Abstract
Purpose:
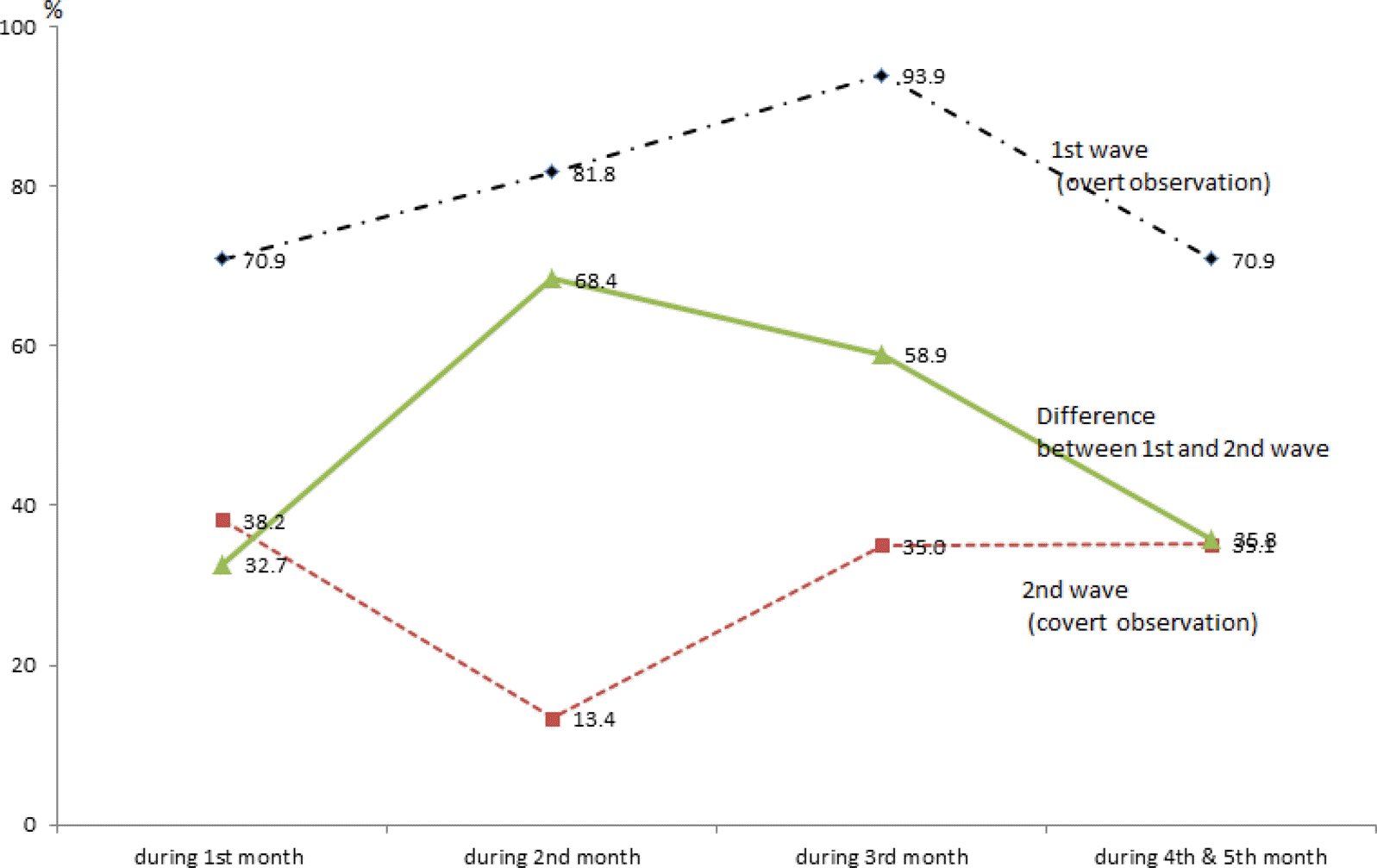
This observational study was aimed to determine the influence of the Hawthorne effect on the adherence to hand hygiene (HH) among healthcare workers (HCWs) in South Korea. Methods: HCWs were monitored in 2 periods regarding adherence to HH when there were indications for HH. In first period, HCWs recognized that their behavior of hand hygiene being observed (overt observation), and did not recognize in second period (covert observation). Results: The overall difference in HH rate between two periods was 45.0% point (77.8% vs 32.8%). There were significant differences between profession but in nurse aids. The differences in HH rate between two periods were 46.1% point in nurses, 29.9% point in physicians, 64.0% in radiologists, 62.5% point in laboratory technicians, 36.4% point in physio-therapist, and 1.0% point in nurse aids. The Hawthorne effect on the adherence to HH lasted more than 3 months. Conclusion: The Hawthorne effect markedly influence on the adherence to HH regardless of profession except nurse aids. Therefore, Hawthorne effect can be useful tool to improve and sustain the adherence to HH among HCWs in South Korea.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1.Allegranzi B., Pittet D. Role of hand hygiene in healthcare-associated infection prevention. J Hosp Infect. 2009 Aug. 73 (4): 305-15.http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jhin.2009.04.019.

2.World Health Organization. WHO guidelines on hand hygiene in health care: First Global Patient Safety Challenge Clean Care Is Safer Care. Geneva: World Health Organization;2009. Available from:. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK144013/.
3.Pittet D., Allegranzi B., Sax H., Dharan S., Pessoa-Silva CL., Donaldson L, et al. Evidence-based model for hand transmission during patient care and the role of improved practices. Lancet Infect Dis. 2006. 6(10):641–52. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(06)70600-4.

4.Cromer AL., Latham SC., Bryant KG., Hutsell S., Gansauer L., Bendyk HA, et al. Monitoring and feedback of hand hygiene compliance and the impact on facility-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Am J Infect Control. 2008. 36:672–7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajic.2007.12.006.

5.Ward MA., Schweizer ML., Polgreen PM., Gupta K., Reisinger HS., Perencevich EN. Automated and electronically assisted hand hygiene monitoring systems: a systematic review. Am J Infect Control. 2014. 42:472–8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajic.2014.01.002.

6.Kohli E., Ptak J., Smith R., Taylor E., Talbot EA., Kirkland KB. Variability in the Hawthorne effect with regard to hand hygiene performance in high- and low-performing inpatient care units. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2009. 30(3):222–5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1086/595692.

7.Eckmanns T., Bessert J., Behnke M., Gastmeier P., Ruden H. Compliance with antiseptic hand rub use in intensive care units: the Hawthorne effect. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2006. 27(9):931–4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1086/507294.

8.Gilboy N., Howard PK. Compliance with hand hygiene guidelines. Adv Emerg Nurs J. 2008. 30(3):193–200. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.TME.0000334370.14034.fc.

9.Buchanan D., Huczynski A. Organizational behavior. 3rd ed.London: Prentice Hall;1997.
10.Hwang SM., Lee RH. Personality as types of self perception of others' evaluation: how Koreans perceive personality. Scientific Study of Subjectivity: Q Methodology and Theory. 2010. 20:121–43.
11.Arenas MD., Sánchez-Payá J., Barril G., García-Valdecasas J., Gorriz JL., Soriano A, et al. A multicentric survey of the practice of hand hygiene in haemodialysis units: factors affecting compliance. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2005. 20(6):1164–71. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfh759.

12.Harbarth S., Pittet D., Grady L., Zawacki A., Potter-Bynoe G., Samore MH, et al. Interventional study to evaluate the impact of an alcohol-based hand gel in improving hand hygiene compliance. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2002. 21(6):489–95.

13.Feil PH., Grauer JS., Gadbury-Amyot CC., Kula K., McCunniff MD. Intentional use of the Hawthorne effect to improve oral hygiene compliance in orthodontic patients. J Dent Educ. 2002. 66(10):1129–35.

Go to : 
Table 1.
The Differences of Hand Hygiene Indications by Observation Method and Profession
Table 2.
The Differences of Hand Hygiene Rate by Observation Method and Profession




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download