Abstract
Purpose:
Insulinoma is a rare disease for which early diagnosis followed by proper surgical management provides a chance for cure. Analyses of clinicopathological features of patients can help optimize the surgical approach in the treatment of insulinoma.
Methods:
The records of 13 patients (seven male, six female mean age 44.3 years; age range 17∼62 years) who were diagnosed clinically and pathologically with insulinoma and who underwent surgery between March 1997 and April 2007 at the Department of Surgery, Seoul National University Hospital. Hospital in English please were retrospectively examined.
Results:
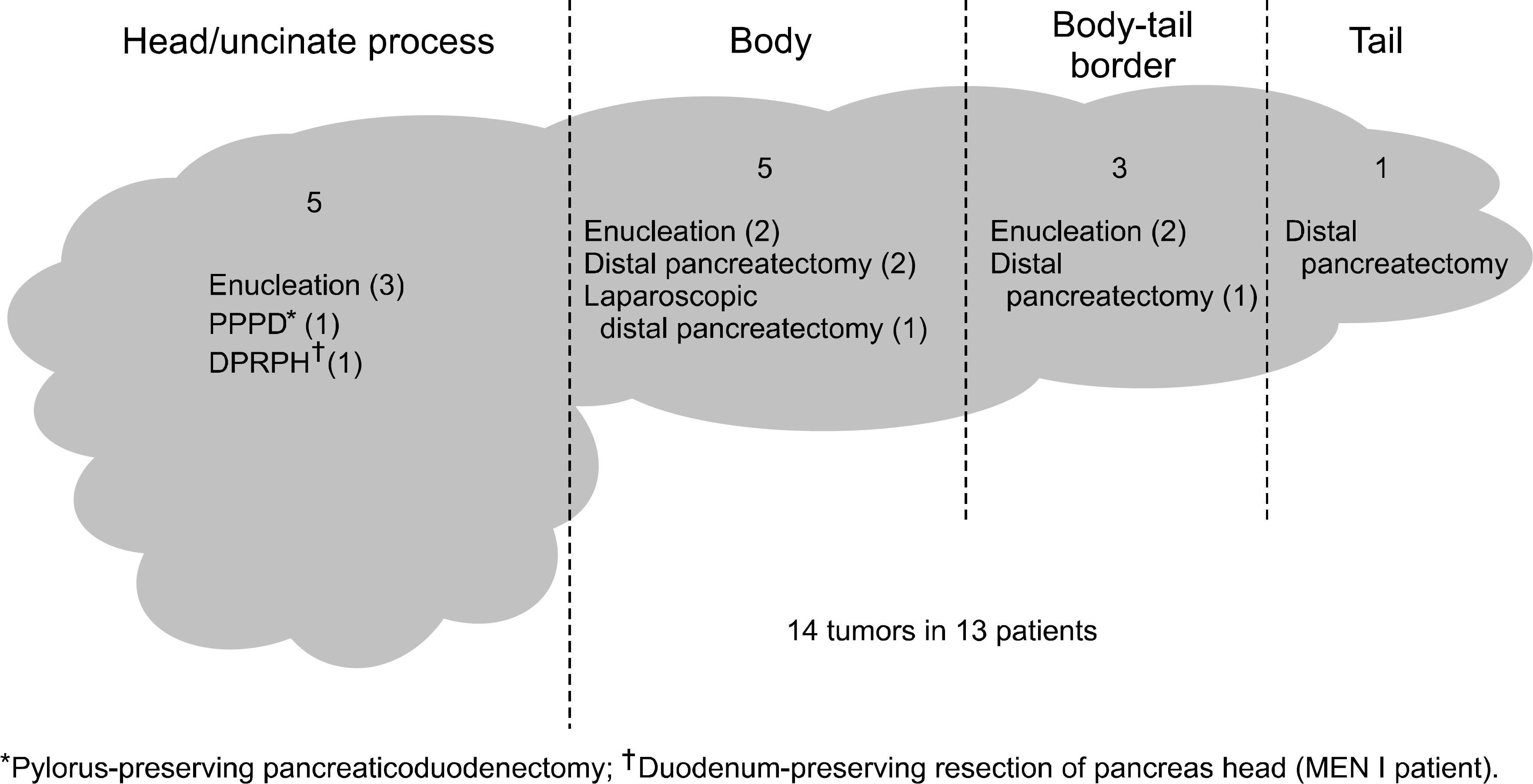
All patients had findings compatible with Whipple's triad. Mean fasting blood sugar was 40.5 mg/dl, serum insulin level was 33.5μU/ml, and insulin-to-glucose ratio was 0.6. A prolonged starvation test was performed on six patients. Tumors were localized in 10 patients with a computed tomography (CT) scan and in three patients with CT angiography. Five tumors were located in the pancreas head and uncinate process, five in the body, and four at the body-tail border and tail. Patients underwent resection of tumorby enucleation, distal pancreatectomy, pylorus-preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy, laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy, and duodenum-preserving resection of pancreas head. Four immediate postoperative complications (fluid collection, pancreatic fistula, delayed gastric emptying) occurred. No symptoms or recurrences were apparent during the median 15 month follow-up.
Conclusion:
Insulinoma is difficult to diagnose correctly without a prolonged duration of symptoms. Localization of insulinoma can be aided by a CT scan and/or CT angiography. Less aggressive operative procedures such as sim-ple enucleation might be a sufficient and feasible procedure for curative resection of benign insulinomas. (Korean J Endocrine Surg 2010;10:99-105)
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1.Abboud B., Boujaoude J. Occult sporadic insulinoma: localization and surgical strategy. World J Gastroenterol. 2008. 14:657–65.

3.Leow MK., Loh KC., Kon WY., Wong DE., Tan BS., Soon PC. Clinical utility of selective intra-arterial calcium-stimulated hepatic venous sampling in regionalisation of insulinomas–the Singapore experience. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 2003. 32:86–91.
4.An JY., Moon HJ., Heo JS., Choi SH., Kim YI. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies for Insulinomas of Pancreas. J Korean Surg Soc. 2004. 67:129–34.
5.Chang HJ., Park KC., Lee KU. Insulinoma of the pancreas. J Korean Surg Soc. 1994. 47:256–66.
6.Kim JH Youn YK., Oh SK. Insulinoma. J Korean Surg Soc. 1996. 50:874–83.
7.Lee SH., Kim JY., Choi GH., Kim KS., Choi JS., Lee WJ, et al. Single institutional experiences of insulinoma. J Korean Surg Soc. 2007. 72:128–32.
8.Yoo YK., Chin HM., Kim KW., Lee KH., Lee S., Kim JG, et al. Insulinoma of the pancreas. J Korean Surg Soc. 2003. 64:498–504.
9.Cryer PE. Symptoms of hypoglycemia, thresholds for their occurrence, and hypoglycemia unawareness. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 1999. 28:495–500. v-vi.

11.Ramage JK., Davies AH., Ardill J., Bax N., Caplin M., Grossman A, et al. Guidelines for the management of gastroentero-pancreatic neuroendocrine (including carcinoid) tumours. Gut. 2005. 54(Suppl 4):iv1–16.

12.Aoki T., Sakon M., Ohzato H., Kishimoto S., Oshima S., Yamada T, et al. Evaluation of preoperative and intraoperative arterial stimulation and venous sampling for diagnosis and surgical resection of insulinoma. Surgery. 1999. 126:968–73.

13.Lo CY., Lo CM., Fan ST. Role of laparoscopic ultrasonography in intraoperative localization of pancreatic insulinoma. Surg Endosc. 2000. 14:1131–5.

14.Morita S., Machida H., Kuwatsuru R., Saito N., Suzuki K., Iihara M, et al. Preoperative localization of pancreatic insulinoma by super selective arterial stimulation with venous sampling. Abdom Imaging. 2007. 32:126–8.

15.Fidler JL., Fletcher JG., Reading CC., Andrews JC., Thompson GB., Grant CS, et al. Preoperative detection of pancreatic insulinomas on multiphasic helical CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003. 181:775–80.

16.Gouya H., Vignaux O., Augui J., Dousset B., Palazzo L., Louvel A, et al. CT, endoscopic sonography, and a combined protocol for preoperative evaluation of pancreatic insulinomas. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003. 181:987–92.

17.King AD., Ko GT., Yeung VT., Chow CC., Griffith J., Cockram CS. Dual phase spiral CT in the detection of small insulinomas of the pancreas. Br J Radiol. 1998. 71:20–3.

18.Rappeport ED., Hansen CP., Kjaer A., Knigge U. Multidetector computed tomography and neuroendocrine pancreaticoduodenal tumors. Acta Radiol. 2006. 47:248–56.

19.Hiramoto JS., Feldstein VA., LaBerge JM., Norton JA. Intraoperative ultrasound and preoperative localization detects all occult insulinomas; discussion 1025-6. Arch Surg. 2001. 136:1020–5.
20.Huai JC., Zhang W., Niu HO., Su ZX., McNamara JJ., Machi J. Localization and surgical treatment of pancreatic insuli-nomas guided by intraoperative ultrasound. Am J Surg. 1998. 175:18–21.

21.Kalafat H., Mihmanli I., Saribeyoglu K., Belli A. Intraoperative doppler ultrasound: a reliable diagnostic method in insulinoma. Hepatogastroenterology. 2007. 54:1256–8.
22.Wong M., Isa SH., Zahiah M., Azmi KN. Intraoperative ultrasound with palpation is still superior to intra-arterial calcium stimulation test in localising insulinoma. World J Surg. 2007. 31:586–92.

23.Berends FJ., Cuesta MA., Kazemier G., van Eijck CH., de Herder WW., van Muiswinkel JM, et al. Laparoscopic detection and resection of insulinomas. Surgery. 2000. 128:386–91.

24.Jaroszewski DE., Schlinkert RT., Thompson GB., Schlinkert DK. Laparoscopic localization and resection of insulinomas. Arch Surg. 2004. 139:270–4.

25.Doherty GM., Doppman JL., Shawker TH., Miller DL., Eastman RC., Gorden P, et al. Results of a prospective strategy to diagnose, localize, and resect insulinomas. Surgery. 1991. 110:989–96. discussion 96-7.
26.Soga J., Yakuwa Y., Osaka M. Insulinoma/hypoglycemic syndrome: a statistical evaluation of 1085 reported cases of a Japanese series. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 1998. 17:379–88.
27.Ayav A., Bresler L., Brunaud L., Boissel P. Laparoscopic approach for solitary insulinoma: a multicentre study. Langen-becks Arch Surg. 2005. 390:134–40.

28.Sa Cunha A., Beau C., Rault A., Catargi B., Collet D., Masson B. Laparoscopic versus open approach for solitary insulinoma. Surg Endosc. 2007. 21:103–8.

29.Iihara M., Obara T. Minimally invasive endocrine surgery: laparoscopic resection of insulinomas. Biomed Pharmacother. 2002. 56(Suppl 1):227s–30s.
Go to : 




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download