Abstract
Purpose
Materials and Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
 | Fig. 1Vector map for the construction of rERA and ERAG3G strain. These full-length cDNA plasmids and three helper plasmids (N, P, and L plasmid) were transfected into BHK/T7-9 cells producing RNA polymerase, respectively. |
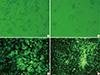 | Fig. 2Cytopathic effects observed in BHK/T7-9 cell inoculated with rERA (A, ×100) and ERAG3G (B, ×200) and immunofluorescence rERA (C, ×200) and ERAG3G (D, ×100) strain by indirect fluorescent assay test using monoclonal antibodies against rabies virus (RABV) in BHK/T7-9 cells. The RABV specific fluorescent appeared in the cytoplasm of the infected cell. |
 | Fig. 3Rabies virus particles in cytoplasm of BHK-T7 cells inoculated with rERA (A, ×50,000) and ERAG3G (B, ×50,000) strains showing bullet shape. |
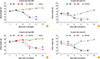 | Fig. 4Change in body weight in 4-week-old (A, B) and 6-week-old mice (C, D) inoculated with ERA, rERA, and ERAG3G strains via intramuscular (IM; A, C) or intracranial (IC; B, D) route. |
 | Fig. 5Safety test in 4-week-old (A, B) and 6-week-old mice (C, D) inoculated with ERA, rERA, and ERAG3G strains via intramuscular (IM; A, C) or intracranial (IC; B, D) route. The 4-week-old mice inoculated with ERA and rERA strains respectively died at 12 or 13 days postinoculation. Fifty percent of the 6-week-old mice inoculated with ERA and rERA IM were alive and all of the mice inoculated with ERA and rERA IC died at 13 days postinoculation. On the contrary, both 4- and 6-week-old mice inoculated with ERAG3G IM or IC were 100% alive as control group. |
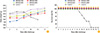 | Fig. 6Change of body weight (A) and survival rate (B) in 4- and 6-week-old mice immunized with ERAG3G strain via intramuscular (IM) or intracranial (IC) route and challenged with highly pathogenic rabies virus strain (CVSN2c). The average body weight of ERAG3G group mice increased for 17 days after challenge and survival rates did not change for 17 days after challenge. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download