Abstract
Chemical investigation on a colonial marine tunicate, Didemnum sp. led to the isolation of a series of indole alkaloids including a new (1) and two known metabolites (2-3). Based on the spectroscopic analysis including 1D and 2D NMR along with MS spectra, the structure of 1 (16-epi-18-acetyl herdmanine D) was elucidated as a new amino acid derivative. The absolute configuration of 1 was determined by comparison of specific rotation with the known compound. The structures of compounds 2 and 3 were also identified as bromoindole containing compounds N-(6-bromo-1H-indole-3-carbonyl)-L-arginine and (6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl) oxoacetamide, respectively, based on 1H and 13C NMR data, MS data and specific rotation value. Their pharmacological potentials as antibacterial agents and FXR antagonists were investigated, but no significant activity was found. However, the structural similarity of compound 1 to compound 4 suggested the anti-inflammatory potential of compound 1.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
(1). Menna M., Aiello A.The Chemistry of Marine Tunicates. Fattorusso E., Gerwick W. H., Taglialatela-Scafati O., editorsSpringer;Germany: 2012. p. 295–385.
(2). Andersen R. J., Faulkner D. J., He C. H., Van Duyne G. D., Clardy J. J.Am. Chem. Soc. 1985; 107:5492–5495.
(3). Ham J., Kang H.Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2002; 23:163–166.
(4). Carroll A. R., Bowden B. F., Coll J. C.Aust. J. Chem. 1993; 46:489–501.
(5). Kang H., Fenical W. J.Org. Chem. 1997; 62:3254–3262.
(6). Chou T. C.WO Patent, 2006026496. 2006.
(7). Kobayash J., Cheng J., Nakamura H., Ohizumi Y., Hirata Y., Sasaki T., Ohta T., Nozoe S.Tetrahedron Lett. 1988; 29:1177–1180.
(8). Oku N., Matsunaga S., Fusetani N. J.Am. Chem. Soc. 2003; 125:2044–2045.
(9). Fahy E., Potts B. C. M., Faulkner D. J., Smith K. J.Nat. Prod. 1991; 54:564–569.
(10). Schumacher R. W., Davidson B. S.Tetrahedron. 1995; 51:10125–10130.
(11). Britton R., de Oliveira J. H., Andersen R. J., Berlinck R. G. J.Nat. Prod. 2001; 64:254–255.
(12). Segraves N. L., Robinson S. J., Garcia D., Said S. A., Fu X., Schmitz F. J., Pietraszkiewicz H., Valeriote F. A., Crews P. J.Nat. Prod. 2004; 67:783–792.
(13). Finlayson R., Pearce A. N., Page M. J., Kaiser M., Bourguet-Kondracki M. L., Harper J. L., Webb V. L., Copp B. R. J.Nat. Prod. 2011; 74:888–892.
(14). Li J. L., Han S. C., Yoo E. S., Shin S., Hong J., Cui Z., Li H., Jung J. H. J.Nat. Prod. 2011; 74:1792–1797.
(15). Shin J., Seo Y., Cho K. W., Rho J. R., Sim C. J. J.Nat. Prod. 1999; 62:647–649.
(16). Bao B., Sun Q., Yao X., Hong J., Lee C. O., Cho H. Y., Jung J. H. J.Nat. Prod. 2007; 70:2–8.
(17). Garcia A., Vazquez M. J., Quinoa E., Riguera R., Debitus C. J.Nat. Prod. 1996; 59:782–785.
(18). Bao B., Zhang P., Lee Y., Hong J., Lee C. O., Jung J. H.Mar. Drugs. 2007; 5:31–39.
Go to : 
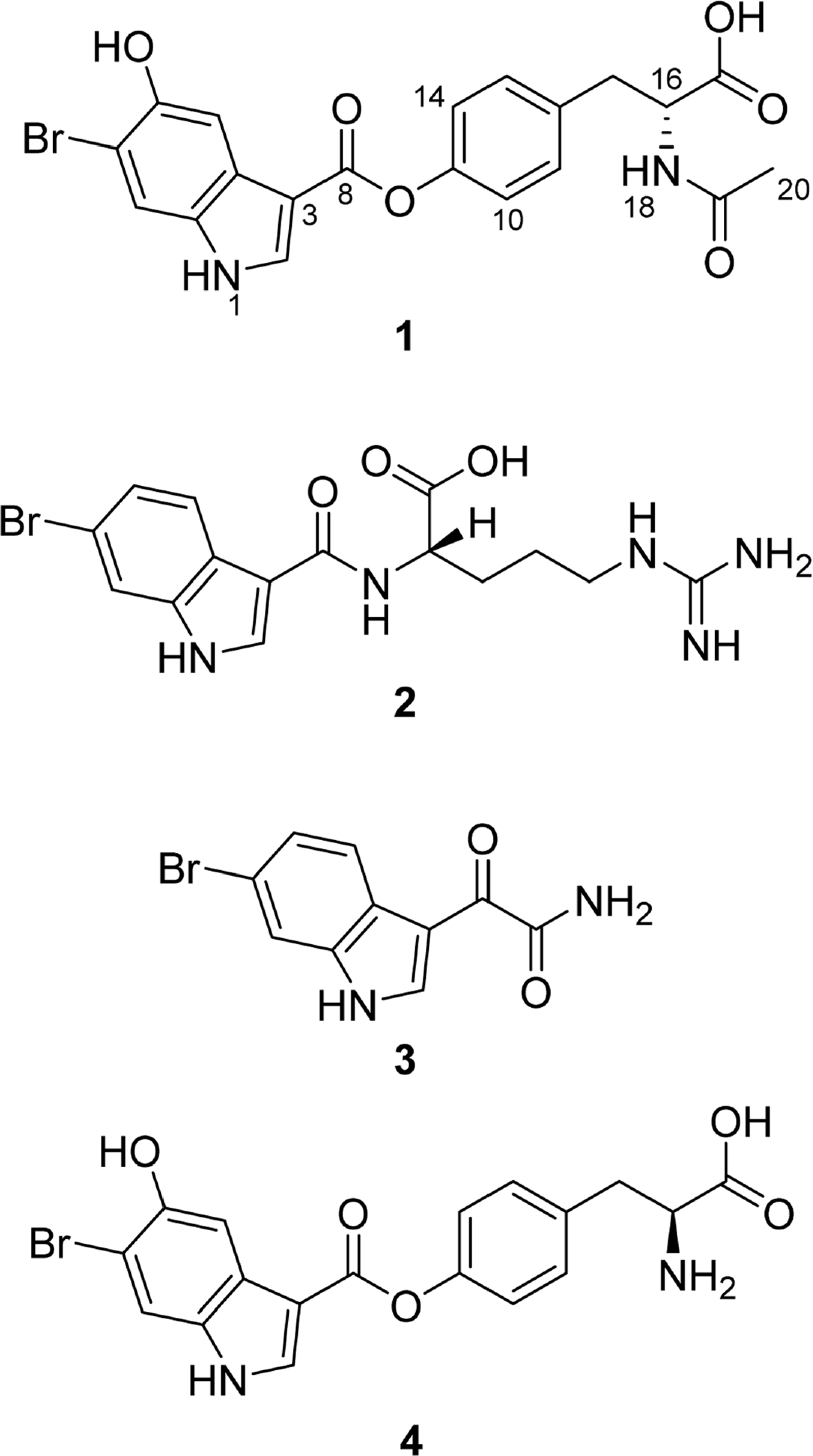 | Fig. 1.Structures of compounds 1 - 3 from a marine colonial tunicate Didemnum sp. and herdmanine D (4). |
Table 1.
NMR data of compound 1 in DMSO-d6 at 500 MHz (1H) and 125 MHz (13C)




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download