Abstract
Induced sputum and sputum cell count analysis is a test for the diagnosis of various respiratory diseases. In particular, it has long been used as an important biomarker in the diagnosis or characterization of asthma or eosinophilic bronchitis. Despite a relatively long history of this test, there has been no consensus report for conducting and interpreting the analyses in Korea. Based on this awareness and necessity, the Korean Academy of Asthma, Allergy and Clinical Immunology launched the Standardization Committee to review the international guidelines and the literature and to develop a consensus report on the diagnostic procedure and interpretation of the sputum induction test.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1. Bickerman HA, Sproul EE, Barach AL. An aerosol method of producing bronchial secretions in human subjects: a clinical technic for the detection of lung cancer. Dis Chest. 1958; 33:347–62.

2. Pin I, Gibson PG, Kolendowicz R, Girgis-Gabardo A, Denburg JA, Hargreave FE, et al. Use of induced sputum cell counts to investigate airway inflammation in asthma. Thorax. 1992; 47:25–9.

3. Fahy JV, Wong H, Liu J, Boushey HA. Comparison of samples collected by sputum induction and bronchoscopy from asthmatic and healthy subjects. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995; 152:53–8.

4. Pizzichini E, Pizzichini MM, Efthimiadis A, Dolovich J, Hargreave FE. Measuring airway inflammation in asthma: eosinophils and eosinophilic cationic protein in induced sputum compared with peripheral blood. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997; 99:539–44.

5. al-Ali MK, Howarth PH. Nitric oxide and the respiratory system in health and disease. Respir Med. 1998; 92:701–15.

7. Cataldo D, Foidart JM, Lau L, Bartsch P, Djukanovic R, Louis R. Induced sputum: comparison between isotonic and hypertonic saline solution inhalation in patients with asthma. Chest. 2001; 120:1815–21.
8. Efthimiadis A, Spanevello A, Hamid Q, Kelly MM, Linden M, Louis R, et al. Methods of sputum processing for cell counts, immunocytochemistry and in situ hybridisation. Eur Respir J Suppl. 2002; 37:19s–23s.
9. Spanevello A, Confalonieri M, Sulotto F, Romano F, Balzano G, Migliori GB, et al. Induced sputum cellularity. Reference values and distribution in normal volunteers. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000; 162(3 Pt 1):1172–4.
10. Belda J, Leigh R, Parameswaran K, O'Byrne PM, Sears MR, Hargreave FE. Induced sputum cell counts in healthy adults. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000; 161(2 Pt 1):475–8.

11. Kim MY, Jo EJ, Lee SE, Lee SY, Song WJ, Kim TW, et al. Reference ranges for induced sputum eosinophil counts in Korean adult population. Asia Pac Allergy. 2014; 4:149–55.

12. Jatakanon A, Lim S, Barnes PJ. Changes in sputum eosinophils predict loss of asthma control. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000; 161:64–72.

13. Pavord ID, Brightling CE, Woltmann G, Wardlaw AJ. Non-eosinophilic corticosteroid unresponsive asthma. Lancet. 1999; 353:2213–4.
14. Green RH, Brightling CE, McKenna S, Hargadon B, Parker D, Bradding P, et al. Asthma exacerbations and sputum eosinophil counts: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2002; 360:1715–21.

15. Reddel HK, Taylor DR, Bateman ED, Boulet LP, Boushey HA, Busse WW, et al. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: asthma control and exacerbations: standardizing end-points for clinical asthma trials and clinical practice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009; 180:59–99.
16. Lougheed MD, Lemiere C, Ducharme FM, Licskai C, Dell SD, Rowe BH, et al. Canadian Thoracic Society 2012 guideline update: diagnosis and management of asthma in preschoolers, children and adults. Can Respir J. 2012; 19:127–64.

17. Maestrelli P, Calcagni PG, Saetta M, Di Stefano A, Hosselet JJ, Santonas-taso A, et al. Sputum eosinophilia after asthmatic responses induced by isocyanates in sensitized subjects. Clin Exp Allergy. 1994; 24:29–34.

18. Jayaram L, Parameswaran K, Sears MR, Hargreave FE. Induced sputum cell counts: their usefulness in clinical practice. Eur Respir J. 2000; 16:150–8.

19. Eltboli O, Brightling CE. Eosinophils as diagnostic tools in chronic lung disease. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2013; 7:33–42.

20. D'Urso V, Doneddu V, Marchesi I, Collodoro A, Pirina P, Giordano A, et al. Sputum analysis: non-invasive early lung cancer detection. J Cell Physiol. 2013; 228:945–51.
21. Olivieri D, D'Ippolito R, Chetta A. Induced sputum: diagnostic value in interstitial lung disease. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2000; 6:411–4.

Go to : 
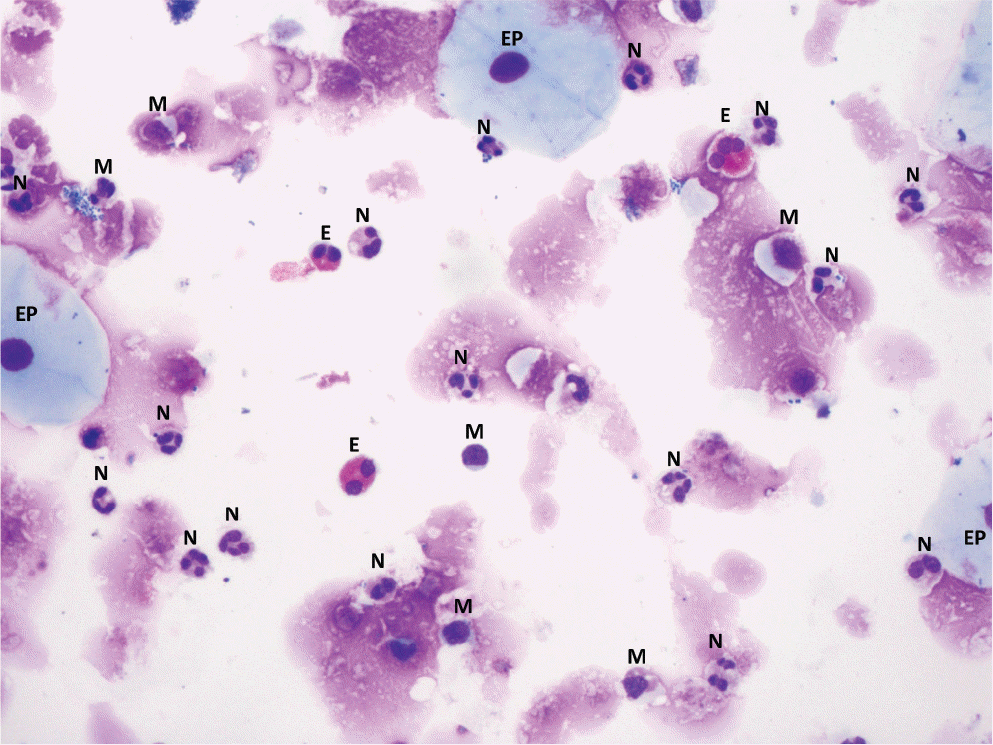 | Fig. 1.Image of the sputum cells (×200). M, macrophage; N, neutrophil; E, eo-sinophil; EP, epithelial cell. |
Table 1.
Equipment for sputum induction
Table 2.
Process of sputum induction
Table 3.
Process of induced sputum preparation
Table 4.
Report form of induced sputum processing
| Cell counts | % | |
|---|---|---|
| Bronchial epithelial cells | ||
| Macrophages | ||
| Neutrophils | ||
| Eosinophils | ||
| Lymphocytes | ||
| Total cell counts | 400 (500)∗ | 100 |
Table 5.
Causes of increase in specific cell type of induced sputum examination




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download