Abstract
An antimicrobial compound has been isolated from the leaves of Glochidion superbum. The compound was determined as methyl 3, 4, 5-trihydroxybenzoate (methyl gallate), based on ultraviolet (UV), infrared (IR), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and mass spectroscopy (MS) analysis. The isolated compound exhibited potent antimicrobial activity against three clinical isolates of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) by qualitative agar disc diffusion method and quantitative broth dilution method. Agar disc diffusion was done in a dose-dependent manner for each bacterial isolate at disc potencies of 25, 50, 100, and 150 µg/disc. The zones of inhibition were on average equal to 12.27, 14.20, 15.43, and 24.17 mm respectively. The inhibition zones were compared with that of vancomycin disc at 30 µg as a reference standard. The MIC and MBC values were 50 µg/mL and 100 µg/mL respectively. The results of anti MRSA activity were analyzed using one-way ANOVA with Turkey's HSD and Duncan test. In conclusion, methyl gallate which was isolated from G. superbum showed the inhibition activity against methicillin resistant S. aureus.
Go to : 
References
(1). Sandhya S.., Chaintanya R. S. N. A. K. K.., Vinod K. R.., Rao K. N.V.; Banji, D.; Sudhakar, K.; &Swetha, R., Arch. Appl. Sci. Res. 2010. 2:309–322.
(2). Otsuka H.., Hirata E.., Shinzato T.., Takeda Y.Phytochemistry. 2003. 62:763–768.
(3). Joshi A.R.; Joshi, K Ethnobotanical Leaflets. 2007. 15:235–246.
(5). Bailey A. E.., Asplund R. O.., and Ali M. S. J.Natrod. 1986. 9:1149–1150.
(6). Choi J. G.., Mun S. H.., Chahar H. S.., Bharaj P.., Kang O. H.., Kim S. G.., Kwon D.Y.PLOS One. 2014. 9:1149–1150.
(7). Wang, K. J; ang C. R.., Zhang Y. J.Food Chemistry. 2007. 101:365–371.
(8). Saxena G.., McCutcheon A. R.., Farmer S.., Towers G. H.., Hancock R. E. J.Ethnopharmacol. 1994. 42:95–99.
(9). Ekaprasada M. T.., Nurdin H.., Ibrahim S.., Dachriyanus D.Int. J. Advan. Sci. EngineerInforma. Technology. 2015. 5:280–282.
(10). Kärpänoja P.., Nissinen A.., Huovinen P.., Sarkkinen H.Finnish Study Group for AntimicrobialResistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004. 53:660–663.
(11). Raeisi M.., Tajik H.., Razavi R. S.., Maham M.., Moradi M.., Hajimohammadi B.., Mehdizadeh T.Iran. J. Microbiol. 2012. 4:30–34.
(12). Rahman N. A.., Muliawan H. S.., Rashid N.N.; Muhamad, M.;Yusof, R.N. Dengue Bull. 2006. 30:260–269.
(13). Ekaprasada M. T.., Nurdin H.., Ibrahim S.., Dachriyanus D.Indo. J. Chem. 2010. 9:457–460.
(14). Tan Y. P.., Chan E. W. C.., Lim C. S. Y.Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2015. 42:650–656.
Go to : 
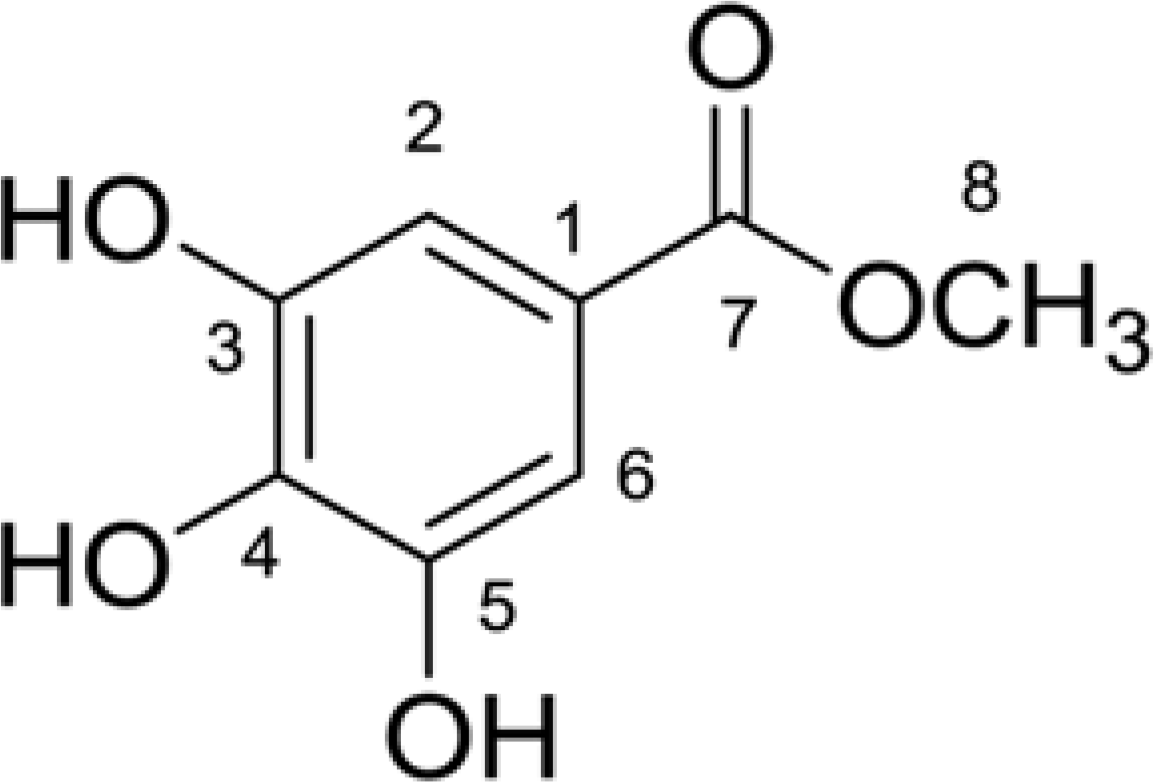 | Fig. 1.The structure of methyl 3, 4, 5 trihydroxybenzoate (methyl gallate) isolated from G. superbum. |
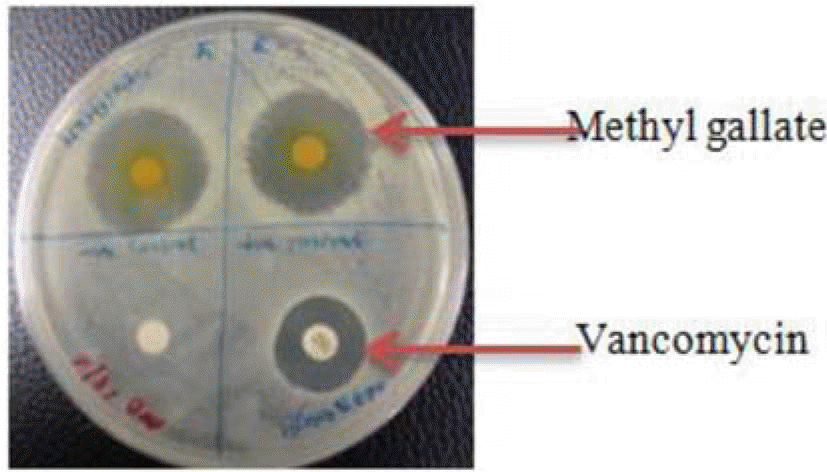 | Fig. 2.Zone of inhibition of methyl gallate against the hospital isolates of MRSA. Zone of inhibition of methyl gallate against a hospital isolate of MRSA at a concentration of 150 µg/disc and Vancomycin zone of inhibition at 30 µg/disc, on Mueller-Hinton agar plate. |
Table 1.
Zones of inhibition of methyl gallate against three Hospital isolates of MRSA
| MRSA Isolates | 25 µg/mL | 50 µg/mL | 100 µg/mL | 150 µg/mL | Vanco-30 µg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P5116 | 12.27 ± 0.25 | 14.20 ± 0.10b | 15.43 ± 0.12a | 24.17 ± 0.15b | 18.30 ± 0.10a |
| B460 isolate | 12.63 ± 0.15 | 14.77 ± 0.15c | 17.50 ± 0.30b | 24.63 ± 0.15c | 18.53 ± 0.15a |
| T175 | 12.20 ± 0.10 | 13.47 ± 0.15a | 15.63 ± 0.15a | 20.60 ± 0.20a | 18.37 ± 0.15a |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download