Abstract
Purpose
Bacterial/viral coinfection is not uncommon in children with community acquired pneumonia. However, the data about viral coinfection in Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia is limited. The aim of this study was to investigate the frequency and clinical characteristics of respiratory viral coinfection in pediatric M. pneumoniae pneumonia.
Methods
A retrospective cross sectional study was performed in 432 children hospitalized with M. pneumoniae pneumonia in a tertiary teaching hospital between June 2015 and May 2016.
Results
One hundred forty patients (32.4%) were coinfected with M. pneumoniae and respiratory viruses. Among coinfected viruses, rhinovirus (44.4%) was most commonly detected. Viral coinfection was more likely to occur under the age of 5 years in winter and spring. As compared with patients infected with M. pneumoniae monoinfection, patients coinfected with respiratory viruses showed a lower mean age and shorter total febrile days. Although total leukocyte count was higher, relative proportion of neutrophils and C-reactive protein level were significantly lower in these patients.
Figures and Tables
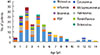 | Fig. 3Age distribution of patients coinfected with Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia and respiratory virus. RSV, respiratory syncytial virus. |
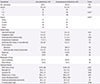
Table 1
clinical characteristics of virus coinfection group versus Mycoplasma pneumoniae monoinfection group in children with M. pneumoniae pneumonia
References
1. Juvén T, Mertsola J, Waris M, Leinonen M, Meurman O, Roivainen M, et al. Etiology of community-acquired pneumonia in 254 hospitalized children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2000; 19:293–298.

2. Wang YJ, Vuori-Holopainen E, Yang Y, Wang Y, Hu Y, Leboulleux D, et al. Relative frequency of Haemophilus influenzae type b pneumonia in Chinese children as evidenced by serology. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2002; 21:271–277.

3. Michelow IC, Olsen K, Lozano J, Rollins NK, Duffy LB, Ziegler T, et al. Epidemiology and clinical characteristics of community-acquired pneumonia in hospitalized children. Pediatrics. 2004; 113:701–707.

4. Honkinen M, Lahti E, Österback R, Ruuskanen O, Waris M. Viruses and bacteria in sputum samples of children with community-acquired pneumonia. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2012; 18:300–307.

5. Ghani AS, Morrow BM, Hardie DR, Argent AC. An investigation into the prevalence and outcome of patients admitted to a pediatric intensive care unit with viral respiratory tract infections in Cape Town, South Africa. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2012; 13:e275–e281.

6. Kurz H, Göpfrich H, Huber K, Krugluger W, Asbott F, Wabnegger L, et al. Spectrum of pathogens of in-patient children and youths with community acquired pneumonia: a 3 year survey of a community hospital in Vienna, Austria. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2013; 125:674–679.

7. Atkinson TP, Balish MF, Waites KB. Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, pathogenesis and laboratory detection of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2008; 32:956–973.

8. Lee KY. Pediatric respiratory infections by Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2008; 6:509–521.
9. Lee SH, Noh SM, Lee KY, Lee HS, Hong JH, Lee MH, et al. Clinico-epidemiologic Study of Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia(1993 through 2003). Korean J Pediatr. 2005; 48:154–157.
10. Kim JW, Seo HK, Yoo EG, Park SJ, Yoon SH, Jung HY, et al. Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in Korean children, from 1979 to 2006-a meta-analysis. Korean J Pediatr. 2009; 52:315–323.

11. Ferwerda A, Moll HA, de Groot R. Respiratory tract infections by Mycoplasma pneumoniae in children: a review of diagnostic and therapeutic measures. Eur J Pediatr. 2001; 160:483–491.

12. Nilsson AC, Björkman P, Welinder-Olsson C, Widell A, Persson K. Clinical severity of Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MP) infection is associated with bacterial load in oropharyngeal secretions but not with MP genotype. BMC Infect Dis. 2010; 10:39.
13. Tanaka H, Narita M, Teramoto S, Saikai T, Oashi K, Igarashi T, et al. Role of interleukin-18 and T-helper type 1 cytokines in the development of Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in adults. Chest. 2002; 121:1493–1497.

14. Waites KB, Talkington DF. Mycoplasma pneumoniae and its role as a human pathogen. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2004; 17:697–728.

15. Ruiz M, Ewig S, Marcos MA, Martinez JA, Arancibia F, Mensa J, et al. Etiology of community-acquired pneumonia: impact of age, comorbidity, and severity. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999; 160:397–405.
17. Brown JS. Geography and the aetiology of community-acquired pneumonia. Respirology. 2009; 14:1068–1071.

18. File TM Jr. New diagnostic tests for pneumonia: what is their role in clinical practice? Clin Chest Med. 2011; 32:417–430.

19. Pavia AT. What is the role of respiratory viruses in community-acquired pneumonia?: What is the best therapy for influenza and other viral causes of community-acquired pneumonia? Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2013; 27:157–175.
20. Chen CJ, Lin PY, Tsai MH, Huang CG, Tsao KC, Wong KS, et al. Etiology of community-acquired pneumonia in hospitalized children in northern Taiwan. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2012; 31:e196–e201.

21. Chiu CY, Chen CJ, Wong KS, Tsai MH, Chiu CH, Huang YC. Impact of bacterial and viral coinfection on mycoplasmal pneumonia in childhood community-acquired pneumonia. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2015; 48:51–56.

22. O'Brien KL, Walters MI, Sellman J, Quinlisk P, Regnery H, Schwartz B, et al. Severe pneumococcal pneumonia in previously healthy children: the role of preceding influenza infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2000; 30:784–789.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download