Abstract
Reserpine is a well-known medicine for the treatment of hypertension, however the role of reserpine in cell signaling is not fully understood. Here, we report that reserpine treatment induces the phosphorylation of AMP activated protein kinase (AMPK) at threonine 172 (T172) in PC12 cells. Phosphorylation of AMPK T172 is regulated by upstream signaling molecules, and the increase of phospho-T172 indicates that AMPK is activated. When we examined the FOXO3a dependent transcription by using the FHRE-Luc reporter assay, reserpine treatment repressed the FHRE-Luc reporter activity in a dose dependent manner. Finally, we showed that reserpine treatment induced the phosphorylation of AMPK as well as cell death in MCF-7 cells. These results suggest that AMPK is a potential cellular target of reserpine.
Go to : 
References
(1). Hardie D. G.., Schaffer B. E.., Brunet A.Trends Cell Biol. 2016. 26:190–201.
(2). Shaw R. J.., Kosmatka M.., Bardeesy N.., Hurley R. L.., Witters L. A.., DePinho R. A.., Cantley L. C. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S.A. 2004. 101:3329–3335.
(4). Kemp B. E.., Mitchelhill K. I.., Stapleton D.., Michell B. J.., Chen Z. P.., Witters L. A.Trends Biochem. Sci. 1999. 24:22–25.
(5). Adams J.., Chen Z. P.., Van Denderen B. J.., Morton C. J.., Parker M. W.., Witters L. A.., Stapleton D.., Kemp B. E.Protein Sci. 2004. 13:155–165.
(6). Woods A.., Vertommen D.., Neumann D.., Turk R.., Bayliss J.., Schlattner U.., Wallimann T.., Carling D.., Rider M. H. J.Biol. Chem. 2003. 278:28434–28442.
(7). Li N.., Huang D.., Lu N.., Luo L.Oncol. Rep. 2015. 34:2821–2826.
(8). Ben Sahra I.., Laurent K.., Loubat A.., Giorgetti-Peraldi S.., Colosetti P.., Auberger P.., Tanti J. F.., Le Marchand-Brustel Y.., Bost F.Oncogene. 2008. 27:3576–3586.
(9). Ben Sahra I.., Le Marchand-Brustel Y.., Tanti J. F.., Bost F.Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010. 9:1092–1099.
(10). Plummer A. J.., Earl A.., Schneider J. A.., Trapold J.., Barrett W.Ann. N Y Acad. Sci. 1954. 59:8–21.
(11). López-Muñoz F.., Bhatara V. S.., Alamo C.., Cuenca E.Actas Esp. Psiquiatr. 2004. 32:387–395.
(12). Guo Z.., Liu X.., Huang H.PLoS One. 2015. 10:, e0138619.
(13). Eiden L. E.., Weihe E.Ann. N Y Acad. Sci. 2011. 1216:86–98.
(14). Leão A. H.., Sarmento-Silva A. J.., Santos J. R.., Ribeiro A. M.., Silva R. H.Brain Pathol. 2015. 25:377–390.
(15). Fernandes V. S.., Santos J. R.., Leão A. H.., Medeiros A. M.., Melo T. G.., Izídio G. S.., Cabral A.., Ribeiro R. A.., Abílio V. C.., Ribeiro A. M.., Silva R. H.Behav Brain Res. 2012. 231:154–163.
(16). Lee K. I.., Kim M. J.., Koh H.., Lee J. I.., Namkoong S.., Oh W. K.., Park J.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015. 462:402–408.
(17). Brunet A.., Bonni A.., Zigmond M. J.., Lin M. Z.., Juo P.., Hu L. S.., Anderson M. J.., Arden K. C.., Blenis J.., Greenberg M. E.Cell. 1999. 96:857–868.
(18). Takayama H.., Misu H.., Iwama H.., Chikamoto K.., Saito Y.., Murao K.., Teraguchi A.., Lan F.., Kikuchi A.., Saito R.., Tajima N.., Shirasaki T.., Matsugo S.., Miyamoto K.., Kaneko S.., Takamura T. J.Biol. Chem. 2014. 289:335–345.
(19). Takayama H.., Misu H.., Iwama H.., Chikamoto K.., Raynaud S.., Auberger P.Cancer Res. 2010. 70:1042–1052.
Go to : 
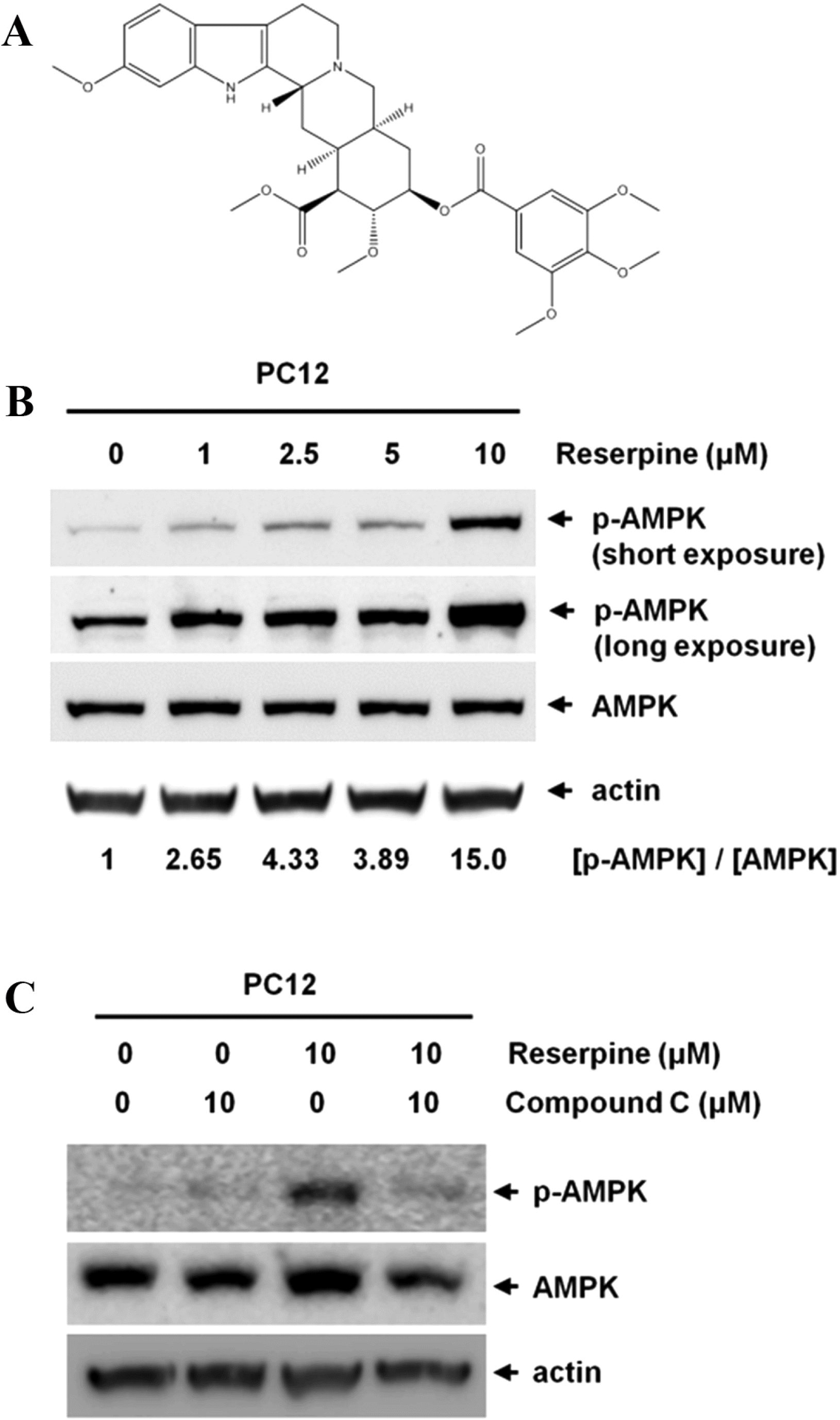 | Fig. 1.Reserpine activates AMPK in PC12 cells. (a) Chemical structure of reserpine (b) Reserpine treatment induced the phosphorylation of AMPK. PC12 cells were incubated with various concentrations of reserpine (0, 1, 2.5, 5 and 10 µM) for 24 h, and the cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting with phospho-AMPK (T172) or AMPK antibodies. Experiments were repeated three times with similar observations, and representative data is shown. The levels of phospho-AMPK/AMPK were analyzed. (c) Compound C treatment inhibited the activation of AMPK induced by reserpine treatment. PC12 cells were incubated with reserpine for 24 h in the presence or absence of Compound C. |
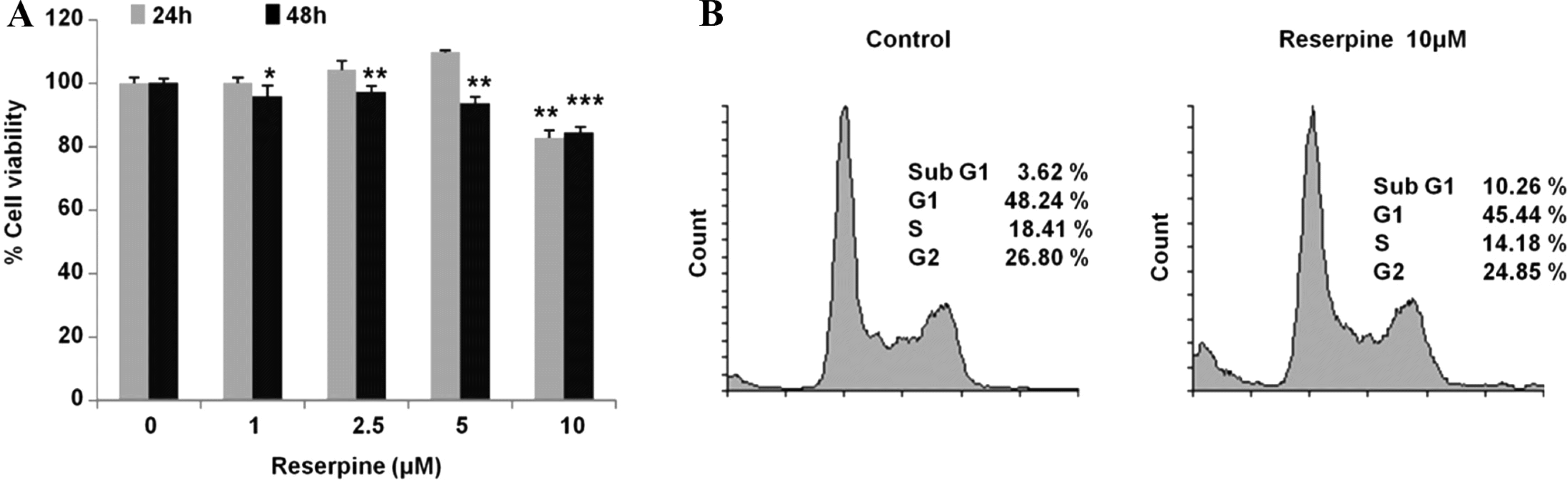 | Fig. 2.Reserpine induces cell death in PC12 cells. (a) Reserpine induces the cell death. PC12 cells were incubated with reserpine for 24 h and 48 h, and cell viability was measured using the MTT assay in quadruplicate. The graph shows the average and the standard deviation (SD). Control vs. reserpine treatment, ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.005, ∗∗∗P < 0.0005. (b) Reserpine induces apoptosis. PC12 cells were treated with reserpine (10 µM) for 24 h. The cells were stained with propidium iodide and analyzed using flow cytometry for DNA content. |
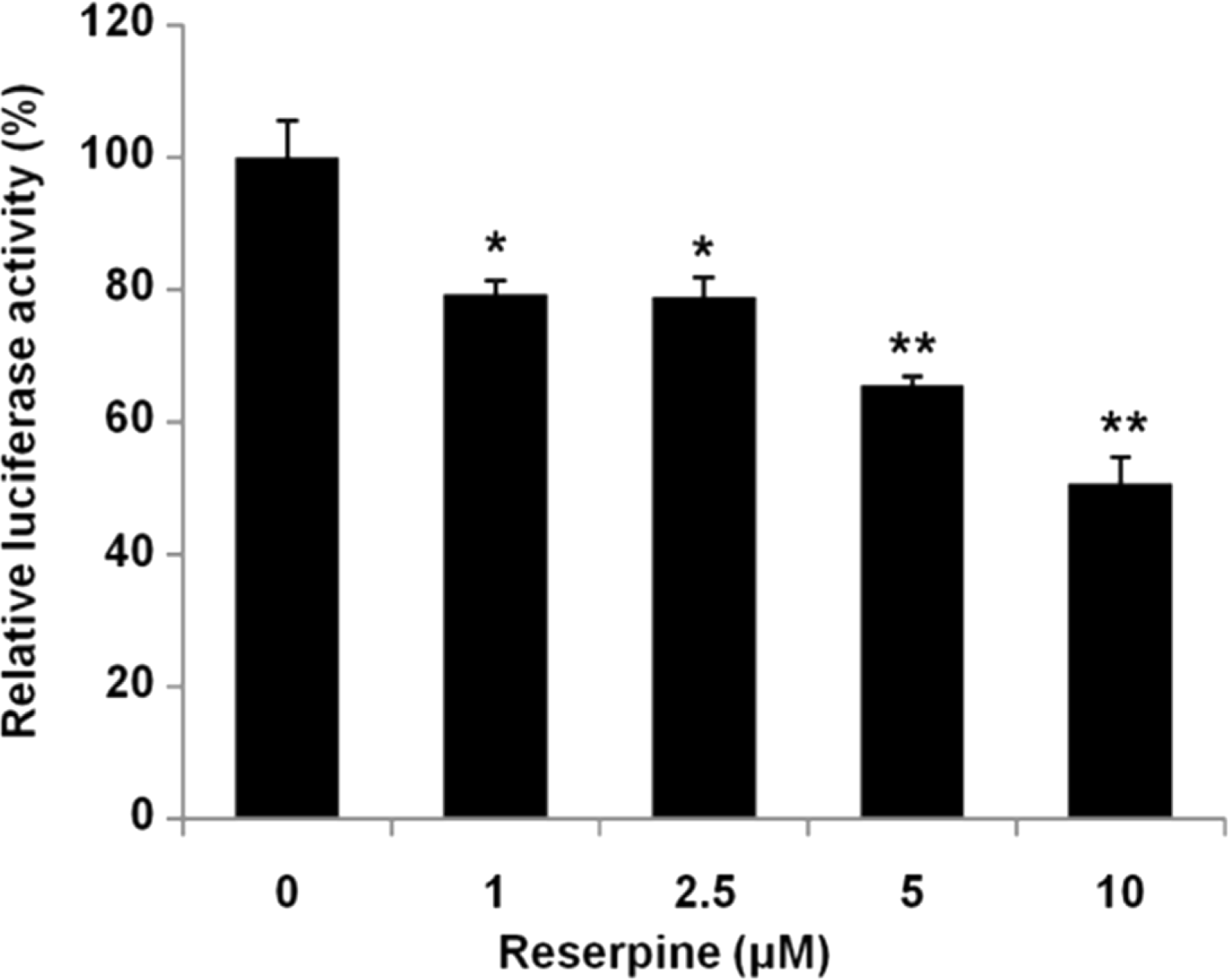 | Fig. 3.Reserpine treatment deregulates the FHRE-Luc reporter activity. HEK293T cells were transfected with FHRE-Luc reporter plasmid. Twenty four h after transfection, cells were treated with various concentrations of reserpine (0, 1, 2.5, 5 and 10 µM) for 24 h and luciferase activity was measured. The luciferase activity was normalized to renilla luciferase activity and the experiment was performed in quadruplicate. The graph shows the average and the standard deviation (SD). Control vs. reserpine treatment, ∗P <0.005, ∗∗P <0.001. |
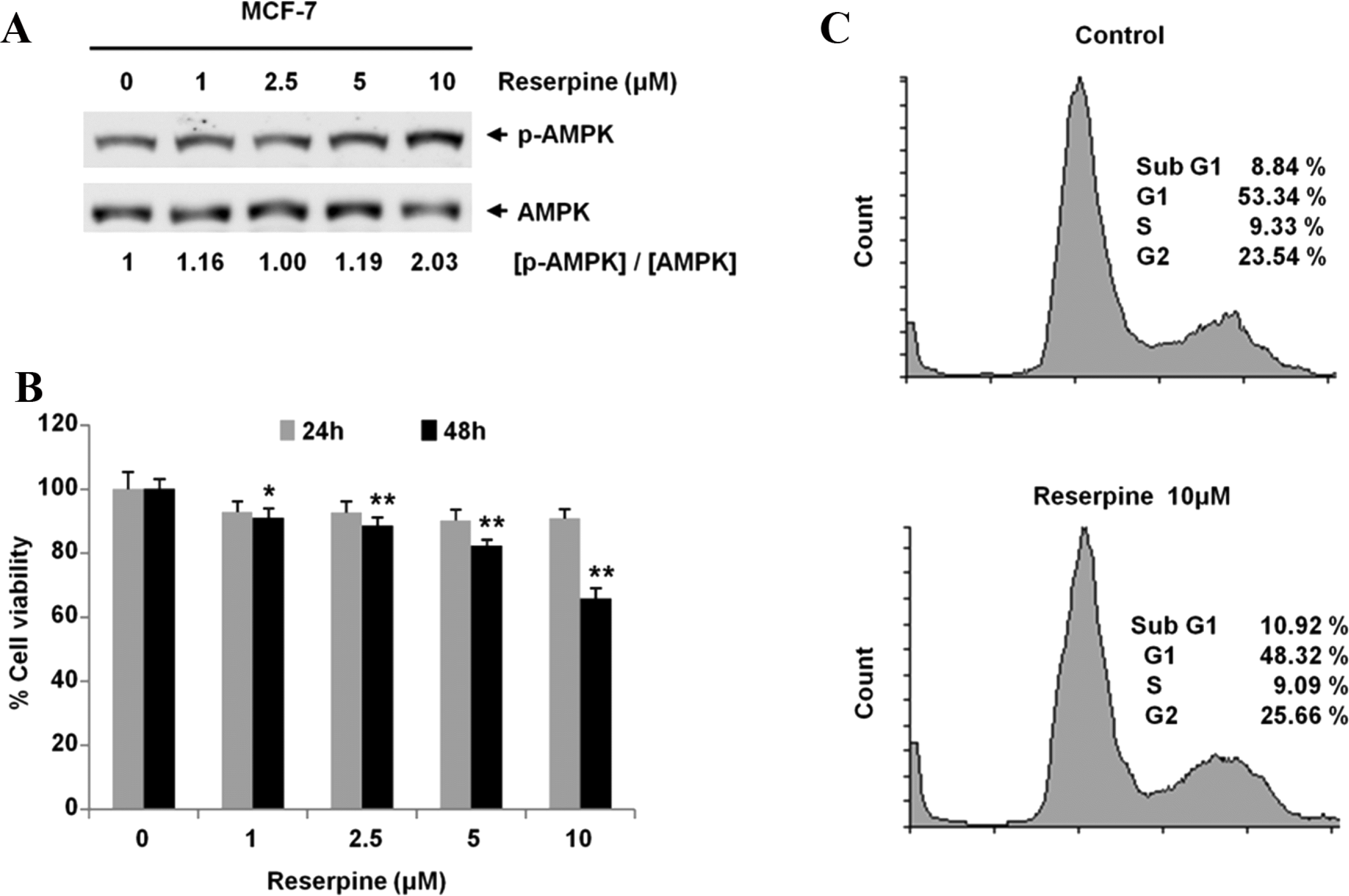 | Fig. 4.Reserpine treatment activates AMPK in MCF-7 cells and induces cell death. (a) MCF-7 cells were incubated with reserpine for 24 h, and the levels of phosphor-AMPK / AMPK in MCF-7 were analyzed. Experiments were repeated three times with similar observations, and representative data is shown. (b) Reserpine treatment induces the cell death. MCF-7 cells were incubated with reserpine for 24 h and 48 h, and cell viability was measured using the MTT assay in quadruplicate. The graph shows the average and the standard deviation (SD). Control vs. reserpine treatment, ∗P < 0.005, ∗∗P < 0.0005. (b) Reserpine increases sub-G1 population. MCF-7 cells were treated with reserpine (10 µM) for 24 h. The cells were stained with propidium iodide and analyzed using flow cytometry for DNA content. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download