INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients
Radiologic evaluation
Classification
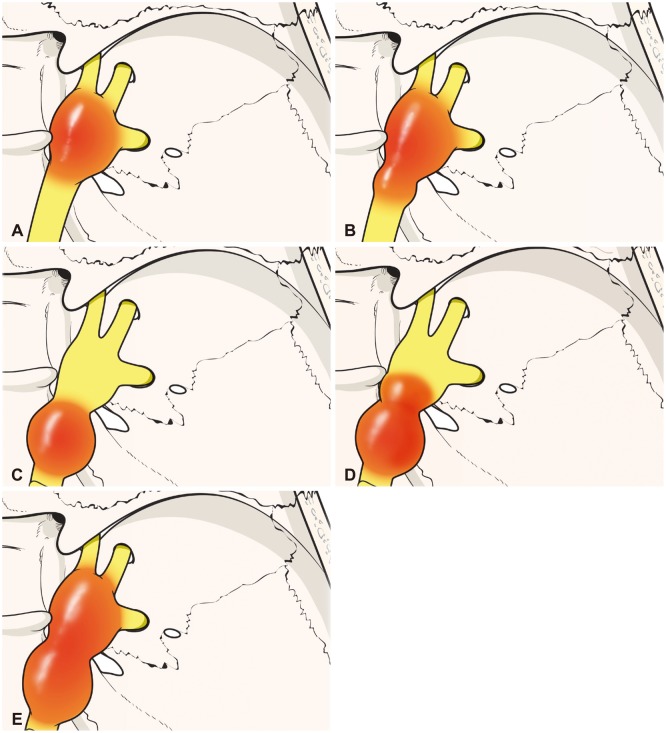 | Fig. 1Classification of trigeminal schwannomas. A: Type M: tumors confined to the middle fossa. B: Type Mp: tumors predominantly located at the middle fossa with posterior fossa extension. C: Type P: tumors confined to the posterior fossa. D: Type Pm: tumors predominantly located at the posterior fossa with middle fossa extension. E: Type MP: tumors involving both middle and posterior fossae. |
RESULTS
Clinical characteristics
Classification and surgical approaches
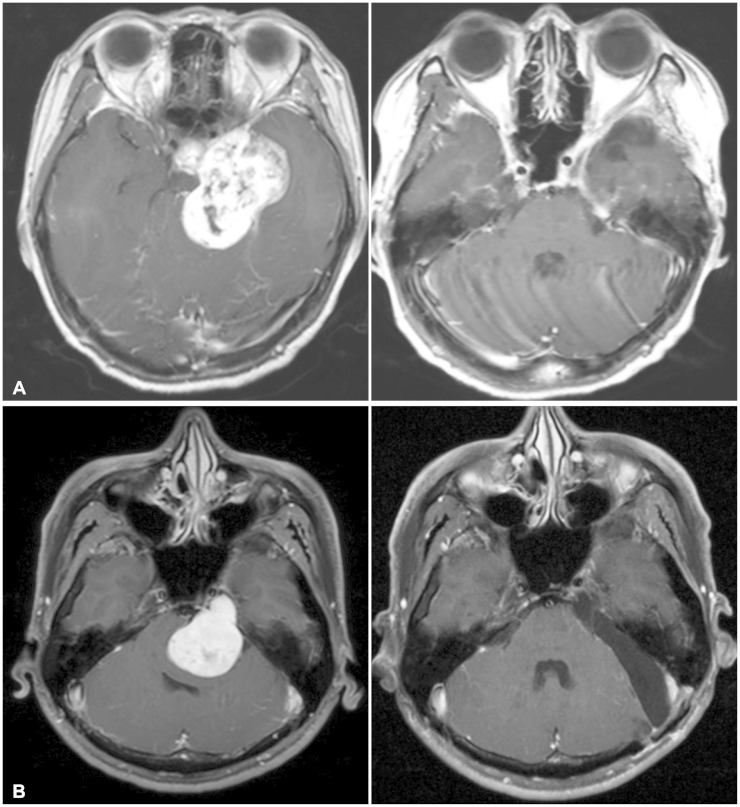 | Fig. 2A: Magnetic resonance images obtained in a 43-year-old woman with an MP-type tumor. Axial preoperative T1-weighted images obtained after administration of gadolinium (left). Postoperative image revealing no residual tumor (right). B: Magnetic resonance images obtained in a 39-year-old woman with a Pm-type tumor. Axial preoperative T1-weighted images obtained after administration of gadolinium (left). Postoperative image revealing no residual tumor (right). |
Table 1
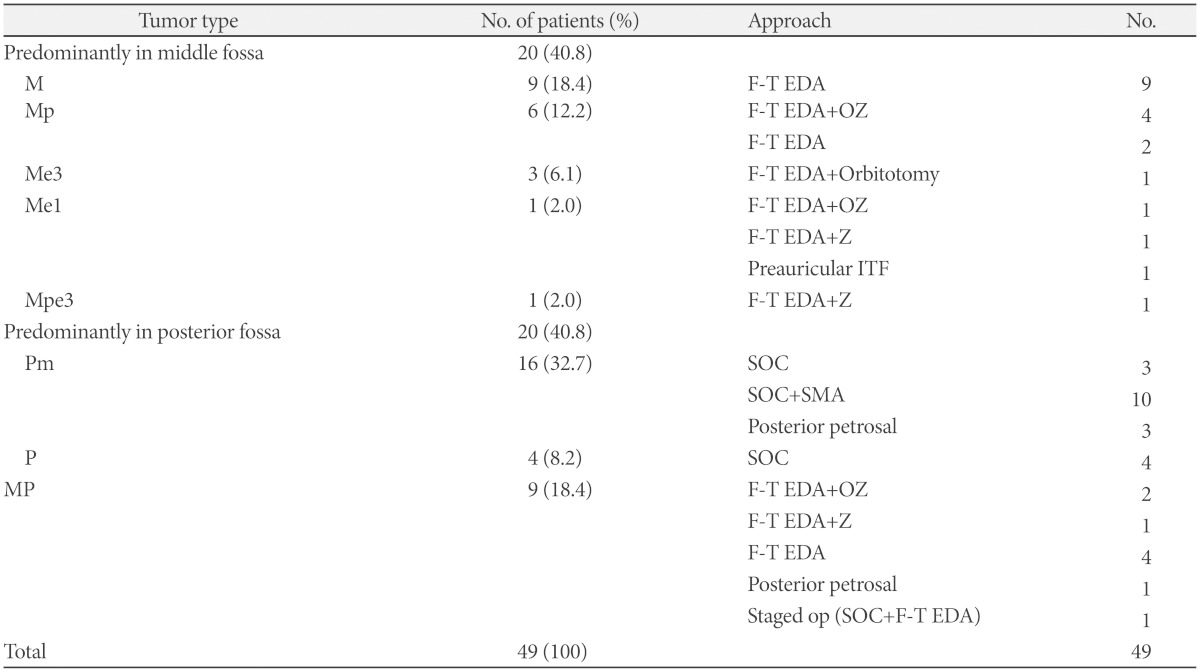
M: tumors confined to middle fossa, Mp: tumors predominantly located at middle fossa with posterior fossa extension, Me1: tumors predominantly located at middle fossa and extended into intracranial V1 branch, Me3: tumors predominantly located at middle fossa and extended into intracranial V3 branch, Mpe3: tumors that predominantly occupy the middle fossa and also involve the posterior fossa and intracranial V3 branch, P: tumors confined to posterior fossa, Pm: tumors predominantly located at posterior fossa with middle fossa extension, MP: tumors involving both middle and posterior fossae, F-T EDA: frontoparietal craniotomy with epidural approach, OZ: orbitozygomatic craniotomy, Z: zygomatic craniotomy, SOC: suboccipital craniotomy, IFT: infratemporal approach, SMA: suprameatal approach
Surgical outcomes
Clinical outcomes
Table 2
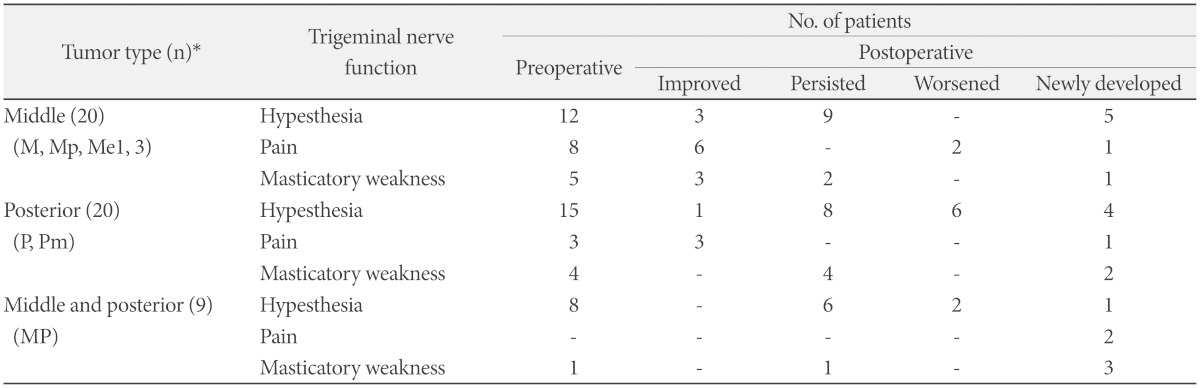
*numbers of patients. M: tumors confined to middle fossa, Mp: tumors predominantly located at middle fossa with posterior fossa extension, Me1: tumors predominantly located at middle fossa and extended into intracranial V1 branch, Me3: tumors predominantly located at middle fossa and extended into intracranial V3 branch, P: tumors confined to posterior fossa, Pm: tumors predominantly located at posterior fossa with middle fossa extension, MP: tumors involving both middle and posterior fossae




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download