Abstract
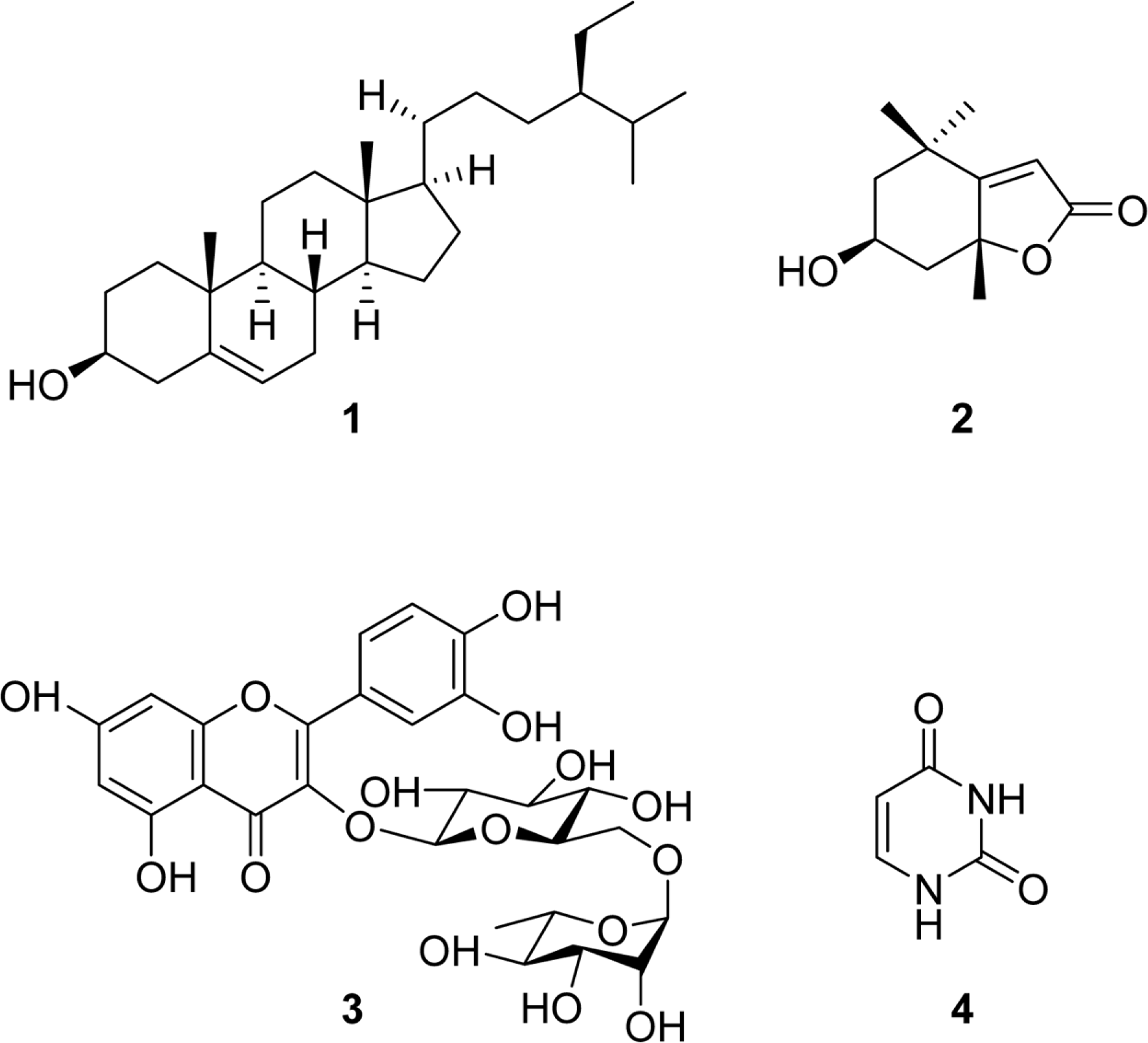
Phytochemicals were isolated from leaves of the fiber crop, ramie (Boehmeria nivea, Bn), using open column chromatography and medium pressure liquid chromatography. Their structures were identified as β-sitosterol, (−)-loliolide, rutin, and pyrimidinedione by MS,1 H-, and13 C-NMR spectroscopic analysis. Among them, (−)-loliolide was isolated for the first time from B. nivea. A content analysis of (−)-loliolide in B. nivea collected from different regions and harvest times was conducted by HPLC. The highest content of (−)-loliolide was found in Bn-23 harvested in September. These results will be helpful to use the plant which harvest in September as a high content phytochemical additive in food, health supplements, and medicinal products.
REFERENCES
(1). Kim S. I., An M. J., Han Y. S., Pyeun J. H. J.Korean Soc. Food Sci Nutr. 1993; 22:603–613.
(2). Liu Z. T., Yang Y., Zhang L., Sun P., Liu Z. W., Lu J., Xiong H., Peng Y., Tang S.Carbohyd. Polym. 2008; 71:18–25.
(3). Kirby R. H.Vegetable fibres: World Crops Books. Leonard Hill;London: 1963. p. 464.
(4). Jarman C. G., Canning A. J., Mykoluk S.Trop. Sci. 1978; 20:91–116.
(5). Lu Y., Weng L., Cao X.Carbohyd. Polym. 2006; 63:198–204.
(6). Xu Q. M., Liu Y. L., Li X. R., Li X., Yang S. L.Nat. Prod. Res. 2011; 25:640–647.
(7). Lin C. C., Yen M. H., Lo T. S., Lin J. M. J.Ethnopharmacol. 1998; 60:9–17.
(8). Kim J. K., Lee H. D., Kim N. H., Choi J. U., Park C. B., Bang J. K. Kor. J.Intl. Agri. 2000; 12:192–196.
(9). Cai X. F., Jin X., Lee D., Yang Y. T., Lee K., Hong Y. S., Lee J. H., Lee J. J. J.Nat. Prod. 2006; 69:1095–1097.
(10). Oyarzu´n M. L., Garbarino J. A., Gambaro V., Guilhem J., Pascard C.Phytochemistry. 1987; 26:221–223.
(11). Liu C., Zou K., Guo Z., Zhao Y., Cheng F., Zhang H.Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2010; 35:1432–1434.
(12). Nho J. W., Hwang I. G., Kim H. Y., Lee Y. R., Woo K. S., Hwang B. Y., Chang S. J., Lee J. S., Jeong H. S.Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2010; 19:383–390.
(13). Chaturvedula V. S. P., Prakash I.Int. Curr. Pharm. J. 2012; 1:239–242.
(14). Jirge S., Tatke P., Gabhe S. Y.IJRAP. 2010; 1:616–623. 1974.
(15). Mori K.Tetrahedron. 1974; 30:1065–1072.
(16). Kimura J., Maki N. J.Nat. Prod. 2002; 65:57–58.
(17). Xian Q., Chen H., Liu H., Zou H., Yin D.Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2006; 13:233–237.
(18). Taylor H. F., Burden R. S.Phytochemistry. 1970; 9:2217–2223.
(19). Ragasa C. Y., De Luna R. D., Hofilena J. G.Nat. Prod. Res. 2005; 19:305–309.
(20). Yu Y. B., Lee J. H., Choi J. S., Ok K. D., Park J. C. Kor. J.Pharmacogn. 1996; 27:219–223.
(21). Middleton E. Jr., Kandaswami C., Theoharides T. C.Pharmacol. Rev. 2000; 52:673–751.
(22). Grinberg L. N., Rachmilewitz E. A., Newmark H.Biochem Pharmacol. 1994; 48:643–649.
(23). Kim Y. S., Lee I. K., Seok S. J., Yun B. S.Mycobiol. 2008; 36:110–113.
(24). Buckheit R. W. Jr., Watson K., Fliakas-Boltz V., Russell J., Loftus T. L., Osterling M. C., Turpin J. A., Pallansch L. A., White E. L., Lee J. W., Lee S. H., Oh J. W., Kwon H. S., Chung S. G., Cho E. H.Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001; 45:393–400.
(25). Karioti A., Skaltsa H., Lazari D., Sokovic M., Garcia B., Harvala C. Z.Naturforsch. C. 2002; 57:75–80.
Fig. 2.
HPLC chromatograms of (−)-loliolide (A) and the MeOH extract of Bn-23 (B) and −90 (C) collected in September.
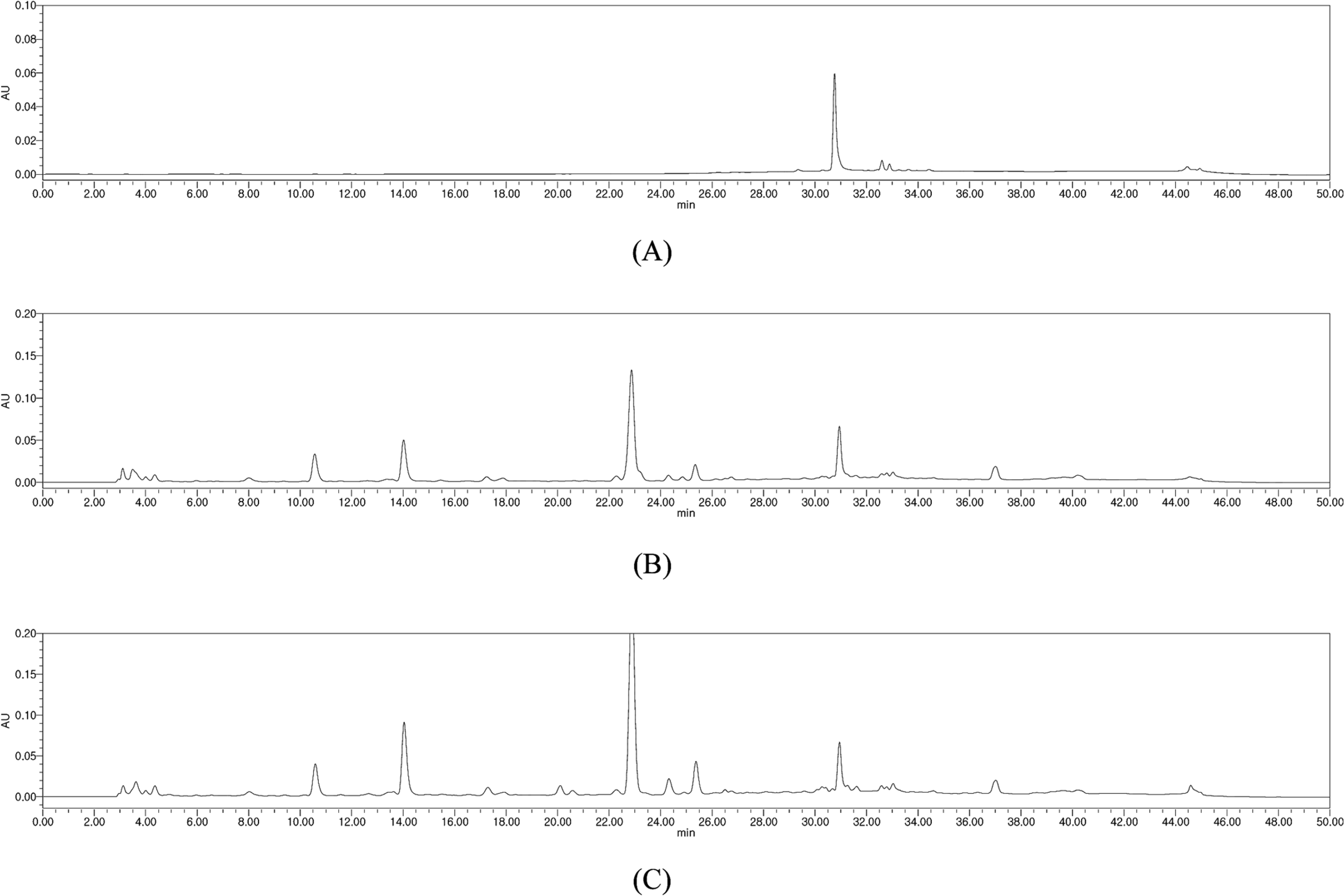
Table 1.
Collection areas for Bn
Table 2.
LOD and LOQ of (−)-loliolide
| Compound | Calibration equationa | r2b | Linear range (mg/mL) | LOD (mg/mL) | LOQ (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (−)-loliolide | Y = 5557.1X − 103.46 | 0.9999 | 0.005–5 | 0.055 | 0.142 |
Table 3.
The content of (−)-loliolide in MeOH extracts of Bn




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download