This article has been corrected. See "Erratum: Acknowledgments Correction. The cause of hemoptysis according to age and the amount of hemoptysis in children" in Volume 4 on page 462.
Abstract
Purpose
Studies on hemoptysis is rare because hemoptysis is an uncommon symptom in children. The aim of this study was to identify the causes of hemoptysis in children.
Methods
Medical chart review of patients with hemoptysis was retrospectively conducted at 2 tertiary hospitals from November 2008 to December 2014. Patients were divided into 3 groups according to age. The amount of hemoptysis was categorized as mild (<20 mL/day), moderate (20–99 mL/day), and massive (≥100 mL/day).
Results
A total of 59 patients were identified, and their mean age was 11.0±5.6 years. Among the causes of hemoptysis, respiratory tract infection was most common. Other causes included vasculitis syndrome, neoplasm in the airway, idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis, cardiac disease, and bronchiectasis. According to age, a significant difference was identified between the age groups in children with pneumonia (<6 years vs. 12–18 years, P=0.001). Differences were verified between the age groups in children with tuberculosis (<6 years vs. 12–18 years and 6–11 years vs. 12–18 years, P=0.023). According to amounts of hemoptysis, no significant difference was identified regardless of the causes.
Conclusion
This study showed that the causes of hemoptysis in children were heterogeneous and the respiratory tract infection was most common. In children with hemoptysis, the age of onset and the amount of hemoptysis are needed to be considered for more precise diagnosis and more proper management of the underlying cause of hemoptysis.
Figures and Tables
Table 1
Characteristics of children with hemoptysis (n=59)
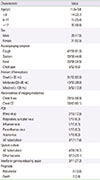
Table 2
Etiology of hemoptysis in children

Table 3
Association between age and etiology of hemoptysis

Table 4
Association between amount and etiology of hemoptysis

References
1. Stedman TL. Stedman's medical dictionary. 27th ed. Philidelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2000.
3. Jean-Baptiste E. Clinical assessment and management of massive hemoptysis. Crit Care Med. 2000; 28:1642–1647.

4. Hirshberg B, Biran I, Glazer M, Kramer MR. Hemoptysis: etiology, evaluation, and outcome in a tertiary referral hospital. Chest. 1997; 112:440–444.

5. Johnston H, Reisz G. Changing spectrum of hemoptysis. Underlying causes in 148 patients undergoing diagnostic flexible fiberoptic bronchoscopy. Arch Intern Med. 1989; 149:1666–1668.

6. Fabian MC, Smitheringale A. Hemoptysis in children: the hospital for sick children experience. J Otolaryngol. 1996; 25:44–45.
7. Coss-Bu JA, Sachdeva RC, Bricker JT, Harrison GM, Jefferson LS. Hemoptysis: a 10-year retrospective study. Pediatrics. 1997; 100:E7.

8. Batra PS, Holinger LD. Etiology and management of pediatric hemoptysis. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2001; 127:377–382.

9. Tom LW, Weisman RA, Handler SD. Hemoptysis in children. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1980; 89(5 Pt 1):419–424.

10. Thompson JW, Nguyen CD, Lazar RH, Stocks RM, Schoumacher RA, Hamdan F, et al. Evaluation and management of hemoptysis in infants and children: a report of nine cases. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1996; 105:516–520.

11. Sim J, Kim H, Lee H, Ahn K, Lee SI. Etiology of hemoptysis in children: a single institutional series of 40 cases. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2009; 1:41–44.

12. Badsha H, Teh CL, Kong KO, Lian TY, Chng HH. Pulmonary hemorrhage in systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2004; 33:414–421.

13. Flume PA, Mogayzel PJ Jr, Robinson KA, Rosenblatt RL, Quittell L, Marshall BC, et al. Cystic fibrosis pulmonary guidelines: pulmonary complications: hemoptysis and pneumothorax. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010; 182:298–306.
15. Genetic testing for cystic fibrosis. NIH Consens Statement. 1997; 15:1–37.
16. Chen HB, Lu XX, Jiang K. Etiology, clinical features, and diagnosis and treatment of recurrent hemoptysis in children. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2014; 16:281–284.
17. Soares Pires F, Teixeira N, Coelho F, Damas C. Hemoptysis: etiology, evaluation and treatment in a university hospital. Rev Port Pneumol. 2011; 17:7–14.
18. Abu-Kishk I, Klin B, Eshel G. Hemoptysis in children: a single institutional experience. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2012; 28:1206–1210.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download