Abstract
Purpose
Dyspnea is the cardinal symptom of asthma, but it is difficult to quantify clinically. Although modified Borg (mBorg) scale has been successfully used in adult, but there has been some difficulties to apply in children. Recently, Pediatric Dyspnea Scale (PDS) was adequately designed and has been widely used. The aim of this study is to compare 2 evaluating scales of dyspnea provoked by induced-bronchoconstriction in childhood asthma.
Methods
Seventy-three clinically suspected children with asthma were enrolled in this study. Each ‘fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO)’ was documented. Forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), mBorg score and PDS score were recorded during methacholine provocation test.
Results
Mapping using canonical plot demonstrated global similarity between 2 scales with some distinctive features. Whereas mBorg score showed more diverse categories in low level of dyspnea, PDS score did in medium level of it. A distribution of dyspnea perception score at a 20% decrease in FEV1 relative to baseline (PS20), a perception score of dyspnea at 20% fall in FEV1 of 2 scales represented similar wide, biphasic feature. Statistical relevance was verified with spearman correlation (R s =0.903, P<0.001) and Bland-Altman analysis. PS20 of both scores and FeNO had no statistical relationship. While relationship between PS20 by mBorg score and the concentration of methacholine at 20% fall in FEV1 (PC20) was not significant (R s =0.224, P=0.154), that between PS20 by PDS and PC20 was weak positive (R s =0.29, P=0.063).
REFERENCES
1. Dyspnea. Mechanisms, assessment, and management: a consensus statement. American Thoracic Society. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999; 159:321–40.
2. National Asthma Education and Prevention Program. Expert Panel Report 3 (EPR-3): Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma-Summary Report 2007. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 120(5 Suppl):S94–138.
4. Adams L, Chronos N, Lane R, Guz A. The measurement of breathlessness induced in normal subjects: validity of two scaling techniques. Clin Sci (Lond). 1985; 69:7–16.

5. Wilson RC, Jones PW. A comparison of the visual analogue scale and modified Borg scale for the measurement of dyspnoea during exercise. Clin Sci (Lond). 1989; 76:277–82.

6. Seo IK, Choi IS, Kim SH, Han ER. Variation of dyspnea perception in re-peatedly hospitalized patients with asthma. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 31:20–6.
7. Khan FI, Reddy RC, Baptist AP. Pediatric Dyspnea Scale for use in hospitalized patients with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 123:660–4.

8. Miller MR, Hankinson J, Brusasco V, Burgos F, Casaburi R, Coates A, et al. Standardisation of spirometry. Eur Respir J. 2005; 26:319–38.
9. Crapo RO, Casaburi R, Coates AL, Enright PL, Hankinson JL, Irvin CG, et al. Guidelines for methacholine and exercise challenge testing-1999. This official statement of the American Thoracic Society was adopted by the ATS Board of Directors, July 1999. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000; 161:309–29.
10. Kang KW, Choi IS, Park SC, Lim H, Jang AS. B lunted dyspnea perception in severe asthmatics. J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999; 19:173–80.
11. Burdon JG, Juniper EF, Killian KJ, Hargreave FE, Campbell EJ. The perception of breathlessness in asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982; 126:825–8.
12. Lansing RW, Gracely RH, Banzett RB. The multiple dimensions of dyspnea: review and hypotheses. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2009; 167:53–60.

13. Lebowitz MD, Thompson HC, Strunk RC. Subjective psychological symptoms in outpatient asthmatic adolescents. J Behav Med. 1981; 4:439–49.

14. Baron C, Lamarre A, Veilleux P, Ducharme G, Spier S, Lapierre JG. Psy-chomaintenance of childhood asthma: a study of 34 children. J Asthma. 1986; 23:69–79.

15. Chetta A, Castagnaro A, Foresi A, Del Donno M, Pisi G, Malorgio R, et al. Assessment of breathlessness perception by Borg scale in asthmatic patients: reproducibility and applicability to different stimuli. J Asthma. 2003; 40:323–9.

16. Boulet LP, Leblanc P, Turcotte H. Perception scoring of induced broncho-constriction as an index of awareness of asthma symptoms. Chest. 1994; 105:1430–3.

17. Chetta A, Gerra G, Foresi A, Zaimovic A, Del Donno M, Chittolini B, et al. Personality profiles and breathlessness perception in outpatients with different gradings of asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998; 157:116–22.

18. Nuijsink M, Hop WC, Jongste JC, Sterk PJ, Duiverman AE. Cato Study Group. Perception of bronchoconstriction: a complementary disease marker in children with asthma. J Asthma. 2013; 50:560–4.

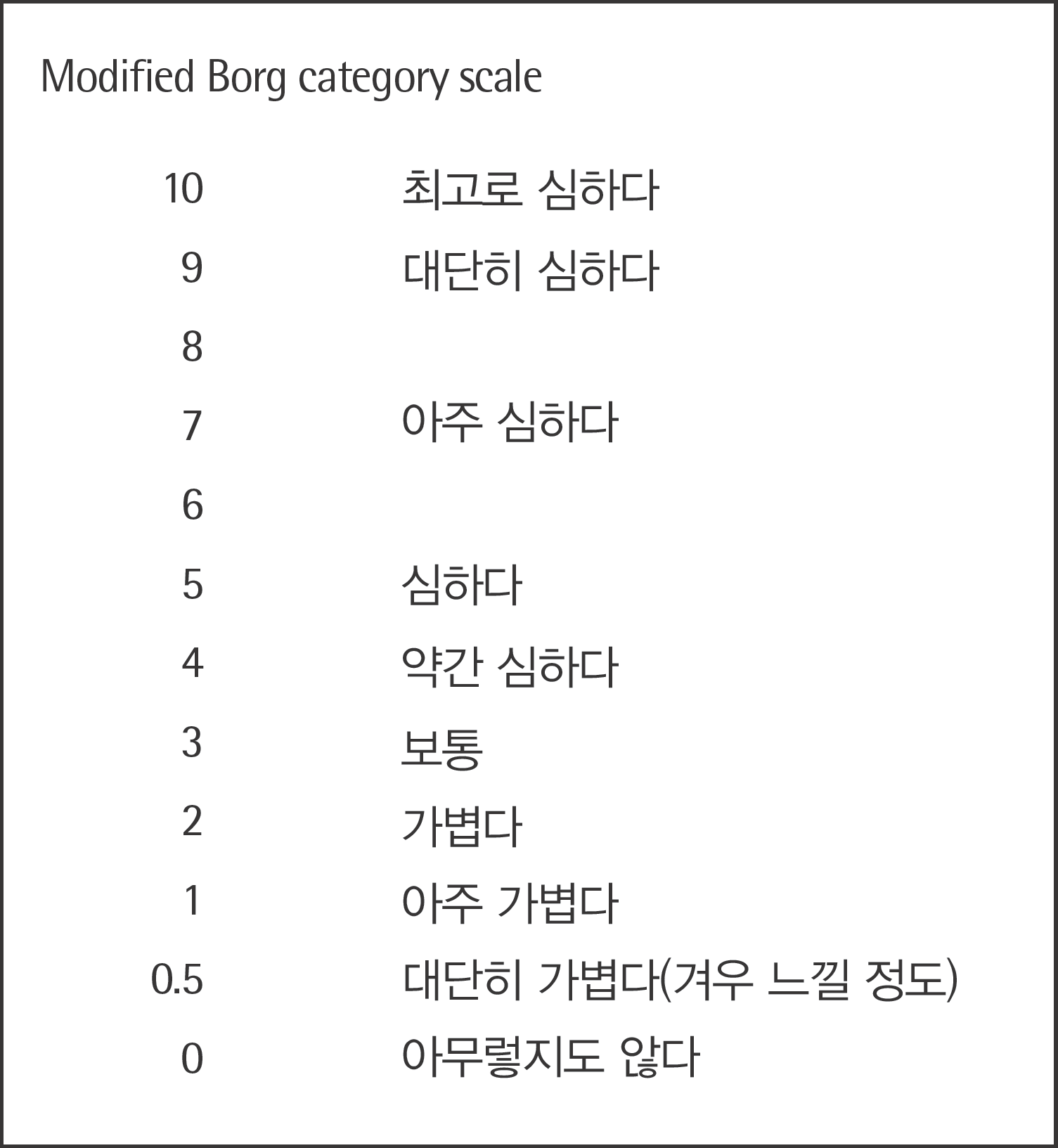
Fig. 1.
Pediatric dyspnea scale which was translated into Korean was used to evaluate the severity of dyspnea.
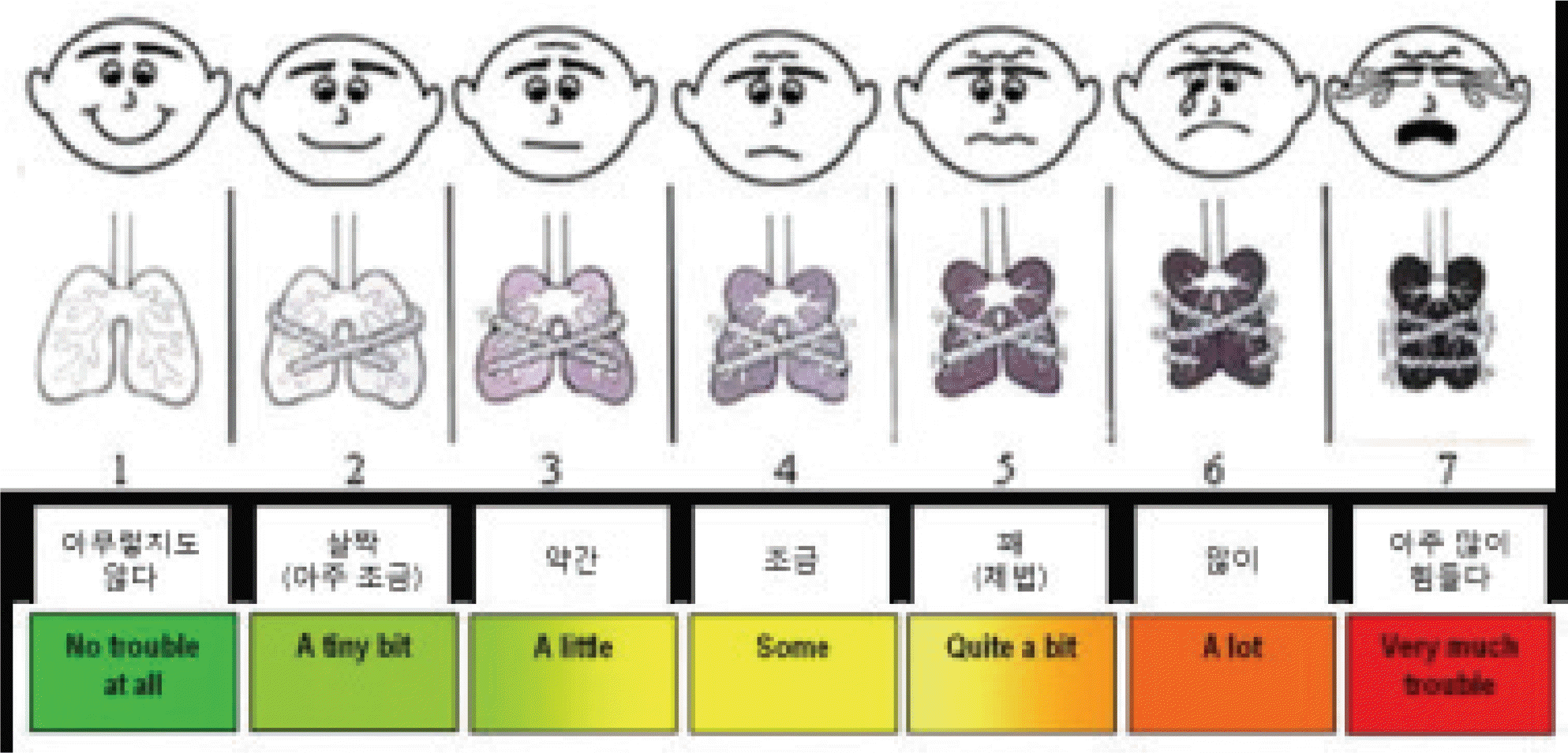
Fig. 2.
Canonical plots of scores from one scale versus mean score of the other scale. For example, when the modified Borg (mBorg) score was 5, modified Pediatric Dyspnea Scale (mPDS) rating averaged 4.67 (solid line), Alternately, when subject rated a PDS score of 3 the Borg score averaged 2.59 (dashed line).
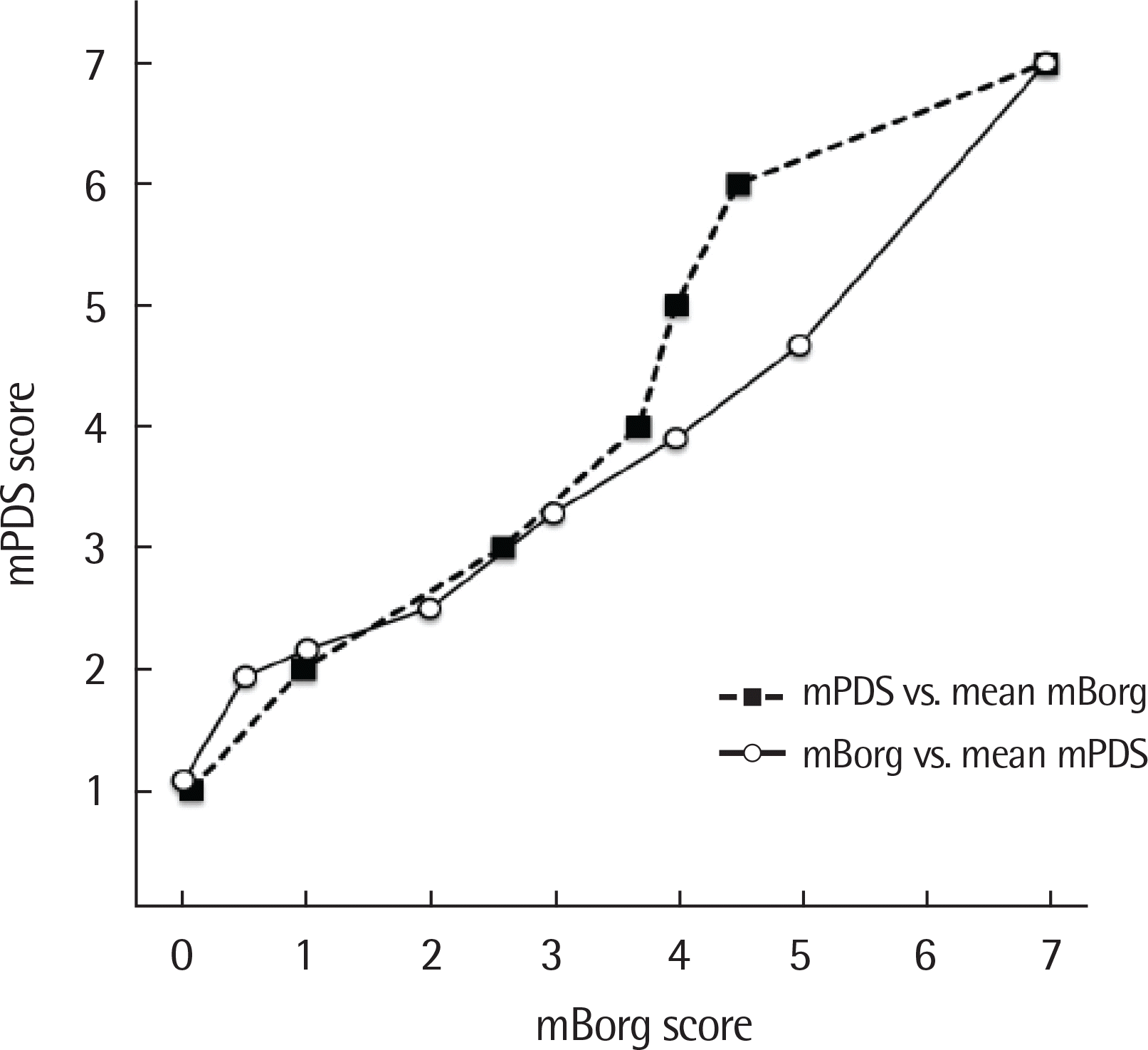
Fig. 3.
The dyspnea perception score at a 20% decrease in forced expiratory volume in 1 second relative to baseline (PS20) was measured by interpolation. mBorg, modified Borg; mPDS, modified Pediatric Dyspnea Scale.
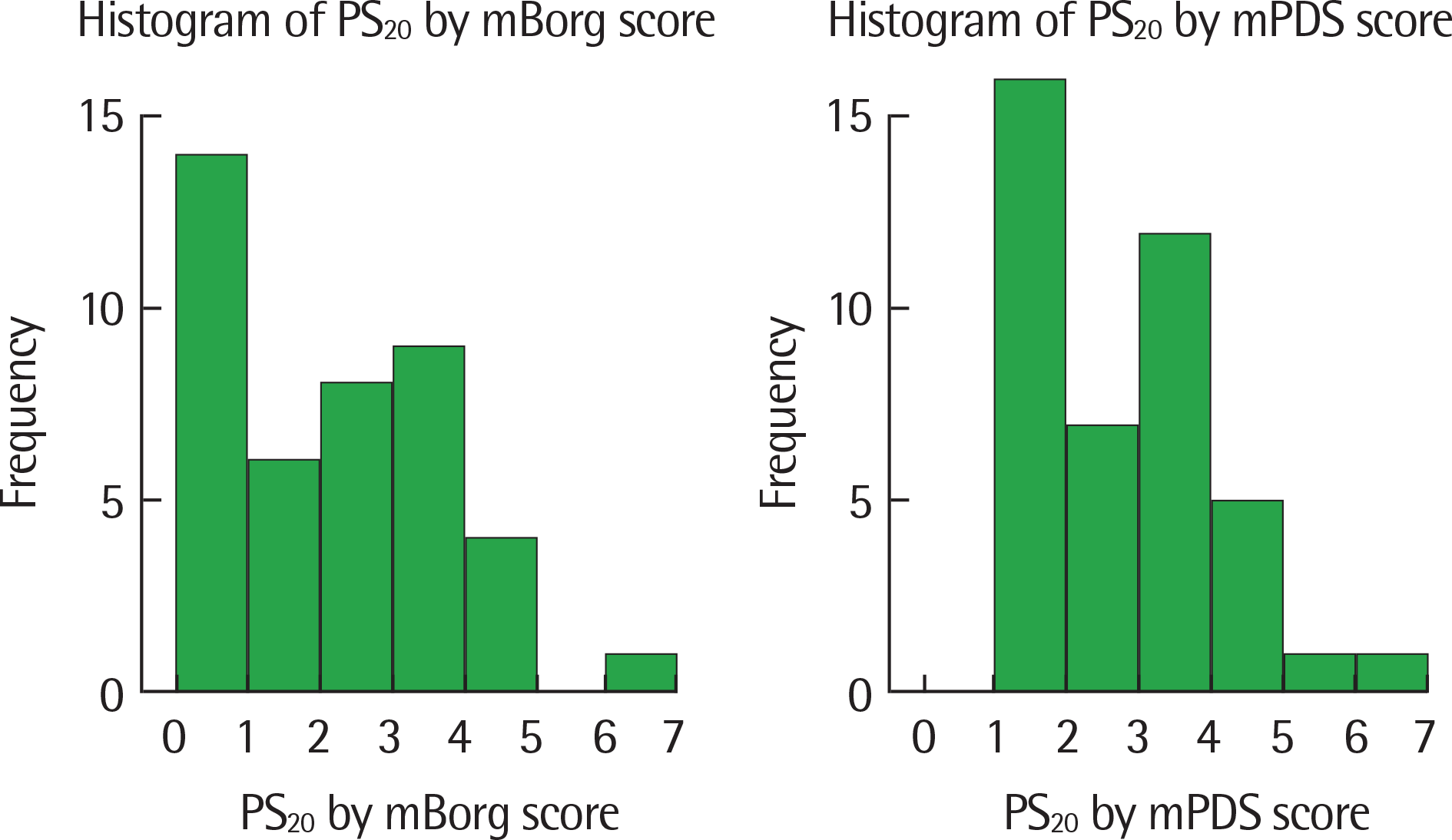
Fig. 4.
Distribution of individual difference in dyspnea perception score at a 20% decrease in forced expiratory volume in 1 second relative to baseline (PS20) between modified Borg scale and modified Pediatric Dyspnea Scale.
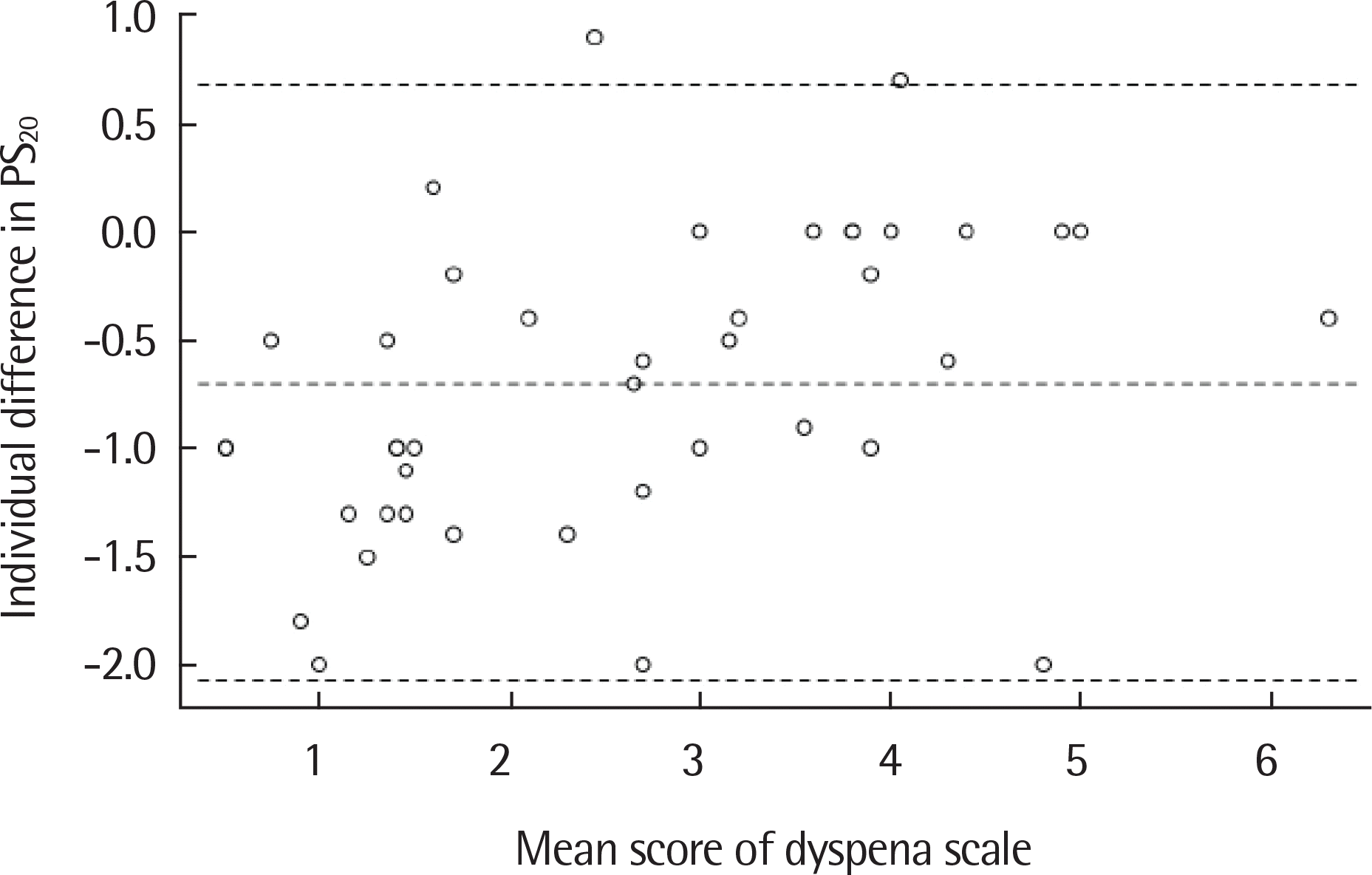
Fig. 5.
Correlation between dyspnea perception score at a 20% decrease in forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) relative to baseline (PS20) and the concentration of methacholine at 20% fall in FEV1 (PC20). mBorg, modified Borg; mPDS, modified Pediatric Dyspnea Scale.
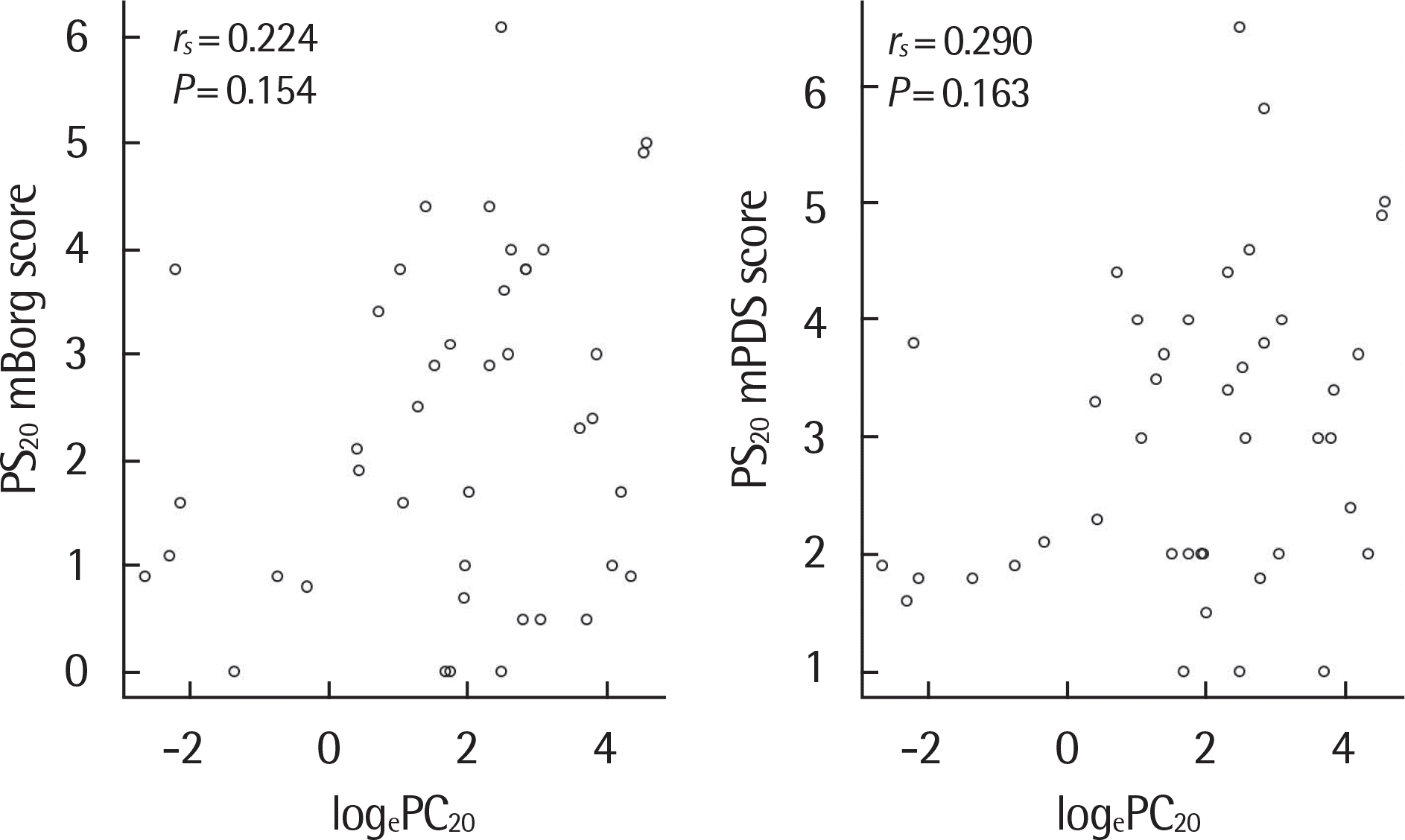
Table 1.
General characteristics of subjects (n=73)




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download