placebo; mean difference 6.07, 95% CI 1.87 to 10.62), but had limitations in smaller number of participants and single-blinded design.
Nebulized ipratropium is currently recommended as an additional bronchodilator for moderate exacerbation by guidelines, and is being widely used in practice. Therefore, the efficacy of IV MgSO4 needs to be examined further in the context of current treatment guidelines. Nevertheless, the use of MgSO4 should not be hesitated in patients with severe life-threatening asthma exacerbation unresponsive to standard treatments, because its toxicity was minimal.
There have been 2 meta-analyses and 1 recent RCT. The Cochrane review conducted by Blitz et al. [22] showed that nebulized MgSO4 improved pulmonary functions (SMD 0.55, 95% CI 0.12 to 0.98) in severe subgroups (FEV1 or peak expiratory flow <50% predicted). However, the results were based on only 87 adult asthmatics from 2 trials. The recent reviews by Mohammed et al. [17] examined more trials and found that nebulized MgSO4 had marginal benefits on pulmonary functions (SMD 0.17, 95% CI -0.02 to 0.36) and on hospital admission rate (RR 0.68, 95% CI 0.46 to 1.02). Considering the heterogeneity in treatment doses, severity of patients and small numbers of pooled studies, they concluded that evidence is insufficient to draw conclusions.
In a recent trial (n = 60) by Gallegos-Solórzano et al. [18], when added to standard treatments of nebulized albuterol and ipratropium, nebulized MgSO4 therapy improved post-bronchodilator lung functions and oxygen saturation, and reduced admission rates at 90 min. However, the largest trial (n = 100) by Aggarwal et al. [23] failed to show any benefit of additional MgSO4 therapy. Taken together, the use of nebulized MgSO4 might be beneficial in treating severe exacerbation, but large trials are required for more definite conclusion.
The dose of IV magnesium was 2 g as a bolus in most trials showing its effectiveness. The Cochrane review examined the safety of 2 g magnesium to find out its minimal risk of significant adverse reaction [20]. A RCT [6] using 2 g reported no major toxicities but only minor ones in 58% of patients (sensation of flushing, mild fatigue and burning sense at IV site). In a trial using 1.2 g bolus [13], the rate of minor side effect was 8% (headache, flushing and dizziness).
For more than two decades, magnesium has been used as a tocolytic agent for preterm labor, at higher doses (such as a 6 g IV load over 20 min and followed by a continuous infusion of 2 to 4 g/h [24]). Major toxicity occurred at serum magnesium level of 9 mg/dL or higher, such as loss of reflexes, blurred vision, lethargy, muscle weakness or pulmonary edema [24]. However, magnesium is usually excreted in urine, and administration of 2 g in a bolus increases the concentration just from 2.2 to 2.8 mg/dL 30 min after the infusion [25]. Therefore, it can be concluded that the usual dose of 2 g for acute asthma has a minimal risk of major toxicity in patients with normal renal function, as suggested by the meta-analyses [20]. The possibility exists that higher dose of IV magnesium is more effective, but still no published report has directly examined the benefit from high dose bolus therapy such as 4 g. One trial evaluated the role of continuous MgSO4 infusion, but failed to find its additional benefit [26].
Hypermagnesemia can be managed by prompt cessation of magnesium infusion in patients with normal renal functions. However, hemodialysis and IV calcium gluconate may be required in high risk patients with renal dysfunctions, bowel obstruction [27], or in elderly patients taking magnesium-containing cathartics [28].
In cases of nebulized magnesium, optimal dosing may be more intricate. MgSO4 is administered by a nebulizer, as a vehicle for β2-agonist (and also as in combination). However, hypertonic or hypotonic nebulized solution can cause bronchoconstriction by itself in asthmatics [29, 30]. Therefore, larger dose of magnesium may not be feasible due to practical reasons such as nebulizer volume, or the need for specific concentration of MgSO4 to make an isotonic solution. For example, in a trial by Aggarwal et al. [23], they made magnesium-containing solutions (10 mL, 295 mosmol/kg) as following: 1 mL of salbutamol solution, 1 mL of MgSO4 (from IV preparation at concentration of 500 mg/mL), plus 8 mL distilled water.
At the moment, there is no available evidence to advocate the use of higher dose of nebulized magnesium for yielding a better efficacy. Moreover, no dose-response relationships (from 0 to 360 mg MgSO4) have been reported [31]. Nebulized MgSO4 therapy can be considered as safe, because no serious side effects were reported [22].
As pre-existing magnesium deficit could be associated with risk of asthma exacerbation [32-35], one might think that serum magnesium level could be measured for adequate supplementation or prediction of treatment response. However, it is predominantly an intracellular ion, and its serum level does not reflect intracellular concentrations or total body stores. Its intracellular concentration was found to be lower in acute exacerbation and returned to normal when controlled, while plasma level remained unchanged [36]. Therefore, serum level does not represent the degree of cellular deficit, and it would not be useful to monitor serum magnesium level for enhancing the efficacy of MgSO4 therapy.
Current guidelines [10-12] suggest the use of IV MgSO4 as an adjunct to standard treatment in acute severe exacerbations (Table 4). Four observational studies evaluated the implementation of treatment guidelines with regard to the use of MgSO4 (Table 5). They were conducted in North America, UK, Australia and New Zealand.
In North America, a large-scale study [37] was conducted on patient cohorts and emergency physicians to investigate the use of IV MgSO4. Among 9745 emergency department (ED) patients, only 2.5% received IV MgSO4. In logistic regression analyses, its use was associated with older age, previous intubation history, higher respiratory rate, lower initial pulmonary functions, higher number of β2-agonists use, and use of systemic corticosteroids. For physicians at ED, 92% had MgSO4 available and 64% had recently used it. They tipped severity (96%) and poor response to initial β2-agonists (87%) as main factors prompting the use of MgSO4.
In an online survey of two national pediatric ED physicians in North America [38], 88% of physicians knew the efficacy of IV MgSO4, but 37.7% of physicians did not use IV MgSO4 in the management of severe acute asthma. Main barriers to the use were lack of needs (31%) and concerns of side effects (24%).
In a postal survey undertaken for all adult EDs within the UK [39], IV MgSO4 was currently being used in 93% of EDs, and more than 80% of severe or life-threatening asthma patients received the therapy. The reasons for using the agent were to improve breathlessness (70%) or reduce admissions (51%). Nebulized MgSO4 was being rarely used (1%), and the main reason was insufficient evidence (51%).
In a study conducted in Australia and New Zealand [40], they compared the gaps between clinical practice guideline (CPG) recommendations and self-reported physician management from 11 pediatric EDs. The gap between CPG and practice was particularly wide for severe to critical asthma. For IV MgSO4, it has been utilized in the practice for 7.7% of severe asthma and 55.1% of critical asthma (in CPG: 18.2% and 45.5%, respectively). The limitation of this study was that discrepancy existed between New Zealand and Australian guidelines on the recommendation of the use of magnesium.
Taken together, overall degree of knowledge among ED physicians appears to be high among examined countries. However, the significant gaps were found between the knowledge and the practice patterns except UK.
There have been four RCTs on the efficacy of MgSO4 from the Asia-Pacific regions (two from India, and Iran and Thailand for each). Their results were conflicting, but did not have notable differences from Western studies in their study designs or outcome measures. No information was available to determine ethnic differences on the efficacy of MgSO4 therapy. However, IV aminophylline has been used at EDs more widely in Korea and Japan than Western countries due to belief that the agent is not very toxic for the Northeast Asian people such as the Korean or the Japanese. In a Japanese prospective safety survey conducted by Ohta et al. [41], IV aminophylline treatment was found to be highly safe among the Japanese adult patients (age: 15-65 years) when administered in accordance with the guidelines and instructions. Its toxicity occurred in 0.29% of 682 patients, and all of them were mild. Thus we guess that the needs for an adjunct magnesium therapy might be lower in the Northeast Asia region than Western countries.
We have no more information on the current status of knowledge and practice regarding the use of MgSO4 for acute asthma in this region.
IV MgSO4 as an adjunct to standard treatment may be beneficial in the treatment of adult patients with severe or life-threatening exacerbation. The role of nebulized MgSO4 is less evident due to insufficient evidence. The use of MgSO4 has excellent safety profile if appropriately administered. Studies are needed to investigate its role and to identify the gaps between guidelines and practice patterns in the Asia-Pacific region.
Figures and Tables
Table 1
Summary of randomized placebo-controlled trials for efficacy of intravenous MgSO4 in acute exacerbation of adult asthmatics
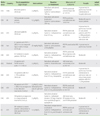
Table 2
Summary of randomized placebo-controlled trials for efficacy of nebulized MgSO4 in acute exacerbation of adult asthmatics

Table 3
Summary of systematic reviews and meta-analyses: randomized placebo-controlled trials for the efficacy of MgSO4 as an adjunct therapy for acute asthma in adults

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This study was supported by grants of the Korean Healthcare technology R&D Project, Ministry of Health, Welfare, Republic of Korea (A102065). The authors thank the committee members of Korean Asthma Management Guideline for Adults, especially, professor Sang-Heon Cho, professor Sae-Hoon Kim from Seoul National University, and professor Soo Young Kim from Hallym University.
References
1. Spivey WH, Skobeloff EM, Levin RM. Effect of magnesium chloride on rabbit bronchial smooth muscle. Ann Emerg Med. 1990; 19:1107–1112.

2. Gourgoulianis KI, Chatziparasidis G, Chatziefthimiou A, Molyvdas PA. Magnesium as a relaxing factor of airway smooth muscles. J Aerosol Med. 2001; 14:301–307.

3. Bois P. Effect of magnesium deficiency on mast cells and urinary histamine in rats. Br J Exp Pathol. 1963; 44:151–155.
4. Del Castillo J, Engbaek L. The nature of the neuromuscular block produced by magnesium. J Physiol. 1954; 124:370–384.

5. Classen HG, Jacob R, Schimatschek H. Interaction of magnesium with direct and indirect-acting sympathomimetic amines. Magnes Bull. 1987; 9:80–87.
6. Kowal A, Panaszek B, Barg W, Obojski A. The use of magnesium in bronchial asthma: a new approach to an old problem. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2007; 55:35–39.

7. Okayama H, Aikawa T, Okayama M, Sasaki H, Mue S, Takishima T. Bronchodilating effect of intravenous magnesium sulfate in bronchial asthma. JAMA. 1987; 257:1076–1078.

8. McNamara RM, Spivey WH, Skobeloff E, Jacubowitz S. Intravenous magnesium sulfate in the management of acute respiratory failure complicating asthma. Ann Emerg Med. 1989; 18:197–199.

9. Skobeloff EM, Spivey WH, McNamara RM, Greenspon L. Intravenous magnesium sulfate for the treatment of acute asthma in the emergency department. JAMA. 1989; 262:1210–1213.

10. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA). Updated 2010. Available from: http://www.ginasthma.com.
11. Expert Panel Report 3 (EPR3): Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma : summary report 2007. National Asthma Education and Prevention Program (National Heart Lung and Blood Institute). Bethesda, MD: U.S. Dept. of Health and Human Services, National Institues of Health, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute;Updated 2008. Available from: http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/guidelines/asthma/asthgdln.htm.
12. British Guideline on the Management of Asthma 2008. British Thoracic Society, Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network. Revised 2011. Available from: http://www.brit-thoracic.org.uk/guidelines/asthmaguidelines.aspx.
13. Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJ, Gavaghan DJ, McQuay HJ. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials. 1996; 17:1–12.

14. Green SM, Rothrock SG. Intravenous magnesium for acute asthma: failure to decrease emergency treatment duration or need for hospitalization. Ann Emerg Med. 1992; 21:260–265.

15. Singh AK, Gaur S, Kumar R. A randomized controlled trial of intravenous magnesium sulphate as an adjunct to standard therapy in acute severe asthma. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008; 7:221–229.
16. Kokturk N, Turktas H, Kara P, Mullaoglu S, Yilmaz F, Karamercan A. A randomized clinical trial of magnesium sulphate as a vehicle for nebulized salbutamol in the treatment of moderate to severe asthma attacks. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2005; 18:416–421.

17. Mohammed S, Goodacre S. Intravenous and nebulised magnesium sulphate for acute asthma: systematic review and meta-analysis. Emerg Med J. 2007; 24:823–830.

18. Gallegos-Solórzano MC, Pérez-Padilla R, Hernández-Zenteno RJ. Usefulness of inhaled magnesium sulfate in the coadjuvant management of severe asthma crisis in an emergency department. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2010; 23:432–437.

19. Bradshaw TA, Matusiewicz SP, Crompton GK, Innes JA, Greening AP. Intravenous magnesium sulphate provides no additive benefit to standard management in acute asthma. Respir Med. 2008; 102:143–149.

20. Rowe BH, Bretzlaff JA, Bourdon C, Bota GW, Camargo CA Jr. Magnesium sulfate for treating exacerbations of acute asthma in the emergency department. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000; CD001490.

21. Rodrigo G, Rodrigo C, Burschtin O. Efficacy of magnesium sulfate in acute adult asthma: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Am J Emerg Med. 2000; 18:216–221.

22. Blitz M, Blitz S, Beasely R, Diner BM, Hughes R, Knopp JA, Rowe BH. Inhaled magnesium sulfate in the treatment of acute asthma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005; CD003898.

23. Aggarwal P, Sharad S, Handa R, Dwiwedi SN, Irshad M. Comparison of nebulised magnesium sulphate and salbutamol combined with salbutamol alone in the treatment of acute bronchial asthma: a randomised study. Emerg Med J. 2006; 23:358–362.

24. Elliott JP, Lewis DF, Morrison JC, Garite TJ. In defense of magnesium sulfate. Obstet Gynecol. 2009; 113:1341–1348.

25. Mathew R, Altura BM. Magnesium and the lungs. Magnesium. 1988; 7:173–187.
26. Tiffany BR, Berk WA, Todd IK, White SR. Magnesium bolus or infusion fails to improve expiratory flow in acute asthma exacerbations. Chest. 1993; 104:831–834.

27. McLaughlin SA, McKinney PE. Antacid-induced hypermagnesemia in a patient with normal renal function and bowel obstruction. Ann Pharmacother. 1998; 32:312–315.

28. Onishi S, Yoshino S. Cathartic-induced fatal hypermagnesemia in the elderly. Intern Med. 2006; 45:207–210.

29. Schoeffel RE, Anderson SD, Altounyan RE. Bronchial hyperreactivity in response to inhalation of ultrasonically nebulised solutions of distilled water and saline. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1981; 283:1285–1287.

30. Boulet LP, Legris C, Thibault L, Turcotte H. Comparative bronchial responses to hyperosmolar saline and methacholine in asthma. Thorax. 1987; 42:953–958.

31. Hill J, Britton J. Dose-response relationship and time-course of the effect of inhaled magnesium sulphate on airflow in normal and asthmatic subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1995; 40:539–544.

32. Britton J, Pavord I, Richards K, Wisniewski A, Knox A, Lewis S, Tattersfield A, Weiss S. Dietary magnesium, lung function, wheezing, and airway hyperreactivity in a random adult population sample. Lancet. 1994; 344:357–362.

34. Kazaks AG, Uriu-Adams JY, Albertson TE, Shenoy SF, Stern JS. Effect of oral magnesium supplementation on measures of airway resistance and subjective assessment of asthma control and quality of life in men and women with mild to moderate asthma: a randomized placebo controlled trial. J Asthma. 2010; 47:83–92.

35. Gontijo-Amaral C, Ribeiro MA, Gontijo LS, Condino-Neto A, Ribeiro JD. Oral magnesium supplementation in asthmatic children: a double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2007; 61:54–60.

36. Zervas E, Papatheodorou G, Psathakis K, Panagou P, Georgatou N, Loukides S. Reduced intracellular Mg concentrations in patients with acute asthma. Chest. 2003; 123:113–118.

37. Rowe BH, Camargo CA Jr. The use of magnesium sulfate in acute asthma: rapid uptake of evidence in North American emergency departments. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 117:53–58.

38. Schuh S, Macias C, Freedman SB, Plint AC, Zorc JJ, Bajaj L, Black KJ, Johnson DW, Boutis K. North American practice patterns of intravenous magnesium therapy in severe acute asthma in children. Acad Emerg Med. 2010; 17:1189–1196.

39. Jones LA, Goodacre S. Magnesium sulphate in the treatment of acute asthma: evaluation of current practice in adult emergency departments. Emerg Med J. 2009; 26:783–785.

40. Babl FE, Sheriff N, Borland M, Acworth J, Neutze J, Krieser D, Ngo P, Schutz J, Thomson F, Cotterell E, Jamison S, Francis P. Paediatric acute asthma management in Australia and New Zealand: practice patterns in the context of clinical practice guidelines. Arch Dis Child. 2008; 93:307–312.

41. Ohta K, Makino S, Adachi M, Kihara N, Nakajima S, Nishima S, Fukuda T, Miyamoto T. Prospective survey on safety evaluation of injectable methylxanthines in Japan. Allergol Int. 2006; 55:295–299.

42. Silverman RA, Osborn H, Runge J, Gallagher EJ, Chiang W, Feldman J, Gaeta T, Freeman K, Levin B, Mancherje N, Scharf S. IV magnesium sulfate in the treatment of acute severe asthma: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Chest. 2002; 122:489–497.
43. Bijani K, Moghadamnia AA, Islami Khalili E. Intravenous magnesium sulfate as an adjunct in the treatment of severe asthmatic patients non-responding to conventional therapy. Acta Medica Iranica. 2001; 39:219–221.
44. Porter RS, Nester BA, Braitman LE, Geary U, Dalsey WC. Intravenous magnesium is ineffective in adult asthma, a randomized trial. Eur J Emerg Med. 2001; 8:9–15.

45. Boonyavorakul C, Thakkinstian A, Charoenpan P. Intravenous magnesium sulfate in acute severe asthma. Respirology. 2000; 5:221–225.

46. Bloch H, Silverman R, Mancherje N, Grant S, Jagminas L, Scharf SM. Intravenous magnesium sulfate as an adjunct in the treatment of acute asthma. Chest. 1995; 107:1576–1581.

47. Hughes R, Goldkorn A, Masoli M, Weatherall M, Burgess C, Beasley R. Use of isotonic nebulised magnesium sulphate as an adjuvant to salbutamol in treatment of severe asthma in adults: randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2003; 361:2114–2117.

48. Bessmertny O, DiGregorio RV, Cohen H, Becker E, Looney D, Golden J, Kohl L, Johnson T. A randomized clinical trial of nebulized magnesium sulfate in addition to albuterol in the treatment of acute mild-to-moderate asthma exacerbations in adults. Ann Emerg Med. 2002; 39:585–591.

49. Nannini LJ Jr, Pendino JC, Corna RA, Mannarino S, Quispe R. Magnesium sulfate as a vehicle for nebulized salbutamol in acute asthma. Am J Med. 2000; 108:193–197.

50. Asthma Management Handbook. National Asthma Council Australia. 2006. Available from: http://www.nationalasthma.org.au/uploads/handbook/370-amh2006_web_5.pdf.
51. Jindal SK, Gupta D, Aggarwal AN, Agarwal R. Guidelines for management of asthma at primary and secondary levels of health care in India. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci. 2005; 47:309–343.
52. Ohta K, Yamaguchi M, Akiyama K, Adachi M, Ichinose M, Takahashi K, Nishimuta T, Morikawa A, Nishima S. Japanese guideline for adult asthma. Allergol Int. 2011; 60:115–145.

53. Korean Asthma Management Guideline for Adults. Korean Academy of Asthma, Allergy and Clinical Immunology. Revised 2011. Available from: http://www.allergy.or.kr/file/2011_new.pdf.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download