Abstract
Purpose
Humulus japonicus pollen (Hop J) is a major cause of inhalant allergy in autumn of the Far East countries, and its allergenic potency has been increasing with climate changes. Allergen immunotherapy has been considered in Hop J-sensitized allergic patients; however, Hop J allergen extracts for immunotherapy are not commercially available. We speculate that Humulus lupulus pollen (Hop L) belonged to the same genus may share cross-reacting allergens with Hop J and evaluated allergenic relationships between these 2 pollens.
Methods
Thirteen patients with allergic rhinitis and/or asthma sensitive to Hop J pollens were enrolled in Ajou University Hospital, Suwon, Korea. Hop J pollens were collected locally and lyophilized extracts were prepared, while lyophilized Hop L extracts were provided by Lofarma S.p.A. IgE-ELISA/enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) inhibition tests, sodium dodecyl sulphate-poly-acrylamide gel electrophoresis and IgE-immunoblot/immunoblot inhibition analysis using sera from the enrolled subjects were performed.
Results
All patients had high serum specific IgE to both Hop J and Hop L extracts by ELISA, but no significant correlation was found between these 2 extracts. ELISA inhibition tests showed significant dose-dependent inhibitions on IgE-bindings to Hop L with serial additions of Hop J extracts in a dose-dependent manner, while minimal inhibitions of IgE binding to Hop J were noted with additions of Hop L. IgE-immunoblot analysis demonstrated that the major allergenic component of Hop J at 12 kDa was inhibited by Hop J, while no inhibitions were noted by Hop L extracts on IgE-immunoblot inhibition analysis.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1. Park HS, Nahm DH, Suh CH, Lee SM, Choi SY, Jung KS, et al. Evidence of Hop Japanese pollinosis in Korea: IgE sensitization and identification of allergenic components. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997; 100:475–9.

3. Jin HJ, Choi GS, Shin YS, Kim JH, Kim JE, Ye YM, et al. The allergenic potency of Japanese hop pollen is increasing with environmental changes in Korea. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2013; 5:309–14.

4. Park HJ, Lee JH, Park KH, Ann HW, Jin MN, Choi SY, et al. A nationwide survey of inhalant allergens sensitization and levels of indoor major allergens in Korea. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2014; 6:222–7.

5. Park HS, Nahm DH, Kim HY, Suh YJ, Cho JW, Kim SS, et al. Clinical and immunologic changes after allergen immunotherapy with Hop Japanese pollen. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2001; 86:444–8.

6. Ye YM, Lee SK, Kim SH, Nahm DH, Suh CH, Park HS. Changes of serum cytokines after the long term immunotherapy with Japanese hop pollen extracts. J Korean Med Sci. 2006; 21:805–10.

7. Reeb-Whitaker CK, Bonauto DK. Respiratory disease associated with occupational inhalation to hop (Humulus lupulus) during harvest and processing. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014; 113:534–8.

8. Spiewak R, Gòra A, Dutkiewicz J. Work-related skin symptoms and type I allergy among eastern-Polish farmers growing hops and other crops. Ann Agric Environ Med. 2001; 8:51–6.
9. Tosunoglu A, Altunoglu MK, Bicakci A, Kilic O, Gonca T, Yilmazer I, et al. Atmospheric pollen concentrations in Antalya, South Turkey. Aero-biologia. 2015; 31:99–109.

10. Saatçioglu G, Tosunoğlu A, Malyer H, Buçakçi A. Airborne pollen grains of Gemlik (Bursa). Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2011; 9:29–36.
11. Weber RW. On the cover. Hop. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008; 100:A4.
12. Estrada JL, Gozalo F, Cecchini C, Casquete E. Contact urticaria from hops (Humulus lupulus) in a patient with previous urticaria-angioedema from peanut, chestnut and banana. Contact Dermatitis. 2002; 46:127.

13. Garcia A. Occupational rhinoconjunctivitis due to hops exposure in a brewery worker. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 113(2 Suppl):S62.
14. Small E. A numerical and nomenclatural analysis of morpho-geographic Taxa of Humulus. Syst Bot. 1978; 3:37–76.

15. Park HS, Jung KS, Jee SY, Hong SH, Kim HY, Nahm DH. Are there any links between Hop Japanese pollen and other weed pollens or food allergens on skin prick tests? Allergy Asthma Proc. 2001; 22:43–6.

16. Kim JH, Oh JW, Lee HB, Kim SW, Kang IJ, Kook MH, et al. Changes in sensitization rate to weed allergens in children with increased weeds pollen counts in Seoul metropolitan area. J Korean Med Sci. 2012; 27:350–5.

17. Park HJ, Lee JH, Park KH, Kim KR, Han MJ, Choe H, et al. A six-year study on the changes in airborne pollen counts and skin positivity rates in Korea: 2008-2013. Yonsei Med J. 2016; 57:714–20.

18. Pillay M, Kenny ST. Chloroplast DNA differences between cultivated hop, Humulus lupulus and the related species H. japonicus. Theor Appl Genet. 1994; 89:372–8.

19. Park JW, Ko SH, Kim CW, Jeoung BJ, Hong CS. Identification and characterization of the major allergen of the Humulus japonicus pollen. Clin Exp Allergy. 1999; 29:1080–6.

20. Jeong KY, Son M, Choi SY, Park KH, Park HJ, Hong CS, et al. Standardization of weed pollen extracts, Japanese hop and mugwort, in Korea. Yonsei Med J. 2016; 57:399–406.

21. Jeong KY, Han IS, Choi SY, Lee JH, Lee JS, Hong CS, et al. Allergenicity of recombinant profilins from Japanese hop, Humulus japonicus. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2013; 23:345–50.
Go to : 
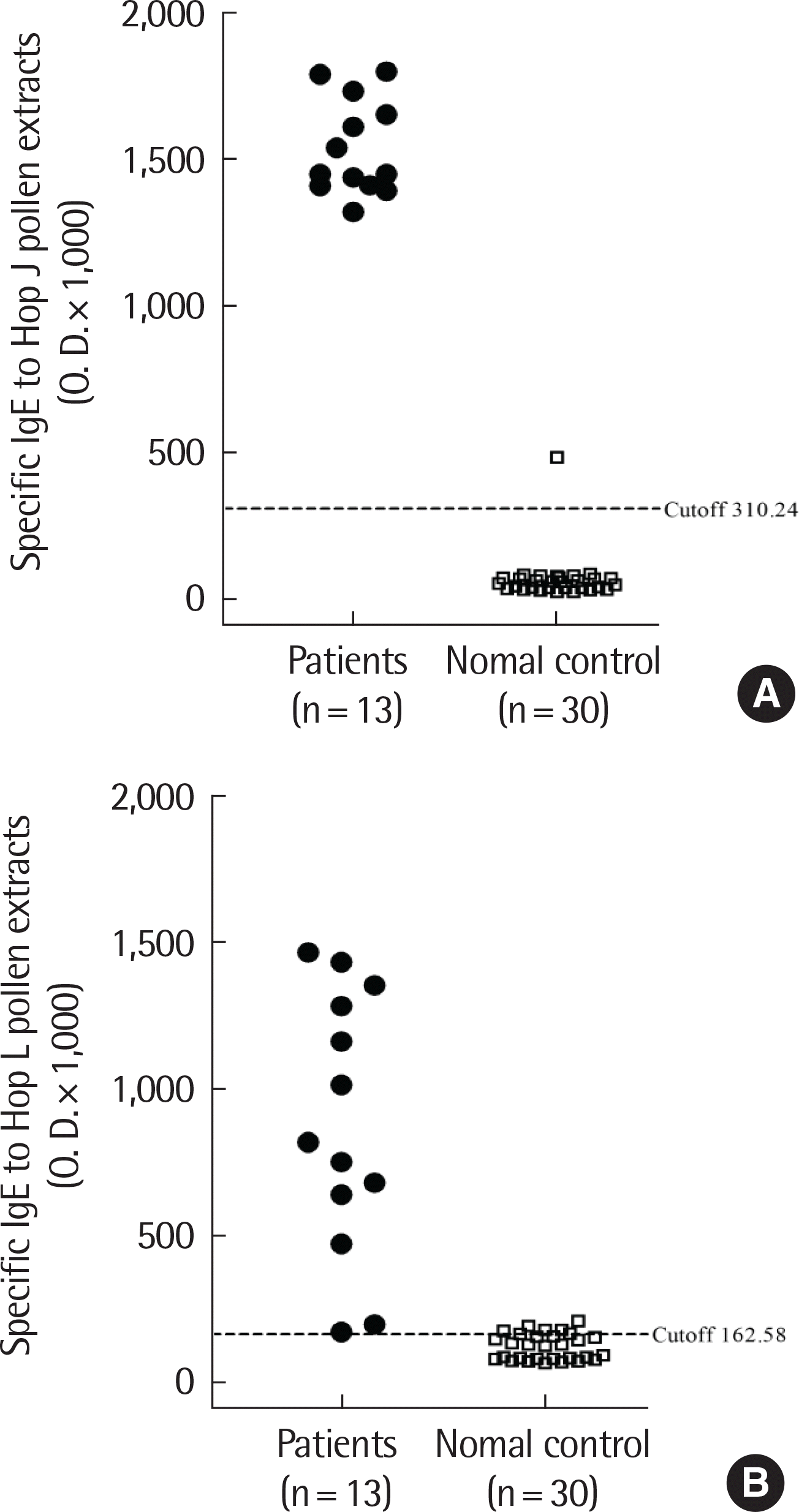 | Fig. 1.Detection of serum specific IgE antibodies to Humulus japonicus (Hop J) (A) and Humulus lupulus (Hop L) (B) pollen extracts by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in sera from 13 allergic rhinitis and/or asthma patients sensitive to Hop J pollens (●) and 30 normal controls (□). Horizontal bars indicate the re-spective cutoff values. |
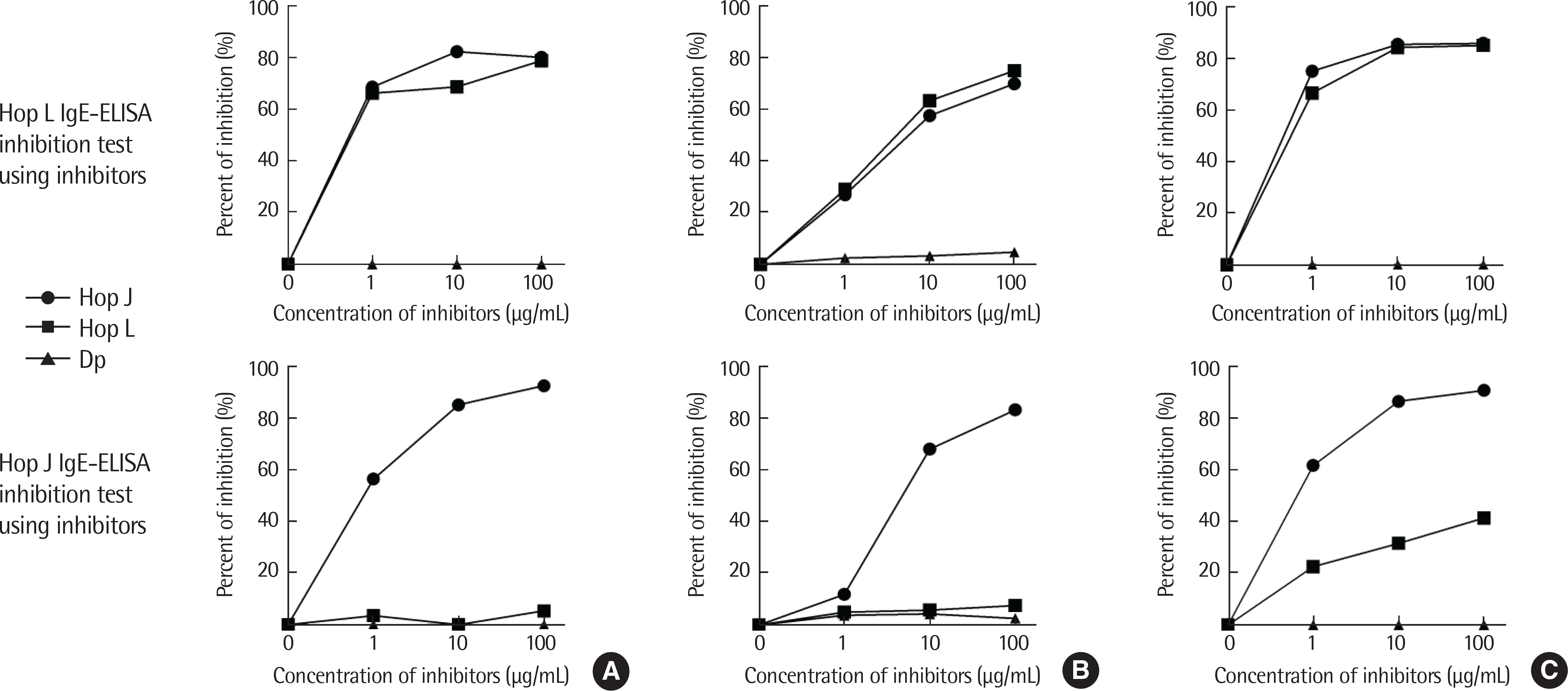 | Fig. 2.IgE-ELISA inhibition tests with serial additions of Humulus japonicus (Hop J) pollen extracts (●), Humulus lupulus (Hop L) pollen extracts (■), and Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus (Dp) extracts (▲) in the sera from allergic rhinitis and/or asthma patients sensitive to Hop J pollens. Patient number 4 (A), number 8 (B), and number 11 (C). ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. |
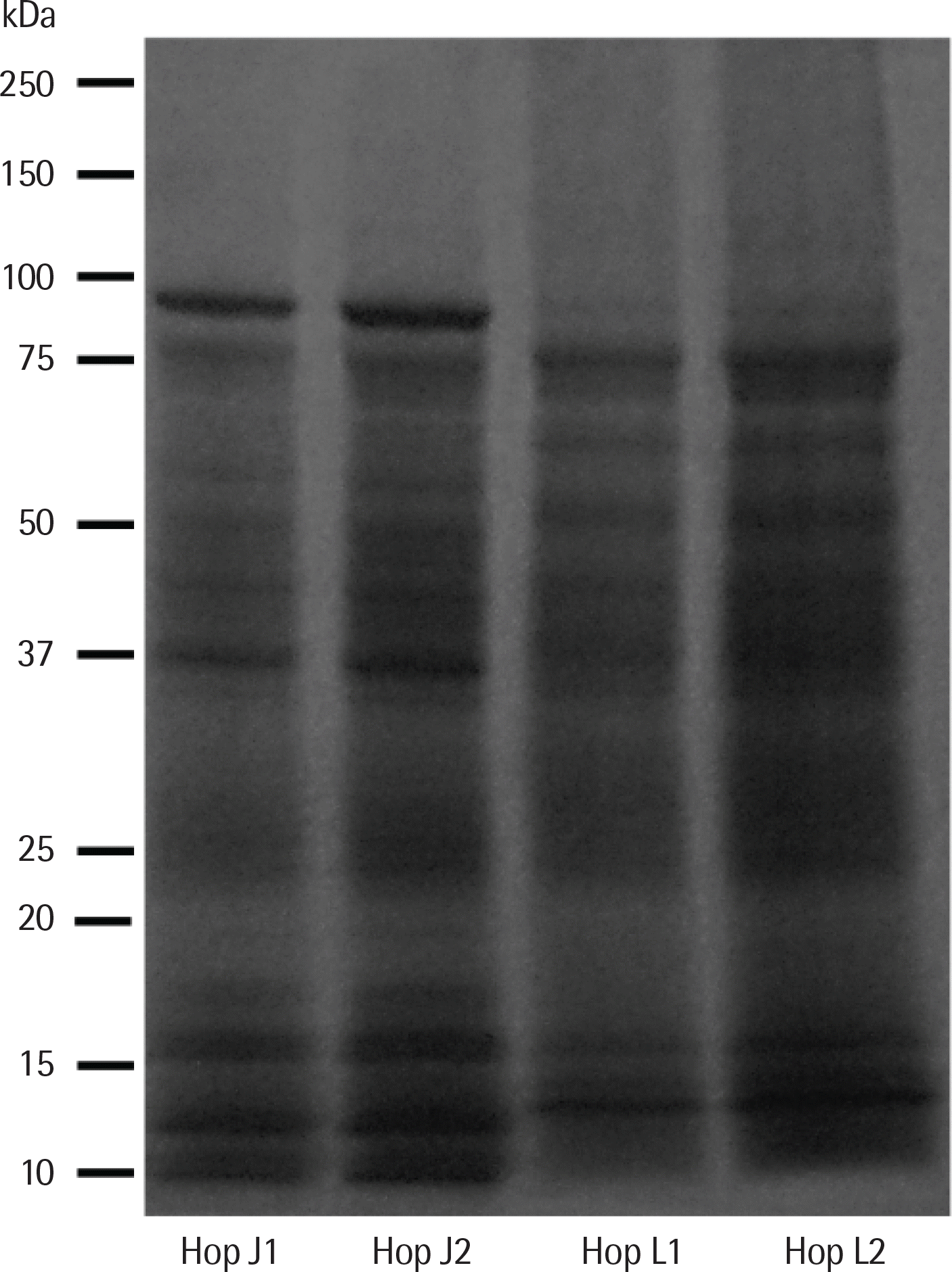 | Fig. 3.Sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis findings of Humulus japonicus and Humulus lupulus pollen extracts using 4%–20% gel. Hop J1, 15 μg of Humulus japonicus pollen extracts; Hop J2, 30 μg of Humulus japonicus pollen extracts; Hop L1, 15 μg of Humulus lupulus pollen extracts; Hop L2, 30 μg of Humulus lupulus pollen extracts. |
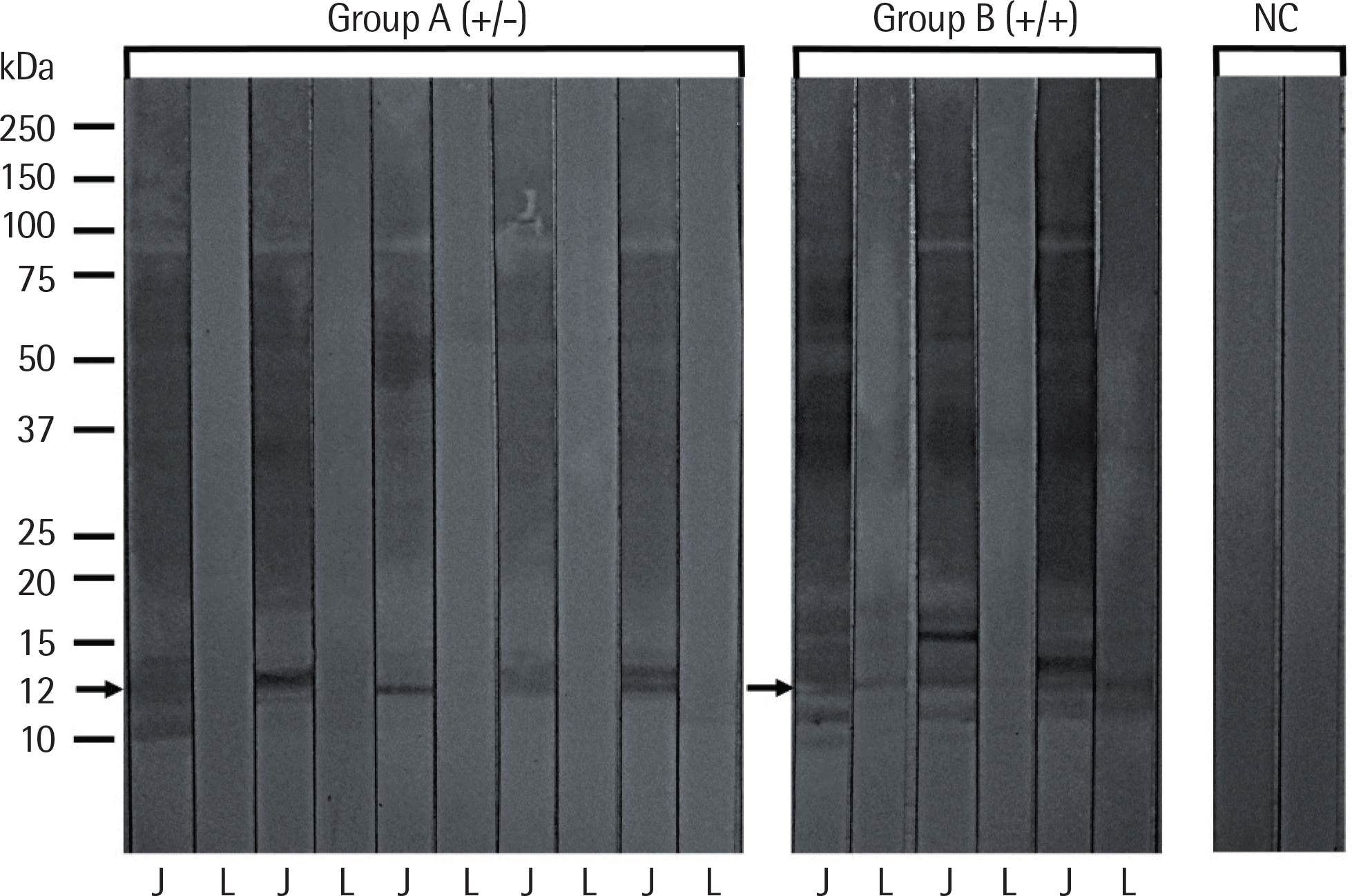 | Fig. 4.IgE-immunoblot analysis of Humulus japonicus and Humulus lupulus pollen extracts in the sera from allergic rhinitis and/or asthma patients sensitive to Hop J pollens. Arrow indicate the major allergenic component of Humulus japonicus pollen extracts. Group A, the subjects having IgE-binding components to Humulus japonicus pollen extracts; group B, the subjects having IgE-binding components to both pollen extracts; J, Using Humulus japonicus pollen extracts; L, Humulus lupulus pollen extracts; NC, normal controls. |
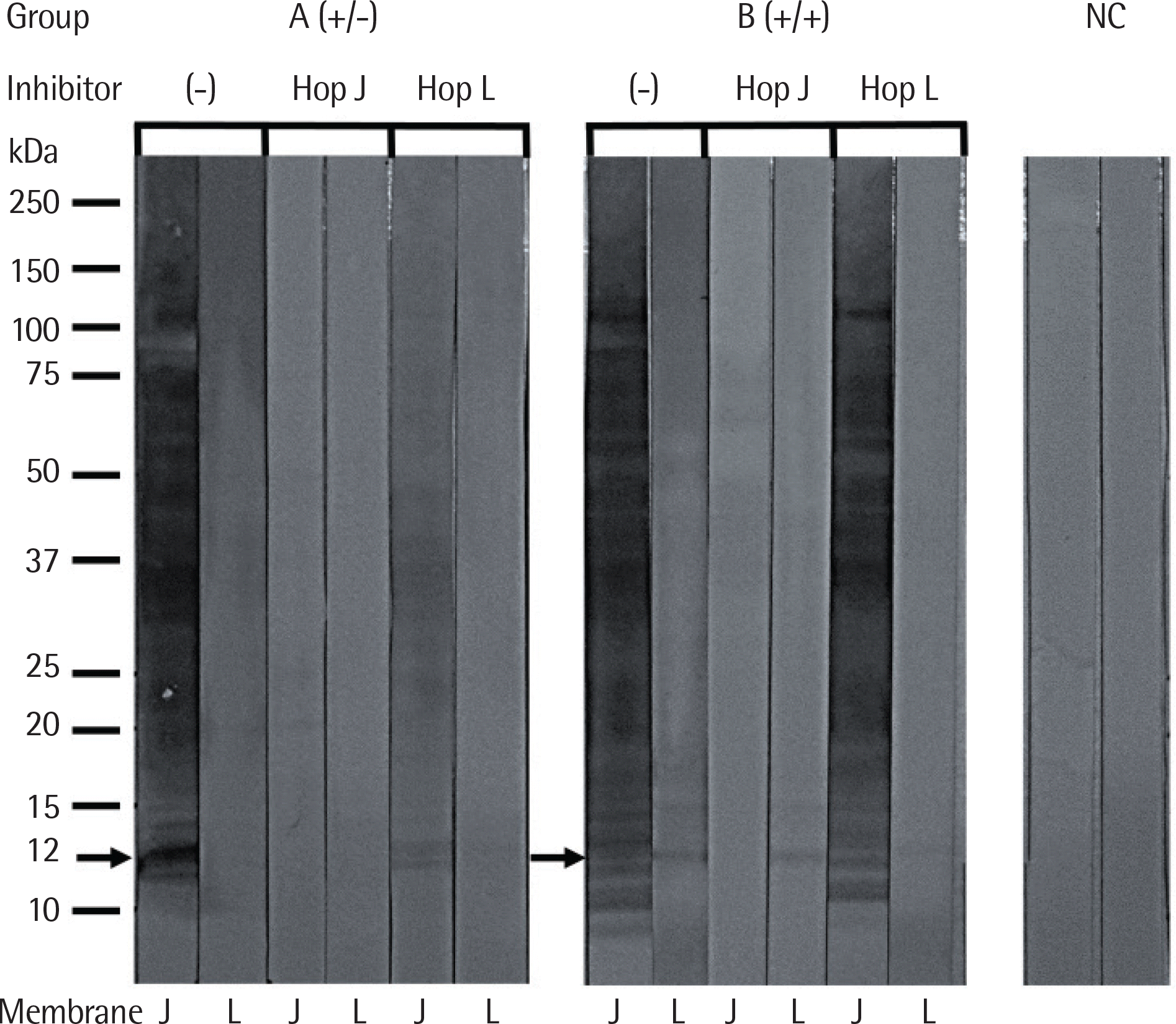 | Fig. 5.IgE-immunoblot inhibition with Humulus japonicus (Hop J) and Humulus lupulus (Hop L) pollen extracts. Group A, the subjects having IgE-binding components to Humulus japonicus pollen extracts; group B, the subjects having IgE-binding components to both pollen extracts; NC, normal controls; J, the membrane of Humulus japonicus pollen extracts; L, the membrane of Humulus lupulus pollen extracts. |
Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of the study patients
| Patient No. | Sex/age (yr) | Diagnosis | Total IgE (kU/L)∗ | sIgE to Hop J (kU/L)∗ | sIgE to Hop J (O. D.×1,000)† | sIgE to Hop L (O. D.×1,000)† |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F/38 | BA+AR+AD | 445 | >100 | 1,790 | 195 |
| 2 | F/53 | AR+AC | 914 | 92.5 | 1,540 | 1,160 |
| 3 | M/16 | BA+AR+AC | 422 | 39.0 | 1,450 | 749 |
| 4 | F/45 | AR+AC+OAS | 119 | 39.7 | 1,412 | 678 |
| 5 | F/49 | BA+AR+AC+OAS | 322 | >100 | 1,733 | 1,352 |
| 6 | F/18 | BA+AR+AD | 1,483 | 99.7 | 1,439 | 1,012 |
| 7 | F/47 | BA+AR+AC | 377 | 72.8 | 1,321 | 470 |
| 8 | M/57 | BA+AR+AC | 998 | >100 | 1,653 | 1,431 |
| 9 | M/14 | BA+AR | >5,000 | >100 | 1,800 | 1,281 |
| 10 | F/51 | BA+AR+AC | 316 | >100 | 1,611 | 638 |
| 11 | F/16 | AR+AC+OAS | 392 | 57.1 | 1,393 | 1,464 |
| 12 | F/49 | BA+AR | 2,938 | 81.5 | 1,450 | 816 |
| 13 | F/35 | AR+AC+AD+OAS | 821 | 27.2 | 1,410 | 169 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download