Abstract
The goal of this study was to determine whether gypenosides (GPS) exert protective effects against dopaminergic neuronal cell death in a 6-hydroxydopamine (OHDA)-lesioned rat model of Parkinson's disease (PD) with or without longterm 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA) treatment. Rats were injected with 6-OHDA in the substantia nigra to induce PD-like symptoms; 14 days after injection, groups of 6-OHDA-lesioned animals were treated for 21 days with GPS (25 or 50 mg/kg) and/or L-DOPA (20 mg/kg). Dopaminergic neuronal cell death was assessed by counting tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)-immunopositive cells in the substantia nigra and measuring levels of dopamine, norepinephrine, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC), and homovanillic acid (HVA) in the striatum. Dopaminergic neuronal cell death induced by 6-OHDA lesions was ameliorated by GPS treatment (50mg/kg). L-DOPA treatment exacerbated 6-OHDA-induced dopaminergic neuronal cell death; however, these effects were partially reversed by GPS treatment (25 and 50 mg/kg). These results suggest that GPS treatment is protective against dopaminergic neuronal cell death in a 6-OHDA-lesioned rat model of PD with longterm L-DOPA treatment. Therefore, GPS may be useful as a phytotherapeutic agent for the treatment of PD.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
(1). Fearnley J. M., Lees A. J.Brain. 1991; 114:2283–2301.
(2). Fahn S. Ann. N. Y.Acad. Sci. 2003; 991:1–14.
(3). Marsden C. D. J.Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry. 1994; 57:672–681.
(4). Jankovic J.Mov. Disord. 2005; 20:S11–S16.
(5). Cheng N., Maeda T., Kume T., Kaneko S., Kochiyama H., Akaike A., Goshima Y., Misu Y.Brain Res. 1996; 16:278–283.
(6). Walkinshaw G., Waters C. M. J.Clin. Invest. 1995; 95:2458–2464.
(7). Shin K. S., Zhao T. T., Park K. H., Park H. J., Hwang B. Y., Lee C. K., Lee M. K.BMC Neurosci. 2015; 16:23.
(8). Bové J., Perier C.Neuroscience. 2012; 211:51–76.
(9). Jackson-Lewis V., Blesa J., Przedborski S.Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2012; 18:S183–S185.
(10). Seidl S. E., Potashkin J. A.Front. Neurol. 2011; 2:68.
(11). Razmovski-Naumovski V., Huang T. H. W., Tran V. H., Li G. Q., Duke C. C., Roufogalis B. D.Phytochem. Rev. 2005; 4:197–219.
(12). Im S. A., Choi H. S., Hwang B. Y., Lee M. K., Lee C.K.Kor. J. Pharmacogn. 2009; 40:35–40.
(13). Choi H. S., Zhao T. T., Shin K. S., Kim S. H., Hwang B. Y., Lee C. K., Lee M. K.Molecules. 2013; 18:4342–4356.
(14). Choi H. S., Park M. S., Kim S. H., Hwang B. Y., Lee C. K., Lee M. K.Molecules. 2010; 15:2814–2824.
(15). Shang L. S., Liu J. C., Zhu Q. J., Zhao L., Feng Y., Wang X., Cao W., Xin H.Brain Res. 2006; 1102:163–174.
(16). Wang P., Niu L., Guo X. D., Gao L., Li W. X., Jia D., Wang X. L, Ma L. T., Gao G. D.Brain Res. Bull. 2010; 83:266–271.
(17). Zhang G., Zhao Z., Gao L., Deng J., Wang B., Xu D., Liu B., Qu Y., Yu J., Li J., Gao G.Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2011; 99:42–51.
(18). Wang P., Niu L., Gao L., Li W. X., Jia D., Wang X. L., Gao G. D. J.Int. Med. Res. 2010; 38:1084–1092.
(19). Paxinos G., Watson C.The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. 2nd ed. Academic Press;Australia: 1986.
(20). Schwarting R. K. W., Huston J. P.Prog. Neurobiol. 1996; 50:275–331.
(21). Mo J., Zhang H., Yu L. P., Sun P. H., Jin G. Z., Zhen X.Neurobiol. Aging. 2010; 31:926–936.
(22). Izurieta-Sánchez P., Sarre S., Ebinger G., Michotte Y.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1998; 353:33–42.
(23). Ljungberg T., Ungerstedt U.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1977; 46:147–151.
(24). Blesa J., Phani S., Jackson-Lewis V., Przedborski S. J.BioMed. Biotechnol. 2012; 2012:845618.
(25). Shin K. S., Zhao T. T., Choi H. S., Hwang B. Y., Lee C. K., Lee M. K.Brain Res. 2014; 1567:57–65.
(26). Cenci M. A.Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2007; 13:S263–S267.
(27). Cohen G.Neurotoxicology. 1984; 5:77–82.
(28). Soto-Otero R., Méndez-Álvarez E., Hermida-Ameijeiras Á., Muñoz-Patiño A. M., Labandeira-Garcia J. L. J.Neurochem. 2000; 74:1605–1612.
(29). Cadet J. L., Brannock C.Neurochem. Int. 1998; 32:117–131.
(30). Fahn S., Cohen G.Ann. Neurol. 1992; 32:804–812. 2004.
(31). Schober A.Cell Tissue Res. 2004; 318:215–224.
(32). Blandini F., Armentero M. T., Martignoni E.Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2008; 14:S124–S129.
(33). Severson J. A., Marcusson J., Winblad B., Finch C. E. J.Neurochem. 1982; 39:1623–1631.
(34). Linert W., Herlinger E., Jameson R. F., Kienzl E., Jellinger K., Youdim M. B.Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1996; 1316:160–168.
(35). Maharaj H., Sukhdev Maharaj D., Scheepers M., Mokokong R., Daya S.Brain Res. 2005; 1063:180–186.
(36). Basma A. N., Morris E. J., Nicklas W. J., Geller H. M. J.Neurochem. 1995; 64:825–832.
(37). Migheli R., Godani C., Sciola L., Delogu M. R., Serra P. A., Zangani D., De Natale G., Miele E., Desole M. S. J.Neurochem. 1999; 73:1155–1163.
(38). Zhang L., Dawson V. L., Dawson T. M.Pharmacol. Ther. 2006; 109:33–41.
(39). Padovan-Neto F. E., Echeverry M. B., Tumas V., Del-Bel E. A.Neuroscience. 2009; 159:927–935.
(40). Nicklas W. J., Vyas I., Heikkila R. E.Life Sci. 1985; 36:2503–2508.
(41). Yacoubian T. A., Standaert D. G.Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2009; 1792:676–687.
(42). Cai T. S., Zhang S. F., Wang M. C.Chin. J. Clin. Rehabil. 2005; 9:106–107.
(43). Tanner M. A., Bu X., Steimle J. A., Myers P. R.Nitric Oxide. 1999; 3:359–365.
Go to : 
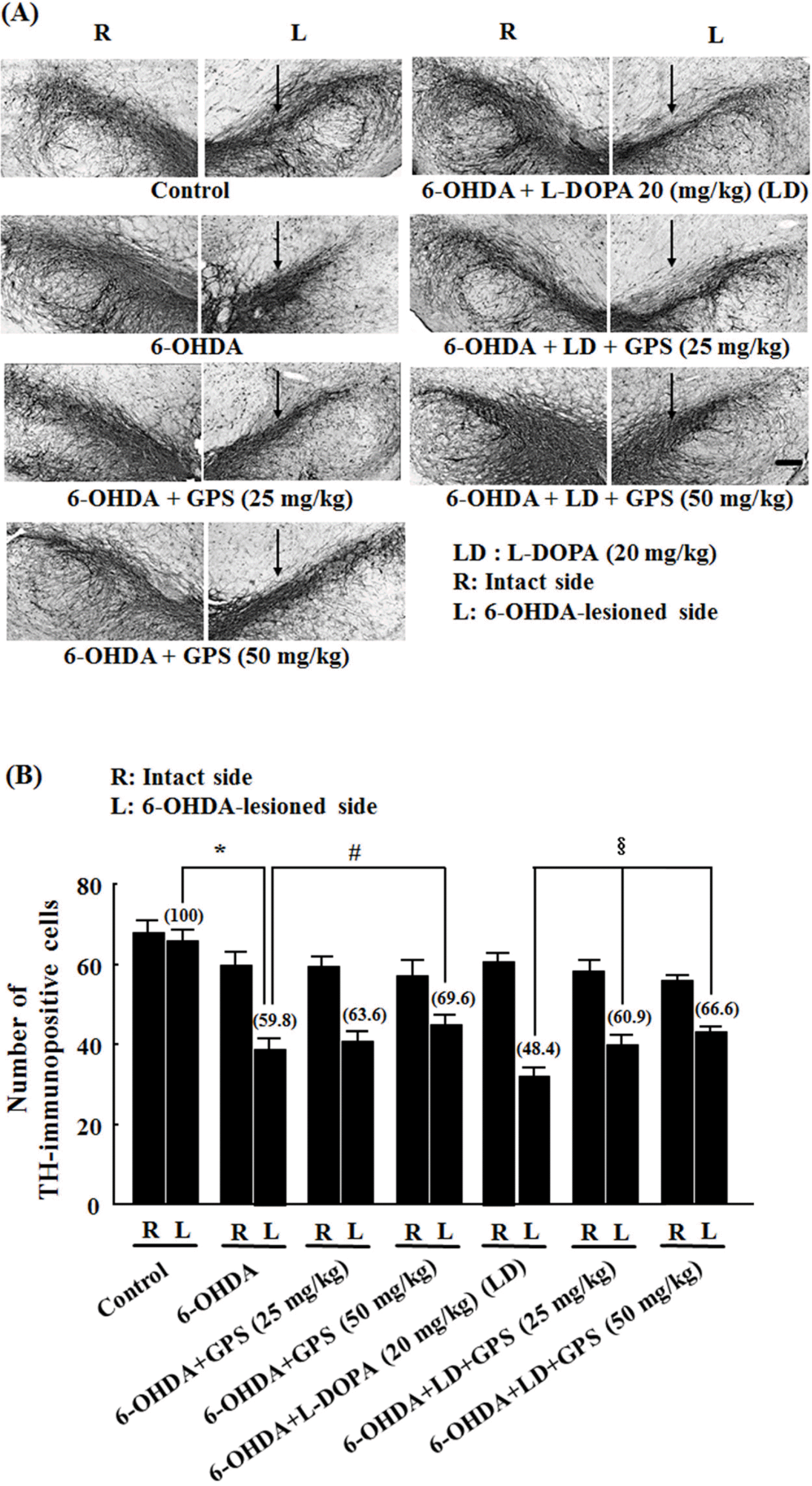 | Fig. 1.Representative photomicrographs of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) immunoreactivity (A) and numbers of surviving TH-immu-nopositive cells (B) in the substantia nigra. Fourteen days after lesions were induced by 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) injection into the substantia nigra, rats were treated for 21 days with gypenosides (GPS) and/or a combination of L-DOPA (LD) and benserazide. (A) Arrows indicate 6-OHDA-lesioned areas. Scale bar = 100 µm. (B) Numbers of TH-immunopositive cells on the lesioned side (L) were analyzed as a percentage of the intact side (R). Results are presented as mean ± S.E.M.; n = 8 – 10 animals per group.∗P <0.05 compared with control group;#P <0.05 compared with 6-OHDA-lesioned group; §P < 0.05 compared with 6-OHDA-lesioned group treated with L-DOPA alone. |
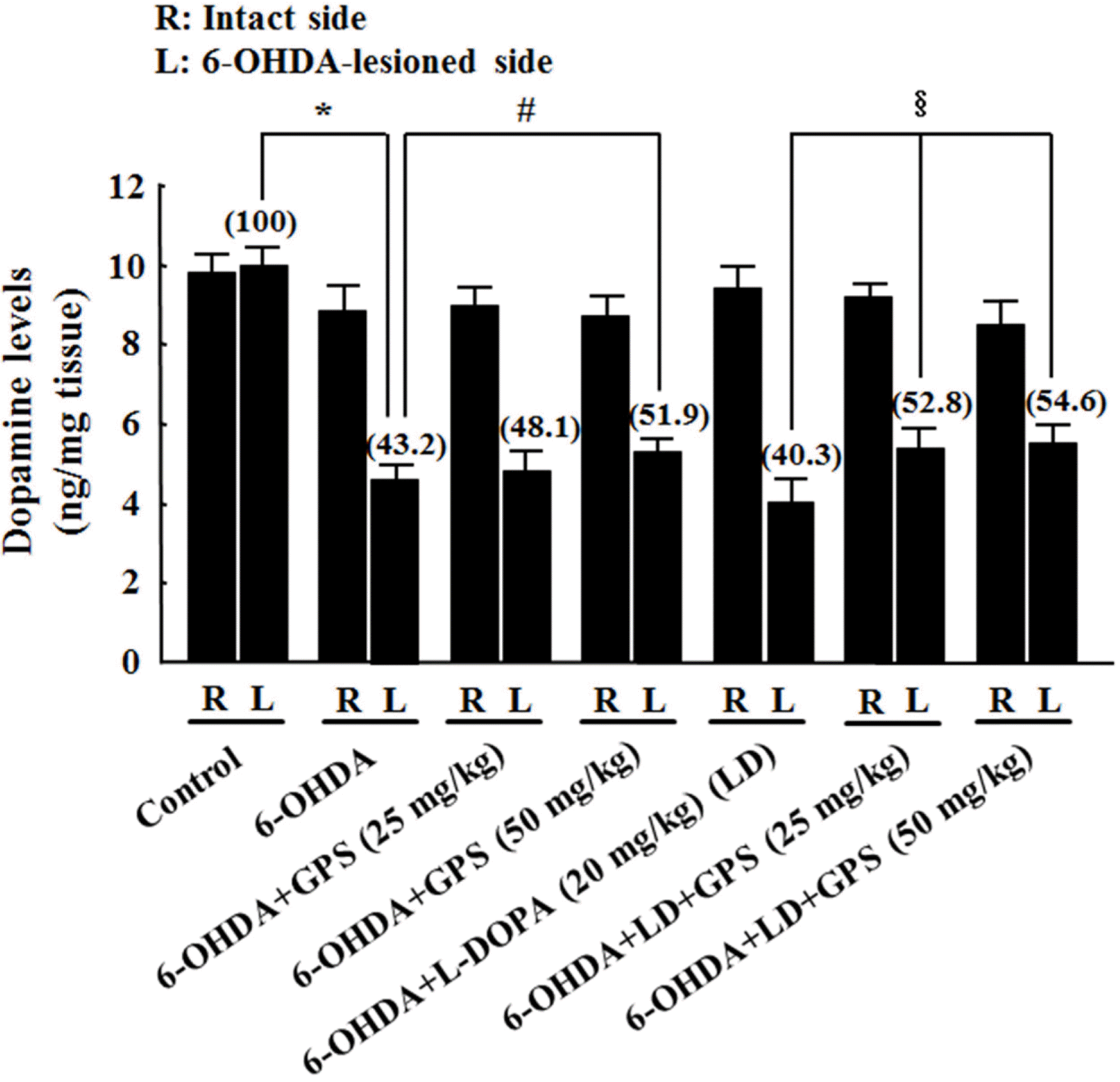 | Fig. 2.Effects of GPS on striatal dopamine levels on the intact (R) and 6-OHDA-lesioned (L) sides. Following 6-OHDA lesion and L-DOPA and/or GPS treatment, levels of dopamine in the striatum were determined using HPLC. Numbers in parentheses represent dopamine levels expressed as percentages of the control group (L). Results are presented as mean ± S.E.M.; n = 8 – 10 animals per group.∗P < 0.05 compared with control group;#P <0.05 compared with 6-OHDA-lesioned group; §P <0.05 compared with 6-OHDA-lesioned group treated with L-DOPA alone. |
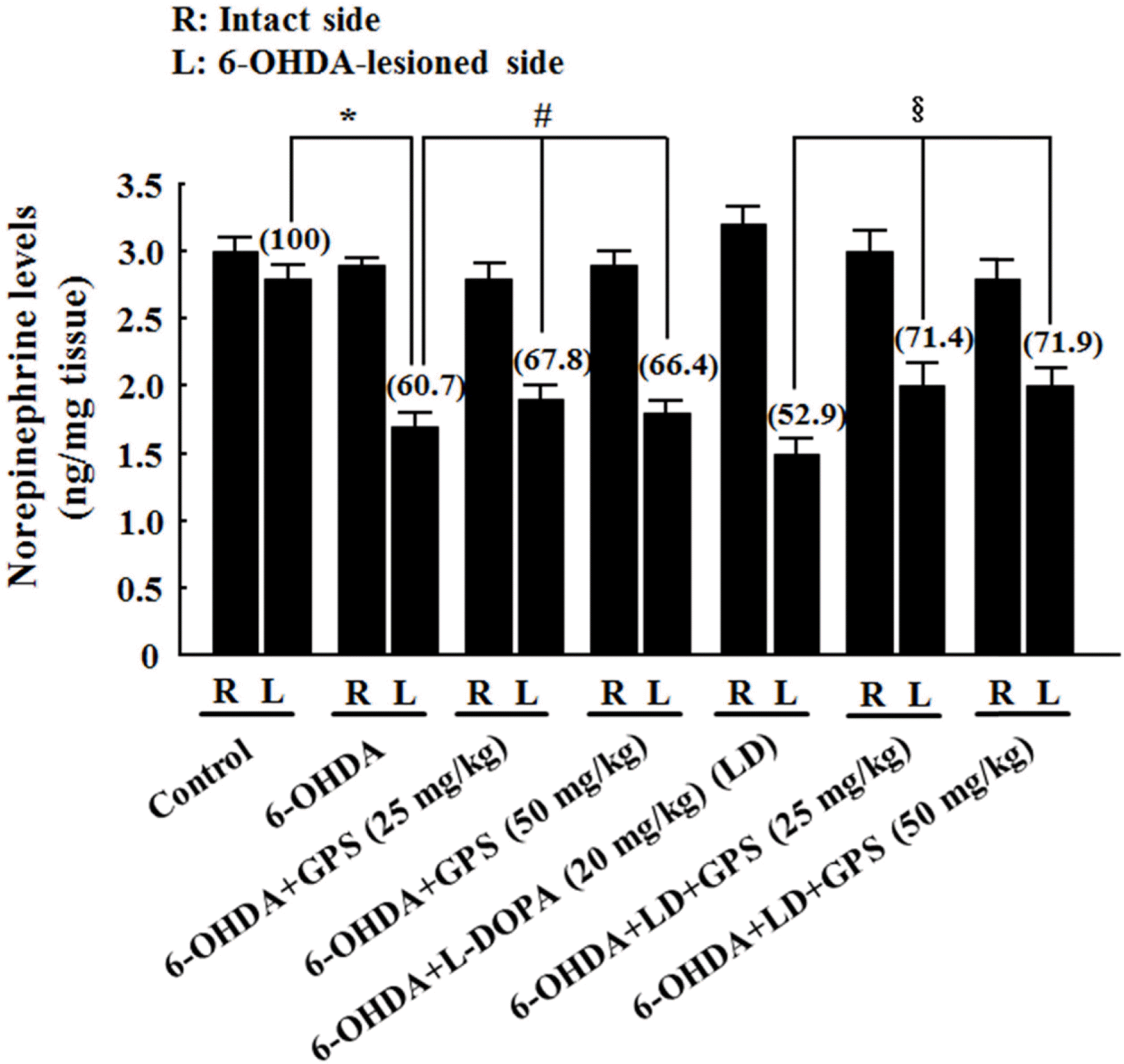 | Fig. 3.Effects of GPS on striatal norepinephrine levels on the intact (R) and 6-OHDA-lesioned (L) sides. Numbers in parentheses represent norepinephrine levels expressed as percentages of the control group (L). Results are presented as mean ± S.E.M.; n =8–10 animals per group.∗P <0.05 compared with control group;#P < 0.05 compared with 6-OHDA-lesioned group;§P < 0.05 compared with 6-OHDA-lesioned group treated with L-DOPA alone. |
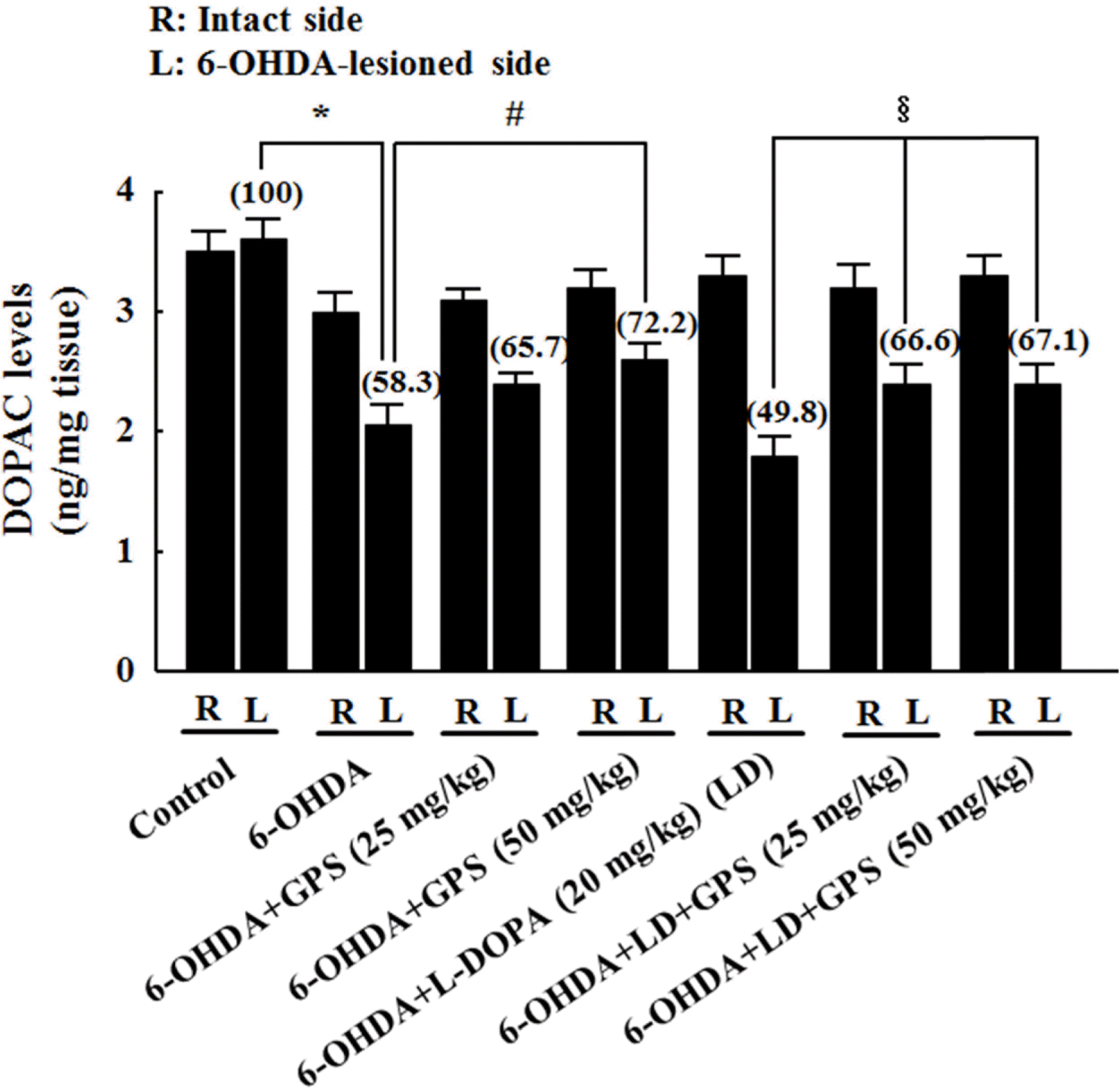 | Fig. 4.Effects of GPS on striatal 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC) levels on the intact (R) and 6-OHDA-lesioned (L) sides. Numbers in parentheses represent DOPAC levels expressed as percentages of the control group (L). Results are presented as mean ± S.E.M.; n=8–10 animals per group.∗P <0.05 compared with control group;#P < 0.05 compared with 6-OHDA-lesioned group;§P < 0.05 compared with 6-OHDA-lesioned group treated with L-DOPA alone. |
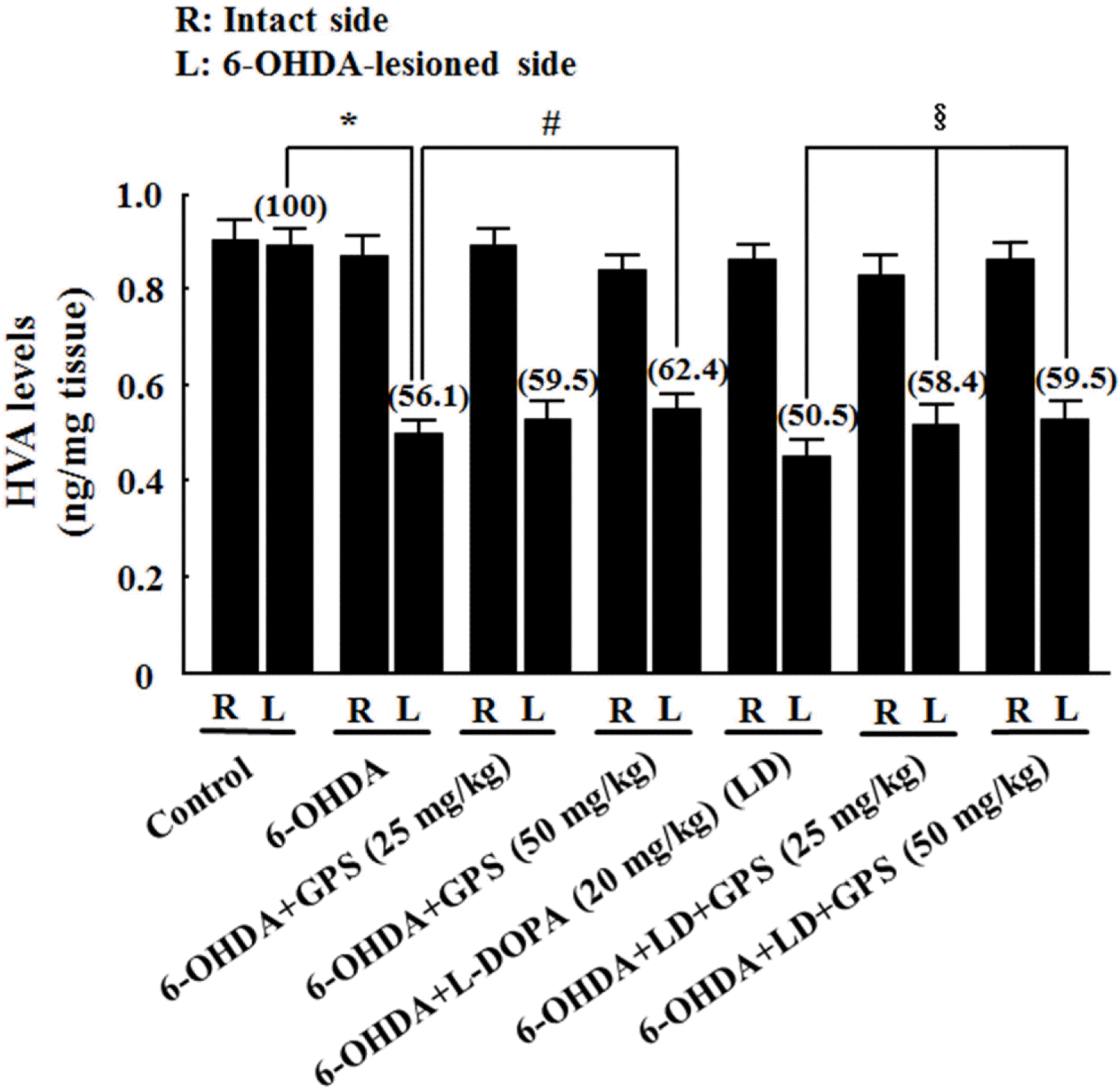 | Fig. 5.Effects of GPS on striatal homovanillic acid (HVA) levels on the intact (R) and 6-OHDA-lesioned (L) sides. Numbers in parentheses represent HVA levels expressed as percentages of the control group (L). Results are presented as mean ± S.E.M.; n=8–10 animals per group.∗P < 0.05 compared with control group; #P < 0.05 compared with 6-OHDA-lesioned group; §P < 0.05 compared with 6-OHDA-lesioned group treated with L-DOPA alone. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download