Abstract
Purpose
Food allergies are adverse immune reactions to food. Despite their importance, there have only been a few studies conducted on situations that may cause food allergies in Korean children. This study aims to obtain basic data that are necessary to provide information on food allergies to both patients and caregivers.
Methods
In this study, a survey was conducted on 97 caregivers of patients below 18 years old. The patients' situation upon occurrence of food allergy was examined by a questionnaire.
Results
Approximately 89.7% of the patients were at 6 years of age or younger. The most common allergens were eggs (37%) and milk (28%) in a total of 163 cases, including multiple responses. Skin symptoms were most common (77.8%). At the time of occurrence, 85% of the patients were with their parents. As for the exposure place, house was 65%, followed by restaurant (16%), nursery (7%), and relative's or neighbor's house (4%). Exclusive of unknown cases, the most common reason of exposure was the caregiver giving the food to the patient for reconfirmation (13.6%).
Figures and Tables
Table 1
Clinical characteristics of the study subjects (n=97)

Table 2
Clinical manifestations of food allergy
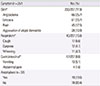
Table 3
Factors related to exposure to food trigger*
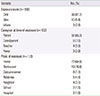
Table 4
The causes of exposure to food triggers* (n=154)

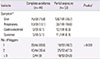
Table 5
Comparisons between complete avoidance and partial exposure
References
2. Seo WH, Jang EY, Han YS, Ahn KM, Jung JT. Management of food allergies in young children at a child care center and hospital in Korean. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2011; 21:32–38.

3. Cho W, Kim J. The current state of food allergy of preschool childcare facilities in hanam. Korean J Community Nutr. 2015; 20:251–258.

4. Gupta RS, Springston EE, Warrier MR, Smith B, Kumar R, Pongracic J, et al. The prevalence, severity, and distribution of childhood food allergy in the United States. Pediatrics. 2011; 128:e9–17.

5. Amin AJ, Davis CM. Changes in prevalence and characteristics of IgE-mediated food allergies in children referred to a tertiary care center in 2003 and 2008. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2012; 33:95–101.

6. Hong SJ, Ahn KM, Lee SY, Kim KE. The prevalences of asthma and allergic diseases in Korean children. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2008; 18:15–25.

7. Hong SJ. Korean ISAAC Study Group of Korean Association of Allergy and Respiratory Diseases: report of Korean ISAAC epidemiologic study for asthma and allergic diseases in children. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2007; 17:1 Suppl. 55–66.
8. Ahn K. Food allergy: diagnosis and management. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 31:163–169.
9. Lee SY, Kim KW, Lee HH, Lim DH, Chung HL, Kim SW, et al. Incidence and clinical characteristics of pediatric emergency department visits of children with severe food allergy. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012; 32:169–175.
10. Lee SY. Food allergy. Korean J Pediatr. 2004; 47:240–246.
11. Barth GA, Weigl L, Boeing H, Disch R, Borelli S. Food intake of patients with atopic dermatitis. Eur J Dermatol. 2001; 11:199–202.
12. Park SJ, Lee JS, Ahn K, Chung SJ. The comparison of growth and nutrient intakes in children with and without atopic dermatitis. Korean J Community Nutr. 2012; 17:271–279.

13. Vale S, Smith J, Said M, Dunne G, Mullins R, Loh R, et al. ASCIA guidelines for prevention of anaphylaxis in schools, pre-schools and childcare: 2012 update. J Paediatr Child Health. 2013; 49:342–345.

14. Rosen J, Albin S, Sicherer SH. Creation and validation of web-based food allergy audiovisual educational materials for caregivers. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2014; 35:178–184.

15. Contreras-Porta J, Ruiz-Baqués A, Gabarron Hortal E, Capel Torres F, Ariño Pla MN, Zorrozua Santisteban A, et al. Evaluation of an educational programme with workshops for families of children with food allergies. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2016; 44:113–119.

16. Choi Y, Ju S, Chang H. Food allergy knowledge, perception of food allergy labeling, and level of dietary practice: a comparison between children with and without food allergy experience. Nutr Res Pract. 2015; 9:92–98.

18. Park JY, Park GY, Han YS, Shin MY. Survey of food allergy in elementary school children in Bucheon-city and relationship between food allergy and other allergic diseases. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013; 1:266–273.

19. Muñoz-Furlong A. Food allergy in schools: concerns for allergists, pediatricians, parents, and school staff. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2004; 93:5 Suppl 3. S47–S50.

20. Uguz A, Lack G, Pumphrey R, Ewan P, Warner J, Dick J, et al. Allergic reactions in the community: a questionnaire survey of members of the anaphylaxis campaign. Clin Exp Allergy. 2005; 35:746–750.

21. Plaut M, Sawyer RT, Fenton MJ. Summary of the 2008 National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases-US Food and Drug Administration Workshop on Food Allergy Clinical Trial Design. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 124:671–678.

22. Lee S. Oral immunotherapy for the treatment of immediate type food allergy. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2014; 2:229–235.

23. Sampson HA, Aceves S, Bock SA, James J, Jones S, Lang D, et al. Food allergy: a practice parameter update-2014. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014; 134:1016–1025.
24. Han SM, Heo YR. Changes of prevalence of food allergy in elementary school student and perception of it in school nutritionist in Korea, 1995~2015. J Nutr Health. 2016; 49:8–17.

25. Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. Food labeling standards. Seoul: Ministry of Food and Drug Safety;2015. 04. 08. Notification No. 2015-20.
26. Lee SY, Kim KW, Ahn K, Kim HH, Pyun BY, Park YM, et al. Consumer’s use and satisfaction of allergic food labels. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2011; 21:294–301.

27. Kim YG, Yu KH, Ly SY. Perception of elementary school parents in Gyeonbuk area on allergenic food labeling system and children’s food allergy status. Korean J Hum Ecol. 2013; 22:491–506.

28. Wootan MG, Osborn M. Availability of nutrition information from chain restaurants in the United States. Am J Prev Med. 2006; 30:266–268.

29. Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration. Food labeling; nutrition labeling of standard menu items in restaurants and similar retail food establishments; final regulatory impact analysis FDA-2011-F-0172. Silver spring (MD): Food and Drug Administration;2014.
30. Taylor CL, Wilkening VL. How the nutrition food label was developed, part 1: the Nutrition Facts panel. J Am Diet Assoc. 2008; 108:437–442.

31. Pak HO, Sohn CY. Recognition of nutrition labeling of Korean restaurants among adults in Gyeonggi-do Area. Korean J Food Nutr. 2013; 26:663–669.

32. Han YS. Management of food allergy in the community. Food Sci Ind. 2015; 48:24–31.
33. Greiwe JC, Pazheri F, Schroer B. Nannies’ knowledge, attitude, and management of food allergies of children: an online survey. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2015; 3:63–67.

34. Ahuja R, Sicherer SH. Food-allergy management from the perspective of restaurant and food establishment personnel. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2007; 98:344–348.

35. Lee IS. Nutrition counseling practice, perception, and nutrition knowledge of nutrition counseling participants and non-participants: elementary students in Gyeongbuk province. J East Asian Soc Diet Life. 2011; 21:146–153.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download