Abstract
Purpose:
There are relatively few results from studies on nodular Hashimoto's thyroiditis. In addition, some Hashimoto's thyroiditis patients present with irregular symptoms, making the distinction from malignant thyroid nodule difficult. Therefore, we performed analyses on ultrasonographic findings of nodular Hashimoto's thyroiditis.
Methods:
A retrospective follow-up study was performed on 76 patients (88 nodules) diagnosed with Hashimoto's thyroiditis after undergoing fine needle aspiration biopsy from January 2009 to December 2010. A frequency analysis was performed to investigate the most common ultrasonographic findings of nodular Hashimoto's thyroiditis. In addition, patients were divided into two groups based on the presence or absence of extensive Hashimoto's thyroiditis on the parenchyma, and ultrasonographic findings were compared and analyzed for nodules in each group.
Results:
The study was performed on 76 patients and 88 nodules. The majority of nodular Hashimoto's thyroiditis were found to be solid on ultrasonography, and echogenicity was mostly hypoechoic, with prominent hypoechoic findings being more common. Most nodules did not have a rim surrounding the margins, and absence of accompanying calcification was also noted. The comparison and analysis of ultrasonographic findings of two patient groups that were divided based on the presence or absence of Hashimoto's thyroiditis across the parenchyma, revealed no significant difference.
Conclusion:
Most nodular Hashimoto's thyroiditis cases do not present with calcification or rims and frequently present as solid and hypoechoic. It can be concluded that such findings are consistent regardless of whether there is accompanying extensive changes at the thyroid parenchyma associated with Hashimoto's thyroiditis.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
2.Lee MJ., Lee BK., Youn HJ., Jung SH. Is Hashimoto's thyroiditis associated with the prognostic factors of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Korean J Endocrine Surg. 2010. 10:29–33.

3.Lim CR., Bae HY., Cho HJ., Kim KC. The clinical feature of patients with thyroid nodule combined with Hashimoto's thyroiditis. J Korean Surg Soc. 2008. 75:171–6.
4.Yeh HC., Futterweit W., Gilbert P. Micronodulation: ultrasonographic sign of Hashimoto thyroiditis. J Ultrasound Med. 1996. 15:813–9.

5.Simeone JF., Daniels GH., Mueller PR., Maloof F., van-Sonnenberg E., Hall DA, et al. High-resolution real-time sonography of the thyroid. Radiology. 1982. 145:431–5.

6.Pedersen OM., Aardal NP., Larssen TB., Varhaug JE., Myking O., Vik-Mo H. The value of ultrasonography in predicting autoimmune thyroid disease. Thyroid. 2000. 10:251–9.

7.Butch RJ., Simeone JF., Mueller PR. Thyroid and parathyroid ultrasonography. Radiol Clin North Am. 1985. 23:57–71.
8.Anderson L., Middleton WD., Teefey SA., Reading CC., Langer JE., Desser T, et al. Hashimoto thyroiditis: Part 1, sonographic analysis of the nodular form of Hashimoto thyroiditis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010. 195:208–15.

9.Langer JE., Khan A., Nisenbaum HL., Baloch ZW., Horii SC., Coleman BG, et al. Sonographic appearance of focal thyroiditis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001. 176:751–4.

10.Weetman AP., McGregor AM. Autoimmune thyroid disease: further developments in our understanding. Endocr Rev. 1994. 15:788–830.

12.Marcocci C., Vitti P., Cetani F., Catalano F., Concetti R., Pinchera A. Thyroid ultrasonography helps to identify patients with diffuse lymphocytic thyroiditis who are prone to develop hypothyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991. 72:209–13.

13.Friedman M., Shimaoka K., Rao U., Tsukada Y., Gavigan M., Tamura K. Diagnosis of chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis (nodular presentation) by needle aspiration. Acta Cytol. 1981. 25:513–22.
14.Jayaram G., Marwaha RK., Gupta RK., Sharma SK. Cytomor-phologic aspects of thyroiditis. A study of 51 cases with functional, immunologic and ultrasonographic data. Acta Cytol. 1987. 31:687–93.
Go to : 
Table 1.
Sonographic features of nodular Hashimoto thyroiditis
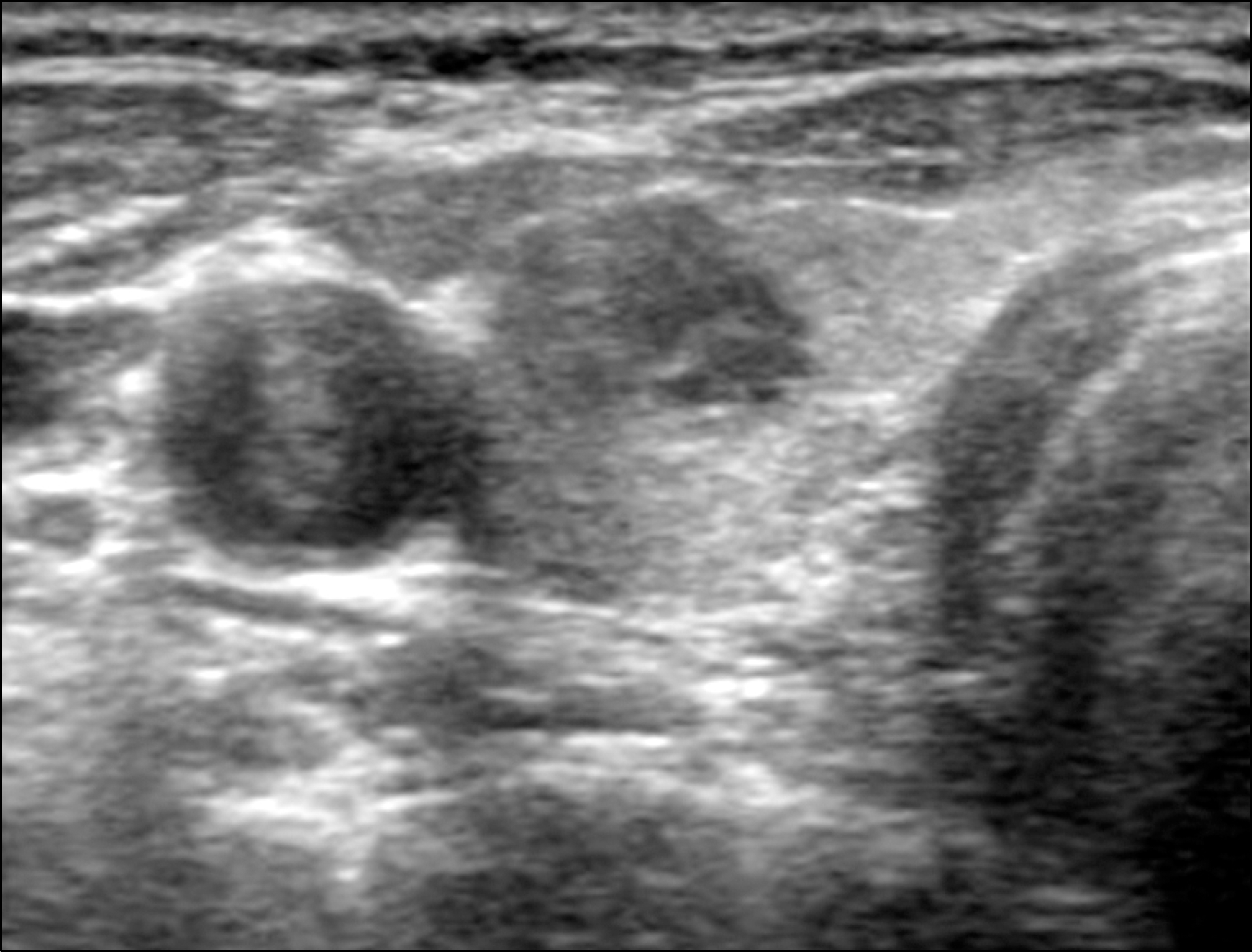 | Fig. 155 year old woman with nodular Hashimoto thyroiditis. Transverse scan shows well defined solid hypoechoic nodule. Background parenchyma is homogenous. |
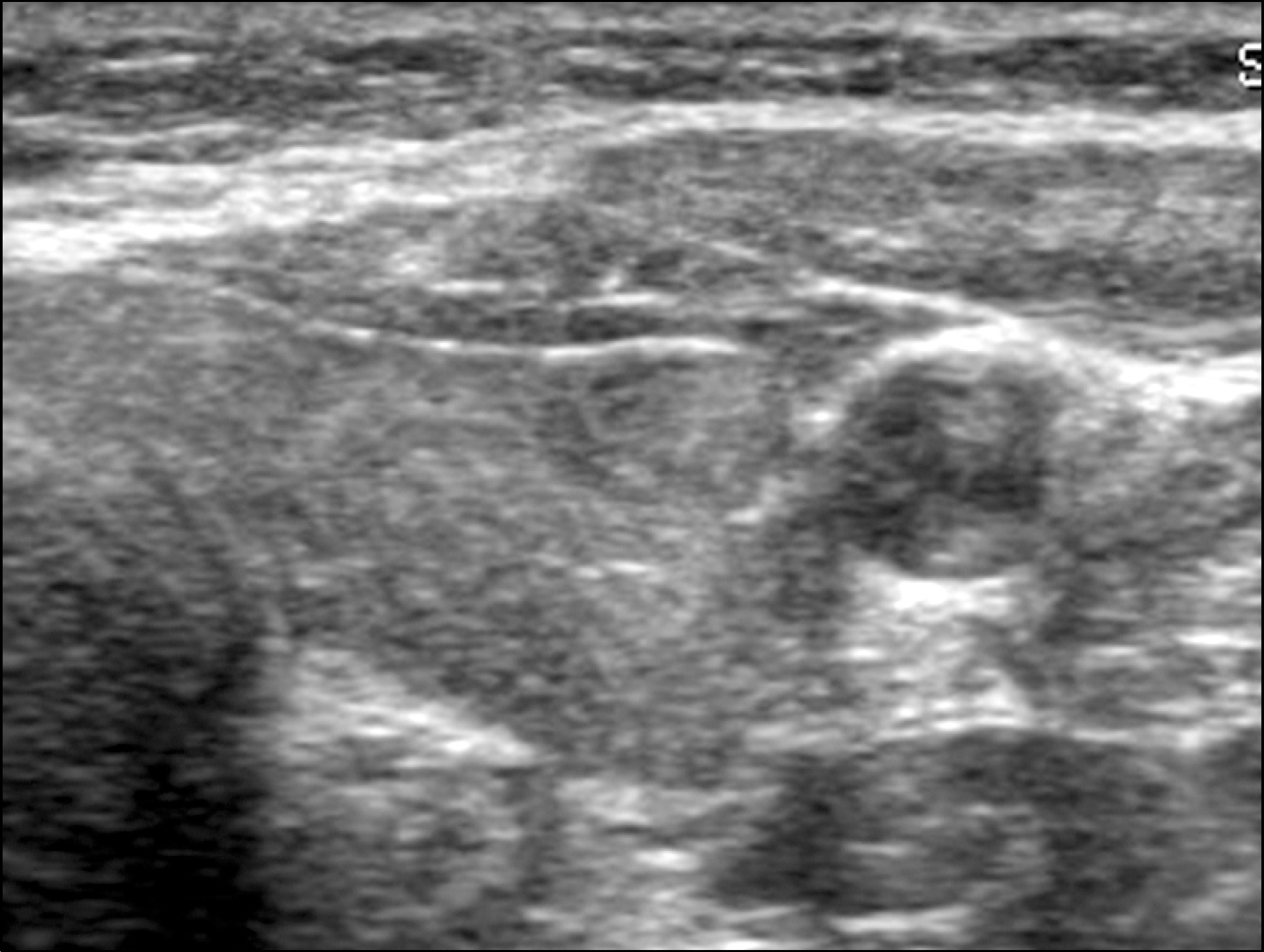 | Fig. 252 year old women with nodular Hashimoto thyroiditis. Transverse scan show well defined oval shaped solid hypoechoic nodule. Background parenchyma is heterogenous and coarse echotexture. |
Table 2.
Comparison of sonographic features of nodular Hashimoto thyroiditis with and without diffuse background parenchymal Hashimoto thyroiditis




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download