Abstract
Seafood is one of the common causes of food allergies to adults. The sea hare Aplysia kurodai is a marine mollusk which belongs to invertebrate gastropod that has been consumed as a food in Korea. Cases of acute toxic hepatitis after ingestion of sea hares have been reported, but few cases of allergic reactions to sea hare have been reported in the literature. A 33-year-old man was referred to our Emergency Department due to urticaria and periorbital/perioral swelling after eating sea hares. Approximately 10 years ago, he experienced similar allergic reactions to it. Skin prick and intradermal tests showed strong positive responses to crude sea hare allergen extract. He was diagnosed with food allergy to sea hares. We herein report the first case of sea hare allergy after ingestion.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
The results of skin prick test (A) and intradermal test (B) to each extract of mollusks show positive reactions to sea hare (A. kurodai, Aplysia kurodai). B. cornutus, Batillus cornutus; H. midae, Haliotis midae.

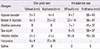
Table 1
Skin prick test and intradermal test results of multiple seafood allergens
References
1. Sicherer SH, Sampson HA. Food allergy: epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014; 133:291–307.

2. Lehrer SB, Ayuso R, Reese G. Seafood allergy and allergens: a review. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2003; 5:339–348.

4. Choe BL, Lee JR. Opisthobranchs (Mollusca: Gastropoda) from Ullung and Dog-do islands, Korea. Korean J Zool. 1994; 37:352–376.
5. Song JH, Kwon TH, Suh JI. Four cases of toxic hepatitis after ingestion of sea hare. Korean J Med. 2015; 88:680–684.

6. Kulis M, Wright BL, Jones SM, Burks AW. Diagnosis, management, and investigational therapies for food allergies. Gastroenterology. 2015; 148:1132–1142.

7. Sicherer SH, Munoz-Furlong A, Sampson HA. Prevalence of seafood allergy in the United States determined by a random telephone survey. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 114:159–165.

8. Tsabouri S, Triga M, Makris M, Kalogeromitros D, Church MK, Priftis KN. Fish and shellfish allergy in children: review of a persistent food allergy. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2012; 23:608–615.

9. Chan CF, Chen PH, Huang CF, Wu TC. Emergency department visits for food allergy in Taiwan: a retrospective study. Pediatr Neonatol. 2014; 55:275–281.

10. Ye YM, Kim MK, Kang HR, Kim TB, Sohn SW, Koh YI, et al. Predictors of the severity and serious outcomes of anaphylaxis in korean adults: a multicenter retrospective case study. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2015; 7:22–29.

11. Motoyama K, Ishizaki S, Nagashima Y, Shiomi K. Cephalopod tropomyosins: identification as major allergens and molecular cloning. Food Chem Toxicol. 2006; 44:1997–2002.

12. Hong SY. Marine invertebrates in Korean coasts. Seoul: Academy Publications;2006.
13. Ishikawa M, Ishida M, Shimakura K, Nagashima Y, Shiomi K. Purification and IgE-binding epitopes of a major allergen in the gastropod Turbo cornutus. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1998; 62:1337–1343.

14. Lopata AL, Zinn C, Potter PC. Characteristics of hypersensitivity reactions and identification of a unique 49 kd IgE-binding protein (Hal-m-1) in abalone (Haliotis midae). J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997; 100:642–648.

15. Masuda K, Tashima S, Katoh N, Shimakura K. Anaphylaxis to abalone that was diagnosed by prick test of abalone extracts and immunoblotting for serum immunoglobulin E. Int J Dermatol. 2012; 51:359–360.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download