Abstract
Purpose
Materials and Methods
Figures and Tables
 | Fig. 1A schematic representation for genomic organization of the dengue virus. The long genomic RNA contains an open reading frame and flanked by 5' and 3' non-coding regions (NCRs), which are shown at the either end. The coding regions of 10 viral proteins are shown by green and brown boxes. |
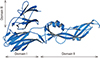 | Fig. 2Three dimensional structure of monomeric form of dengue virus E protein [7]. The potent neutralizing epitopes are located in domain III. |
 | Fig. 3Comparison of amino acid sequences of the four consensus EDIIIs. (A) Sequence alignment of EDIIIs; different amino acid residues between serotypes are indicated in red blocks. The most conserves cysteine residues are showed by green arrows in the positions of 8 and 39. (B) Percentage identity and divergence among EDIIIs of four serotypes. |
 | Fig. 5Prediction of EDIIIF protein secondary structure by PSIpred (A) and GOR4 (B) methods. (A) Formation of α-helix structures in linker segments are showed by H (blue). As described previously for native structure of envelope domain III, each domain contains several β-sheets and coils, which are depicted by the letters of E and C, respectively. (B) The predicted corresponding positions of α-helix structures depicted by arrows in three regions. |
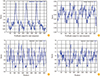 | Fig. 6Predicted properties of EDIIIF protein in secondary structure by using Chou and Fasman method in ProtScale server. The scores for formation of α-helix structures (A), the average flexibility (B), beta-sheets (C), and beta turns (D) throughout the EDIIIF sequence are showed. |
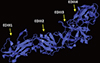 | Fig. 7Homology modeling was used to predict the tertiary structure of the EDIIIF protein. All Four separated EDIII domains (EDIII1, EDIII2, EDIII3, and EDIII4) were presented by arrows. The results were viewed by PyMOL software. |
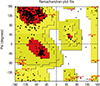 | Fig. 8Evaluation of model stability by using the Ramachandran plot. According to the plot statistics, more than 82% of amino acid residues are in the most favored regions (A, B, L), and 13% are in additional allowed regions (a, b, l, p); whereas only 2.7% are in generously allowed (-a, -b, -l, -p) and 1.7% are in disallowed regions. Accordingly, the constructed model has a good quality. |
Table 1

Table 2

Table 3





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download