Abstract
Purpose
Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
Comparisons of serum specific IgE binding components by IgE immunoblot using Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus (Dp) and Dermatophagoides farinae (Df). Group A, the subjects not having IgE-binding components to groups 1 and 2 allergens; group B, the subjects having IgE-binding components to groups 1 and 2 allergens; a, Using Dp extracts; b, Using Df extracts; PC, positive control which were derived from the results from the patients with higher serum specific IgE levels to both Dp and Df; NC, negative controls.
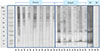
Fig. 2
IgE enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay inhibition tests with serial additions of Dp, Df in sera from group A (A) and group B (B) subjects. Dp, Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus; Df, Dermatophagoides farina.

Table 1
Clinical characteristics of group A subjects

Group A, the subjects not having IgE-binding components to groups 1 and 2 allergens; Dp, Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus; Df, Dermatophagoides farina; ECP, eosinophil cationic protein; TEC, total eosinophil count; ITX, allergen immunotherapy; HDM, house dust mite; AR, allergic rhinitis; AC, allergic conjunctivitis; AICU, aspirin intolerant chronic urticaria; AD, atopic dermatitis; EB, eosinophilic bronchitis; AERD, Aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease; CU, chronic urticaria; BA, bronchial asthma; OAS, oral allergic syndrome; NA, not available; (+), the subject who has the history of immunotherapy with house dust mites or food allergy; (-), the subject has the history of immunotherapy with house dust mites or food allergy.
Table 2
Clinical characteristics of group B subjects

Group B, the subjects having IgE-binding components to groups 1 and 2 allergens; Dp, Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus; Df, Dermatophagoides farinae; ECP, eosinophil cationic protein; TEC, total eosinophil count; ITX, allergen immunotherapy; HDM, house dust mite; AR, allergic rhinitis; BA, bronchial asthma, NA, not available; AD, atopic dermatitis; AC, allergic conjunctivitis; (+), the subject who has the history of immunotherapy with house dust mites or food allergy; (-), the subject has the history of immunotherapy with house dust mites or food allergy.
Table 3
Comparison of clinical features between the 2 groups

Values are presented as mean±standard deviation.
Group A, the subjects not having IgE-binding components to groups 1 and 2 allergens; group B, the subjects having IgE-binding components to groups 1 and 2 allergens; Dp, Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus; Df, Dermatophagoides farinae; ECP, eosinophil cationic protein; TEC, total eosinophil count.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download