1. Yu XJ, Liang MF, Zhang SY, et al. Fever with thrombocytopenia associated with a novel bunyavirus in China. N Engl J Med. 2011; 364:1523–1532. PMID:
21410387.
2. Xiong WY, Feng ZJ, Matsui T, Foxwell AR. Risk assessment of human infection with a novel bunyavirus in China. Western Pac Surveill Response J. 2012; 3:61–66. PMID:
23908943.

3. Elliott RM. Bunyaviruses and climate change. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2009; 15:510–517. PMID:
19604275.

4. Mayo MA. Virus taxonomy: Houston 2002. Arch Virol. 2002; 147:1071–1076. PMID:
12021875.
5. Pepin M, Bouloy M, Bird BH, Kemp A, Paweska J. Rift Valley fever virus (Bunyaviridae: Phlebovirus): an update on pathogenesis, molecular epidemiology, vectors, diagnostics and prevention. Vet Res. 2010; 41:61. PMID:
21188836.

6. Li DX. Fever with thrombocytopenia associated with a novel bunyavirus in China. Zhonghua Shi Yan He Lin Chuang Bing Du Xue Za Zhi. 2011; 25:81–84. PMID:
21863623.
7. Ding S, Yin H, Xu X, et al. A cross-sectional survey of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus infection of domestic animals in Laizhou City, Shandong Province, China. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2014; 67:1–4. PMID:
24451093.

8. Ohagi Y, Tamura S, Nakamoto C, et al. Mild clinical course of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus infection in an elderly Japanese patient. Case Rep Infect Dis. 2014; 2014:918135. PMID:
25574405.

9. Denic S, Janbeih J, Nair S, Conca W, Tariq WU, Al-Salam S. Acute thrombocytopenia, leucopenia, and multiorgan dysfunction: the first case of SFTS Bunyavirus outside China? Case Rep Infect Dis. 2011; 2011:204056. PMID:
22567462.

10. Charrel RN, Moureau G, Temmam S, et al. Massilia virus, a novel Phlebovirus (Bunyaviridae) isolated from sandflies in the Mediterranean. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2009; 9:519–530. PMID:
19055373.

11. Anagnostou V, Pardalos G, Athanasiou-Metaxa M, Papa A. Novel phlebovirus in febrile child, Greece. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011; 17:940–941. PMID:
21529422.

12. McMullan LK, Folk SM, Kelly AJ, et al. A new phlebovirus associated with severe febrile illness in Missouri. N Engl J Med. 2012; 367:834–841. PMID:
22931317.

13. Xu B, Liu L, Huang X, et al. Metagenomic analysis of fever, thrombocytopenia and leukopenia syndrome (FTLS) in Henan Province, China: discovery of a new bunyavirus. PLoS Pathog. 2011; 7:e1002369. PMID:
22114553.

14. Takahashi T, Maeda K, Suzuki T, et al. The first identification and retrospective study of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome in Japan. J Infect Dis. 2014; 209:816–827. PMID:
24231186.
15. Kim KH, Yi J, Kim G, et al. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, South Korea, 2012. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013; 19:1892–1894. PMID:
24206586.

16. Zhan J, Wang Q, Cheng J, et al. Current status of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in China. Virol Sin. 2017; 32:51–62. PMID:
28251515.

17. Saito T, Fukushima K, Umeki K, Nakajima K. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in Japan and public health communication. Emerg Infect Dis. 2015; 21:487–489. PMID:
25695132.

18. Chang MS, Woo JH. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: tick-mediated viral disease. J Korean Med Sci. 2013; 28:795–796. PMID:
23772137.

19. Yoo SJ, Heo ST, Lee KH. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Korean J Crit Care Med. 2014; 29:59–63.

20. Zhang YZ, Zhou DJ, Qin XC, et al. The ecology, genetic diversity, and phylogeny of Huaiyangshan virus in China. J Virol. 2012; 86:2864–2868. PMID:
22190717.

21. Ding F, Zhang W, Wang L, et al. Epidemiologic features of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in China, 2011-2012. Clin Infect Dis. 2013; 56:1682–1683. PMID:
23429379.

22. Heath AC. Vector competence of Haemaphysalis longicornis with particular reference to blood parasites. Surveillance. 2002; 29:12–14.
23. Ding F, Guan XH, Kang K, et al. Risk factors for bunyavirus-associated severe Fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, China. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014; 8:e3267. PMID:
25330383.

24. Zhao L, Zhai S, Wen H, et al. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus, Shandong Province, China. Emerg Infect Dis. 2012; 18:963–965. PMID:
22608264.

25. Chen H, Hu K, Zou J, Xiao J. A cluster of cases of humanto-human transmission caused by severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome bunyavirus. Int J Infect Dis. 2013; 17:e206-8. PMID:
23218674.

26. Liu Y, Li Q, Hu W, et al. Person-to-person transmission of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2012; 12:156–160. PMID:
21955213.

27. Fu Y, Li S, Zhang Z, et al. Phylogeographic analysis of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus from Zhoushan Islands, China: implication for transmission across the ocean. Sci Rep. 2016; 6:19563. PMID:
26806841.

28. Shi J, Hu S, Liu X, et al. Migration, recombination, and reassortment are involved in the evolution of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome bunyavirus. Infect Genet Evol. 2017; 47:109–117. PMID:
27884653.

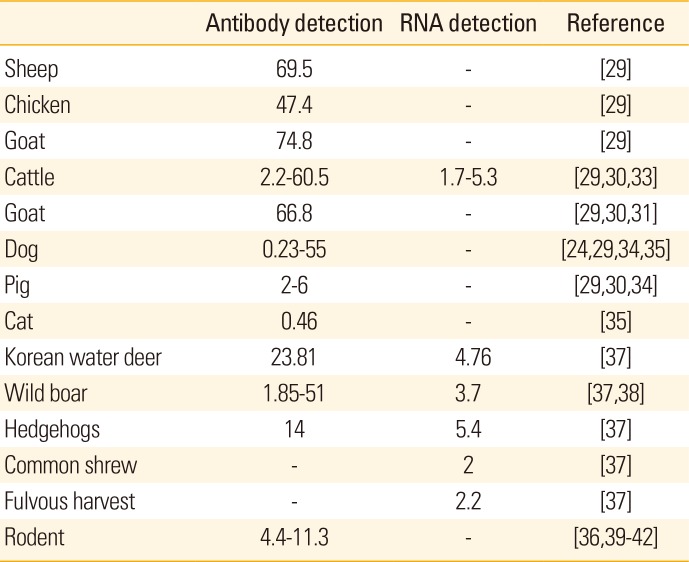
29. Niu G, Li J, Liang M, et al. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus among domesticated animals, China. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013; 19:756–763. PMID:
23648209.

30. Li Z, Hu J, Bao C, et al. Seroprevalence of antibodies against SFTS virus infection in farmers and animals, Jiangsu, China. J Clin Virol. 2014; 60:185–189. PMID:
24793967.

31. Jiao Y, Qi X, Liu D, et al. Experimental and natural infections of goats with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus: evidence for ticks as viral vector. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015; 9:e0004092. PMID:
26485390.

32. Li Z, Bao C, Hu J, et al. Ecology of the tick-borne phlebovirus causing severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in an endemic area of China. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016; 10:e0004574. PMID:
27035712.

33. Tabara K, Fujita H, Hirata A, Hayasaka D. Investigation of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus antibody among domestic bovines transported to slaughterhouse in Shimane Prefecture, Japan. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2016; 69:445–447. PMID:
27169939.

34. Liu Q, He B, Huang SY, Wei F, Zhu XQ. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, an emerging tick-borne zoonosis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014; 14:763–772. PMID:
24837566.

35. Lee SH, Kim HJ, Byun JW, et al. Molecular detection and phylogenetic analysis of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in shelter dogs and cats in the Republic of Korea. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2017; 8:626–630. PMID:
28442241.

37. Oh SS, Chae JB, Kang JG, et al. Detection of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus from wild animals and ixodidae ticks in the Republic of Korea. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2016; 16:408–414. PMID:
27043361.

38. Hayasaka D, Fuxun Y, Yoshikawa A, et al. Seroepidemiological evidence of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus infections in wild boars in Nagasaki, Japan. Trop Med Health. 2016; 44:6. PMID:
27433125.

39. Li S, Xue C, Fu Y, et al. Sporadic case infected by severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome bunyavirus in a non-epidemic region of China. Biosci Trends. 2011; 5:273–276. PMID:
22281541.

40. Liu S, Chai C, Wang C, et al. Systematic review of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: virology, epidemiology, and clinical characteristics. Rev Med Virol. 2014; 24:90–102. PMID:
24310908.
41. Ni H, Yang F, Li Y, et al. Apodemus agrarius is a potential natural host of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS)-causing novel bunyavirus. J Clin Virol. 2015; 71:82–88. PMID:
26322483.

42. Lu YN, Dou XF, Wang XM, et al. Preliminary investigation on the carriage status of the novel bunyavirus among animals and ticks in Beijing area. Int J Virol. 2011; 18:33–36.
43. Reed KD, Meece JK, Henkel JS, Shukla SK. Birds, migration and emerging zoonoses: west nile virus, lyme disease, influenza A and enteropathogens. Clin Med Res. 2003; 1:5–12. PMID:
15931279.

44. Lee KH, Medlock JM, Heo ST. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus, Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus, and migratory birds. J Bacteriol Virol. 2013; 43:235–243.

45. Yun Y, Heo ST, Kim G, et al. Phylogenetic analysis of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in South Korea and migratory bird routes Between China, South Korea, and Japan. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2015; 93:468–474. PMID:
26033016.

46. Choi CY, Kang CW, Kim EM, et al. Ticks collected from migratory birds, including a new record of Haemaphysalis formosensis, on Jeju Island, Korea. Exp Appl Acarol. 2014; 62:557–566. PMID:
24141529.

47. Yoo JR, Heo ST, Park D, et al. Family cluster analysis of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus infection in Korea. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2016; 95:1351–1357. PMID:
27928083.

48. Oh WS, Heo ST, Kim SH, Choi WJ, Han MG, Kim JY. Plasma exchange and ribavirin for rapidly progressive severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Int J Infect Dis. 2014; 18:84–86. PMID:
24161209.

49. Jia Z, Wu X, Wang L, et al. Identification of a candidate standard strain of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus for vaccine quality control in China using a cross-neutralization assay. Biologicals. 2017; 46:92–98. PMID:
28173977.

50. Liu Y, Wu B, Paessler S, Walker DH, Tesh RB, Yu XJ. The pathogenesis of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus infection in alpha/beta interferon knockout mice: insights into the pathologic mechanisms of a new viral hemorrhagic fever. J Virol. 2014; 88:1781–1786. PMID:
24257618.

51. Tani H, Fukuma A, Fukushi S, et al. Efficacy of T-705 (Favipiravir) in the treatment of infections with lethal severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. mSphere. 2016; 1:e00061-15. PMID:
27303697.

52. Chen XP, Cong ML, Li MH, et al. Infection and pathogenesis of Huaiyangshan virus (a novel tick-borne bunyavirus) in laboratory rodents. J Gen Virol. 2012; 93:1288–1293. PMID:
22357748.

53. Jin C, Liang M, Ning J, et al. Pathogenesis of emerging severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in C57/BL6 mouse model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012; 109:10053–10058. PMID:
22665769.

54. Jin C, Jiang H, Liang M, et al. SFTS virus infection in nonhuman primates. J Infect Dis. 2015; 211:915–925. PMID:
25326554.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download